矩形类用线段对象的两个坐标作为自己一条边的位置,它具有另外一个边长,能输出矩形的4个点坐标。给出类的定义并用程序验证它们的功能;
#include < iostream >
#include < cmath >
using namespace std;
class Point//点类
{
protected:
double x, y;
public:
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
double getX()
{
return x;
}
double getY()
{
return y;
}
};
class Line
{
protected:
Point p1, p2;//Point 对象做成员
double length, angle;
public:
Line(double a, double b, double c, double d) :p1(a, b), p2(c, d)//用两对坐标初始化线段
{
init();
}
Line(Point a, Point b)//用两个点的对象初始化线段
{
p1 = a;
p2 = b;
init();
}
void init()//计算线段长度,以及和 x 轴的夹角的度数
{
double x1 = p1.getX(), y1 = p1.getY();
double x2 = p2.getX(), y2 = p2.getY();
length = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2));
angle = atan((y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1));
angle = angle * 180 / 3.141592653;
}
void printXY()
{
cout << "(" << p1.getX() << "," << p1.getY() << "); (" << p2.getX() << "," << p2.getY() << ")" << endl;
}
void printLength()
{
cout << "线段长度:" << length << endl;
}
void printAngle()
{
cout << "与 x 轴的夹角:" << angle << "°" << endl;
}
};
class Rectangle : public Line
{
protected:
Line *line;
public:
Rectangle(double a, double b, double c, double d, double e, double f, double g, double h) :Line(a, b, c, d)
{
line = new Line(e, f, g, h);
}
Rectangle(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) : Line(a, b)//4 个点对象,初始化
{
line = new Line(c, d);
}
void printPoint()
{
cout << "矩形 4 个顶点: ";
printXY();
line->printXY();
}
};
void main()
{
Point p1(0, 0), p2(4, 3), p3(12, 89), p4(10, -50);
Line l1(0, 0, 4, 3);
l1.printXY();
l1.printLength();
l1.printAngle();
Line l2(p1, p2);
l2.printXY();
l2.printLength();
l2.printAngle();
Rectangle r1(12, 45, 89, 10, 10, 23, 56, 1);
r1.printPoint();
Rectangle r2(p1, p2, p3, p4);
r2.printPoint();
system("pause");
}
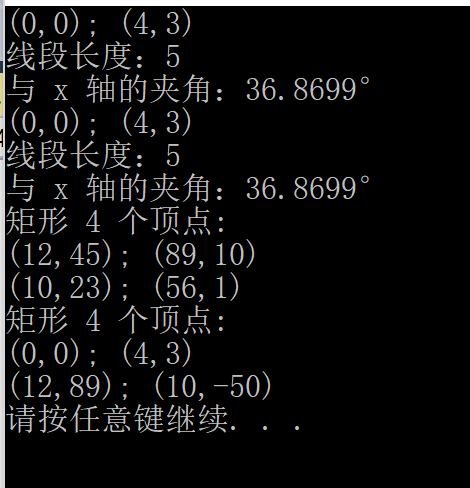
运行结果: