用matplotlib制作的比较满意的蜡烛图
2D图形制作包, 功能强大, 习练了很久, 终于搞定了一个比较满意的脚本.
特点:
- 使用方面要非常简单
- 绘制出来的图要非常的满意, 具有如下的特点
- 时间和空间的比例尺需要固定, 就是说图件的大小需要依据数据的长度和价格的变动幅度自动调整, 至少时间轴上应该如此.
- 时间轴的刻度: 对于日线图而言, 年/月/日/星期几 都应该一目了然.
- Y轴: 对数刻度, 10%等比刻度线, 刻度值的标签应该能反应绝对的股价, 支持双Y轴(右侧的Y轴度量大盘的变化)
- 蜡烛非白即黑, 只要两种颜色(包括边界线)
- 分辨率要足够高, 至少300DPI, 方便原样(无伸缩)打印
- 应该支持非常方便地抽取子集, 然后制图
版本持续升级:
2017.12 的备忘录
在以前的函数式代码的基础上, OOP方式重构代码, 方便以后扩展功能, 也让程序运行得更健硕
结果展示
主块代码
绘图模块的代码
结果展示:
png file from my github:
https://github.com/duanqingshan/learngit/blob/master/均胜电子_20171230_182515__468000.png
gif file from my cnblogs:
https://files.cnblogs.com/files/duan-qs/均胜电子_20171226_220616__255000.gif
主代码块:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
u''' 研究K线形态: 从单个K线做起, 然后K线组合, 然后K线形态
# 1. 定义两个实例
# 2. 加载数据
# 3. 前复权处理
# 4. 计算指标
# 5. 形态研究之: 提取与显示
# 6. 绘图 主图+成交量图
'''
import amipy as ami
import plotter as pl
import pattern as pa
reload(pa)
reload(ami)
context = ami.Context('600699.SH') # 000911
#context = ami.Context('002242.SZ') # 000911
stk = ami.Stock(context)
stk.grab_data_tdxlday(context, num_days=None)
stk.load_tdx_qx()
stk.qfq()
stk.ma20 = ami.TTR.sma(stk.ohlc.close, 20)
stk.cyc61 = ami.TTR.sma(stk.ohlc.close, 120)
pattern = pa.Pattern(stk)
pattern.study_csyx(roc1=0.3/100)
#subset = slice(-250*3, None) # '2017-07' '2017'
subset = slice(-120,None) # '2017-07' '2017'
plotter = pl.Plotter(context,stk,subset,quanxi=None)
# plotter.plot_candle_vol()
#plotter.plot_candle_vol(savefig=True)
#plotter.plot_timing(timing=pattern.csyx)
#plotter.plot_timing(timing=pattern.szx)
plotter.plot_timing(timing=pattern.upgap, savefig=True)
#plotter.plot_timing(timing=pattern.dngap)
绘图代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import datetime
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import (
FixedLocator,
#MultipleLocator,
#LogLocator,
#NullFormatter,
FuncFormatter,
#LogFormatter
)
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
from matplotlib.text import Text
myfont = FontProperties(fname=r"c:windowsfontsmsyh.ttf") #size可不用指定
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
#import amipy as ami
import ttr as TTR
#==============================================================================
# Python中的作用域及global用法 - Summer_cool - 博客园
# https://www.cnblogs.com/summer-cool/p/3884595.html
#
# 函数定义了本地作用域,而模块定义的是全局作用域。
# 如果想要在函数内定义全局作用域,需要加上global修饰符。
#
# 变量名解析:LEGB原则
# 当在函数中使用未认证的变量名时,Python搜索4个作用域:
# [本地作用域(L-local)(函数内部声明但没有使用global的变量),
# 之后是上一层结构def或者lambda的本地作用域(E-enclosure),
# 之后是全局作用域(G-global)(函数中使用global声明的变量或在模块层声明的变量),
# 最后是内置作用域(B)(即python的内置类和函数等)]
# 并且在第一处能够找到这个变量名的地方停下来。
# 如果变量名在整个的搜索过程中都没有找到,Python就会报错。
#
# 补:上面的变量规则只适用于简单对象,当出现引用对象的属性时,则有另一套搜索规则:
# 属性引用搜索一个或多个对象,而不是作用域,并且有可能涉及到所谓的"继承"
# 补2:global修饰符在python里的一个独特现象:
# 在模块层面定义的变量(无需global修饰),
# 如果在函数中没有再定义同名变量,可以在函数中当做全局变量使用.
# 如果在函数中要对它重新赋值的话, 则必须在本函数中事先声明为全局变量, 否则会抛出异常.
#
# #先声明全局本函数里用到的全局变量: 图表, 上下文, 股票对象
# #使用global语句可以清楚地表明变量是在外面的块定义的, 而且在本函数内
# #可以使用或者修改这些变量(前提是必须先声明为全局变量, 以便告诉python
# #解释器这些变量是全局的(主块和函数块共有的)已经是在外部--主代码块里--定义好了的,
# # 或者是本代码块要传递到主代码块里的变量).
#==============================================================================
class Plotter(object):
u'''
Plotter class to make picture of stock's ohlcv data
'''
# define class var
ptype_dict={
'lday':u'日',
'lc5':u'五分钟'} # 这里声明的变量, 不用加global修饰符, 也是全局变量
def __init__(self, context, stk, subset, quanxi=None):
self.context = context
self.stk = stk
self.subset = subset
self.quanxi = quanxi
self.fig = None
self.ax1 = self.ax2 = self.ax3 = None
self.candle_colors = None
self.length = None
self.x = None
def plot_candle_only(self, savefig=False):
u'''仅绘制主图
'''
self.layout(volume_bars=False)
self.candles()
self.primary_curves()
self.savfig(savefig)
#fig #在ipython console里显示整个图表
def plot_candle_vol(self, savefig=False):
u'''主图+成交量图
'''
self.layout(volume_bars=True)
self.candles()
self.primary_curves()
self.vol_bars()
self.savfig(savefig)
pass
def plot_timing(self, timing=None, savefig=False):
u'''画图: timing之K线性形态
candles + (MA20, MA120) + 形态标注
volume bar
para:
timing: Series,
note: str, {'csyx', 'szx', etc}, 长上影线, 十字星等
'''
self.layout(volume_bars=True)
self.candles()
self.primary_curves()
self.vol_bars()
self.annotate(timing)
self.savfig(savefig)
def layout(self, volume_bars=True):
u'''
'''
if volume_bars:
self.fig, (self.ax1, self.ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, gridspec_kw={'height_ratios': [3,1]} )
else:
self.fig,self.ax1 = plt.subplots(1,1)
#res = fig, ax1
#return res
def candles(self,
col_func=None):
u'''
subset:
slice object, slice(start,stop,step)
that is:
slice(100)
slice(-100,None)
slice(100,200)
slice(-200,-100,2)
'2011-09'
'2017'
'''
def default_col_func(index, open1, close, low, high):
return 'black' if open1[index] > close[index] else 'white' # r g b cyan black white
subset=self.subset
col_func= col_func or default_col_func
ohlc = self.stk.ohlc[subset] if self.subset else self.stk.ohlc
open1,high,low,close = ohlc.open, ohlc.high, ohlc.low, ohlc.close
self.length = length = len(close)
self.x = x = np.arange(length)
candle_colors = [col_func(i, open1, close, low, high) for i in x]
self.candle_colors = candle_colors
# 计算出 每日的开盘价/收盘价里的最大值和最小值
oc_min = pd.concat([open1, close], axis=1).min(axis=1)
oc_max = pd.concat([open1, close], axis=1).max(axis=1)
#candles = ax1.bar(x, oc_max-oc_min, bottom=oc_min, color=candle_colors, linewidth=0)
#lines = ax1.vlines(x + 0.4, low, high, color=candle_colors, linewidth=1)
candles = self.ax1.bar(x-0.4, oc_max-oc_min, bottom=oc_min, color=candle_colors, linewidth=0.2, edgecolor='black')
shadlines_up = self.ax1.vlines(x, oc_max, high, color=['black']* length, linewidth=0.3)
shadlines_dn = self.ax1.vlines(x, low, oc_min, color=['black']* length, linewidth=0.3)
#print candles.__class__, shadlines_up.__class__, shadlines_dn.__class__
isinstance(candles, matplotlib.container.BarContainer) == True
isinstance(shadlines_dn, matplotlib.collections.LineCollection)
isinstance(shadlines_up, matplotlib.collections.LineCollection)
self.custom_figure()
self.custom_yaxis()
pass
def primary_curves(self): #subset=None):
#ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
#close = ohlc.close
subset = self.subset
if (isinstance(self.stk.ma20, pd.Series) and isinstance(self.stk.cyc61, pd.Series)):
ma20 = self.stk.ma20[subset] if subset else self.stk.ma20
cyc61 = self.stk.cyc61[subset] if subset else self.stk.cyc61
indicators = [ma20, cyc61]
x=self.x
for ind in indicators:
self.ax1.plot(x, ind, 'o-', lw=0.1, markersize=0.7, markeredgewidth=0.1, label=ind.name) #带圆圈标记的实线
self.ax1.legend()
self.custom_xaxis(ax=self.ax1)
def secondary_curves(self, ax):
# ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
pass
def vol_bars(self):
u'''
'''
subset = self.subset
ohlc = self.stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else self.stk.ohlc
volume = ohlc['volume']
#open1,high,low,close = ohlc.open, ohlc.high, ohlc.low, ohlc.close
x = self.x
volume_scale = None
scaled_volume = volume
if volume.max() > 1000*1000:
volume_scale = u'百万股' #'M'
scaled_volume = volume / 1000.0/1000.0
elif volume.max() > 1000:
volume_scale = u'千股'
scaled_volume = volume / 1000.0
self.ax2.bar(x-0.4, scaled_volume, color=self.candle_colors, linewidth=0.2, edgecolor='black')
volume_title = 'Volume'
if volume_scale:
volume_title = 'Volume (%s)' % volume_scale
#ax2.set_title(volume_title) # 太难看了
self.ax2.set_ylabel(volume_title, fontdict=None)
self.ax2.xaxis.grid(False)
#plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), fontsize=6)
self.custom_xaxis(self.ax2)
pass
def annotate(self, timing):
u'''在主图上标注给定的K线形态:
param:
timing: event of Series of k-pattern
note: str, 对应于事件的标注文本
example:
>>> plotter.annotate(csyx) #长上影线
'''
#ax=plt.gca()
#xx = self.action.p_DJR.index
c = self.stk.ohlc.close[self.subset] if self.subset else self.stk.ohlc.close
self.timing = timing[self.subset] if self.subset else timing
ptn_dt = c[self.timing].index # True 逻辑选择 选出长上影线的时机(日期索引)
note = self.note = self.timing.name[:3]
ax = self.ax1
xx = map(lambda dt: c.index.get_loc(dt), ptn_dt)
yy = c * 1.1
#strings = self.action['value'].values.astype(str)
#strings = self.action['bonus'].values.astype(str)
#strings = map(lambda x: u'派'+str(x), strings)
for i,x in enumerate(xx):
#ax.text(x, yy[i], strings[i])
print i, c.index[x], x, yy[x], c[x]
ax.annotate(note, xy=(x, yy[x]*1.05/1.1), xytext=(x, yy[x]+0.0),
arrowprops=dict(
facecolor='black',
color='red',
#shrink=0.05,
arrowstyle='->',
),)
def custom_yaxis(self):
u'''
# 设定 Y 轴上的刻度
#==================================================================================================================================================
python - Matplotlib log scale tick label number formatting - Stack Overflow
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21920233/matplotlib-log-scale-tick-label-number-formatting
每个坐标轴都有7大属性:
ax1.set_yscale, ylim, ylabel, yticks, yticklabels, ybound, ymargin
'''
#use_expo=True;
expbase=1.1 # 2 e 10
yaxis= self.ax1.get_yaxis()
isinstance(yaxis, matplotlib.axis.YAxis)
self.ax1.set_yscale(value='log', basey=expbase)
pass
def custom_figure(self):
u''' '''
# 依据绘图数据的长度和时间轴的比例尺(比如1:16)确定图表的长度:
#fig = plt.gcf()
#fig.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
self.fig.set_size_inches(self.length/16.0, 6) # /18 /20 /16 diff time-scales
title = u'%s(%s)%s周期蜡烛图'%(self.context.name, self.context.symbol, self.ptype_dict[self.context.ptype])
self.ax1.set_title(title)
pass
def custom_xaxis(self, ax):
u'''
'''
subset = self.subset
ohlc = self.stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else self.stk.ohlc
close = ohlc.close
length = self.length # len(close)
ax.set_xlim(-2, length+10)
xaxis= ax.get_xaxis()
yaxis= ax.get_yaxis()
# 设定 X 轴上的主刻度/次刻度位置
#==================================================================================================================================================
mdindex, wdindex, sdindex= self.ohlc_find_idx_fdim(close)
xMajorLocator= FixedLocator(np.array(mdindex)) # 针对主刻度,实例化一个"固定式刻度定位"
xMinorLocator= FixedLocator(np.array(wdindex)) # 确定 X 轴的 MinorLocator
# 确定 X 轴的 MajorFormatter 和 MinorFormatter
# 自定义的刻度格式(应该是一个function)
datelist = close.index.date.tolist()
def x_major_formatter_1(idx, pos=None):
u'''
格式函数的功能: idx 是位置location, 依据位置, 返回对应的日期刻度标签
'''
#return datelist[idx].strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
return datelist[idx].strftime('%m
%Y')
def x_major_formatter_2(idx, pos=None):
return datelist[idx].strftime('
%m
%Y')
def x_minor_formatter_1(idx, pos=None):
#return datelist[idx].strftime(u'一
%d') # 周一
return datelist[idx].strftime(u'M
%d') # 周一
def x_minor_formatter_2(idx, pos=None):
return datelist[idx].strftime('%m-%d')
xMajorFormatter_1 = FuncFormatter(x_major_formatter_1)
xMajorFormatter_2 = FuncFormatter(x_major_formatter_2)
xMinorFormatter_1 = FuncFormatter(x_minor_formatter_1)
# 设定 X 轴的 Locator 和 Formatter
xaxis.set_major_locator(xMajorLocator)
xaxis.set_minor_locator(xMinorLocator)
xaxis.set_major_formatter(xMajorFormatter_1)
if self.ax2 is None:
xaxis.set_major_formatter(xMajorFormatter_2)
xaxis.set_minor_formatter(xMinorFormatter_1)
if self.ax2 is None: # 仅绘制主图
# 设定不显示的刻度标签:
if ax==self.ax1:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), visible=True) #主刻度标签 可见
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True), visible=True) #次刻度标签 可见
elif ((self.ax1 != None) and (self.ax2 != None)): # case of 主图+成交量图
if ax==self.ax2:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True), visible=False) #次刻度标签 隐藏
elif ax==self.ax1:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), visible=False) #主刻度标签 隐藏
# 设定 X 轴主刻度和次刻度标签的样式(字体大小)
for malabel in ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False):
malabel.set_fontsize(12) # 6号也太小了
#malabel.set_horizontalalignment('right')
#malabel.set_rotation('45')
# if ax == ax1 or ax2:
for milabel in ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True):
milabel.set_fontsize(12) # 5 太小了
#milabel.set_horizontalalignment('right')
#milabel.set_rotation('45')
#milabel.set_fontdict=myfont
#milabel.set_fontproperties=myfont
#milabel.set_prop=myfont
# 设置两个坐标轴上的 grid
#==================================================================================================================================================
#xaxis_2.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='solid', linewidth=0.2)
xaxis.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.3)
xaxis.grid(True, 'minor', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
#yaxis_2.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=0.2)
yaxis.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
yaxis.grid(True, 'minor', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
yaxis.get_major_ticks()[2].label =
Text(0,28.1024,u'28.10 $\mathdefault{1.1^{35}}$')
def ohlc_find_idx_fdim(self, ohlc):
u'''
功能: index of first trading-day in month
------
- 获取每个月的第一个交易日的下标(又称0轴索引).
从数据框的时间索引里提取对应的日期, 然后检索出下标.
- 另外, 也获取每个交易周的第一个交易日的下标
输入:
- ohlc: pandas数据框
返回:
- list
例子:
-------
>>> mdindex, wdindex, sdindex= ohlc_find_idx_fdim(ohlc_last60)
'''
#datelist= [ datetime.date(int(ys), int(ms), int(ds)) for ys, ms, ds in [ dstr.split('-') for dstr in pdata[u'日期'] ] ]
#last60 = ohlc[-250:]
last60 = ohlc
datelist = last60.index.date.tolist()
# 确定 X 轴的 MajorLocator
mdindex= [] # 每个月第一个交易日在所有日期列表中的 index, 月日期索引
years= set([d.year for d in datelist]) # 所有的交易年份
for y in sorted(years):
months= set([d.month for d in datelist if d.year == y]) # 当年所有的交易月份
for m in sorted(months):
monthday= min([dt for dt in datelist if dt.year==y and dt.month==m]) # 当月的第一个交易日
mdindex.append(datelist.index(monthday))
wdindex =[] # weekday index, 每周的第一个交易日的索引
for y in sorted(years):
weeknum= set([int(d.strftime('%U')) for d in datelist if d.year==y])
for w in sorted(weeknum):
wd= min([dt for dt in datelist if dt.year==y and int(dt.strftime('%U'))==w])
wdindex.append(datelist.index(wd))
#==============================================================================
# wdindex= [] # 每周第一个交易日在所有日期列表中的 index, 每周的第一个交易日的索引
# for d in datelist:
# if d.weekday() == 0: wdindex.append(datelist.index(d))
#
#==============================================================================
# === 检索每个季末交易日的下标: sdindex: end of season day index ===
# 对ndarray or list 进行逻辑运输时, 需要用np.logical_or()方法才是正确的方法:
#filter1= (months==3) or (months==6)
#filter1= (months==3).tolist() or (months==6).tolist()
#ValueError: The truth value of an array with more than one element is ambiguous. Use a.any() or a.all()
dt= last60.index.date # 得到ndarray of date,
# dti= last60.index # 得到pd.ts.index.DtetimeIndex of date,
months= last60.index.month #得到ndarray of month, 取值范围为: 1~12
# nextbar_m= last60.index.shift(1, freq='D').month # 当移动时间下标时, 数据的频率不能为空
# 这样做还是有问题的, pd的做法是: 引用未来1 Day的日期, 也就是当前的日期+1day的日期
# 比如: 当前的日期是 2016-12-30, 2017-01-03
# .shift(1)的日期是: 2016-12-31, 2017-01-04
# ==> 误判了4季末的日期变更线坐标位置
# 解决办法: 应该让freq= 'per index bar', 查询一下pd的doc吧...
# 变通办法: .drop first element value or .delete(0) the first location
# and then .insert one value at end, to make the same length
# 变通办法之: 用 freq='BQ', 来生成一个dtindex:
# pd.date_range(start=mi[0], end=mi[-1], freq='BQ') # BQ business quarter endfrequency
# Time Series / Date functionality — pandas 0.19.2 documentation
# http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/timeseries.html#offset-aliases
#
# === 还有更简洁的办法: 就是dti.quarter属性直接提供了第几个季节 ===
i_index= last60.index.delete(0)
i_index= i_index.insert(-1, last60.index[-1]) # -1 表示最后一个下标位置
nextbar_m= i_index.month #
endMar= np.logical_and(months==3, nextbar_m==4)
endJun= np.logical_and(months==6, nextbar_m==7)
endSep= np.logical_and(months==9, nextbar_m==10)
endDec= np.logical_and(months==12, nextbar_m==1)
tmp1= np.logical_or(endMar, endJun)
tmp2= np.logical_or(endSep, endDec)
mask= np.logical_or(tmp1, tmp2)
sdindex= [dt.tolist().index(i) for i in dt[mask] ]
#print u'
==> 季节变更坐标线:'
#print u' 每个季末的x轴的位置下标: %r' % sdindex
#print u' 每个季末的x轴的位置时间: %r' % last60.index[sdindex]
return mdindex, wdindex, sdindex
def savfig(self, savefig=False):
if savefig:
now = datetime.datetime.now()
now_s = now.strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S_')
microsec = str(now.microsecond)
#fn= '%s_%s_%s.pdf' %(context.name, now_s, microsec )
#fig.savefig(fn, dpi=300)
#print u'
==> 该pdf文件被创建: %s' %fn
fn= '%s_%s_%s.png' %(self.context.name, now_s, microsec )
self.fig.savefig(fn, dpi=300)
print u'
==> 该png文件被创建: %s' %fn
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
代码(2017.11)
- 主块代码
- 绘图模块的代码
- 结果展示
结果展示1:
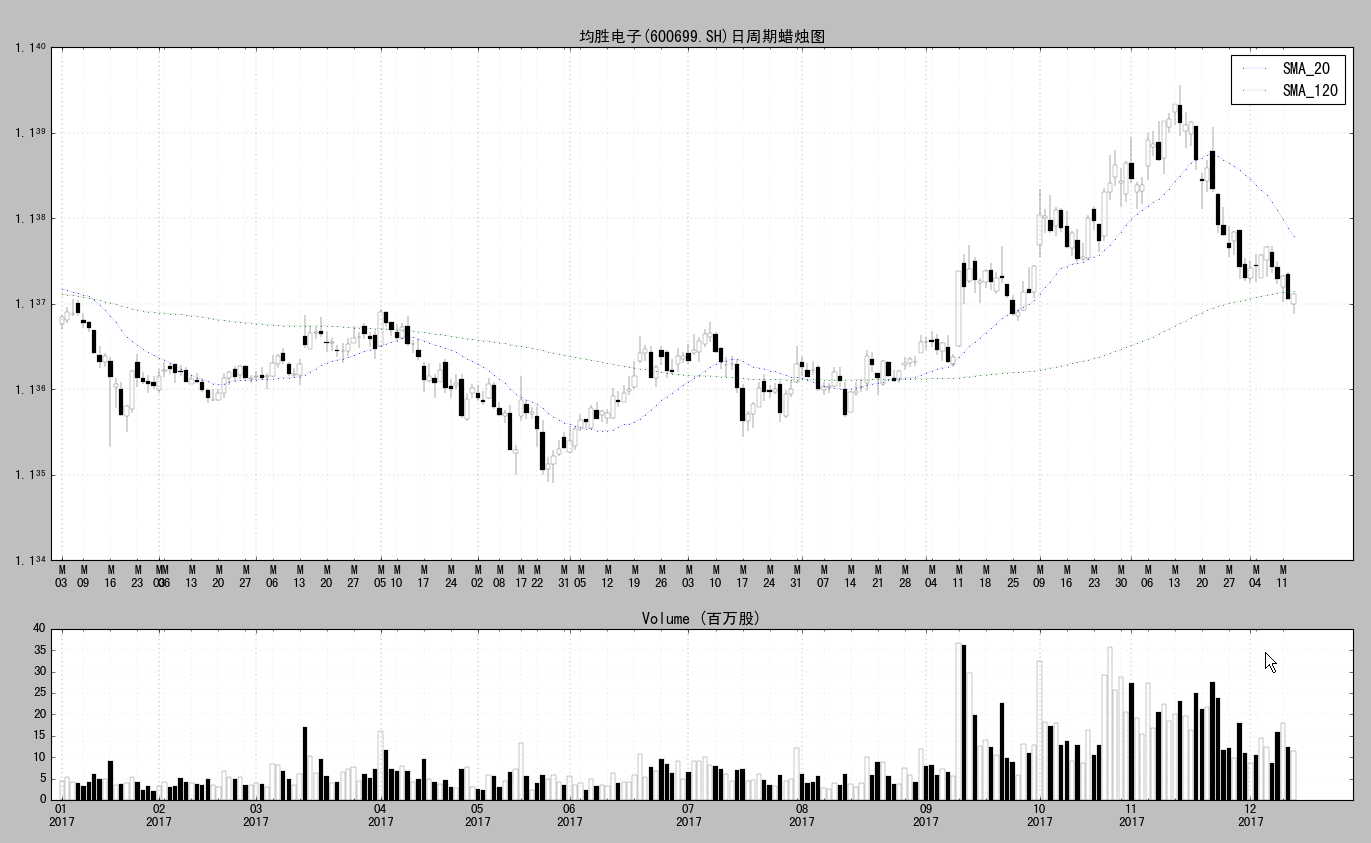
结果展示2:
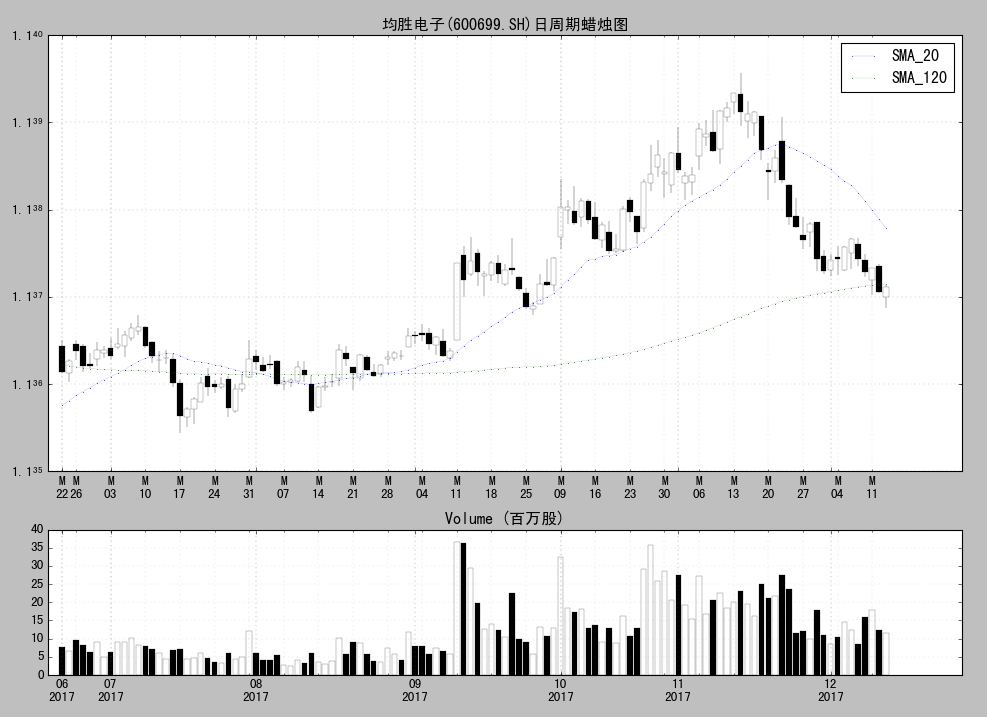
主块代码: test1_load.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
import amipy as ami
reload(ami)
import do_plot as dp
reload(dp)
#context = ami.Context('600699.SH')
context = ami.Context('000911.SZ')
stk = ami.Stock(context) #None,None)
stk.grab_data_tdxlday(context, num_days=None)
stk.ohlc = stk.ohlc_raw
stk.ma20 = ami.TTR.sma(stk.ohlc.close, 20)
stk.cyc61 = ami.TTR.sma(stk.ohlc.close, 120)
subset = slice(-120,None) # '2017-07' '2017'
subset = '2017' #slice(-120,None) # '2017-07' '2017'
datas = (context, stk, subset)
# 仅绘制主图
#dp.plot_candle_only(datas)
# 主图+成交量图
dp.plot_candle_vol(datas)
绘图模块代码 do_plot.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import (
FixedLocator,
#MultipleLocator,
#LogLocator,
#NullFormatter,
FuncFormatter,
#LogFormatter
)
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
myfont = FontProperties(fname=r"c:windowsfontsmsyh.ttf") #size可不用指定
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
#import amipy as ami
#==============================================================================
# Python中的作用域及global用法 - Summer_cool - 博客园
# https://www.cnblogs.com/summer-cool/p/3884595.html
#
# 函数定义了本地作用域,而模块定义的是全局作用域。
# 如果想要在函数内定义全局作用域,需要加上global修饰符。
#
# 变量名解析:LEGB原则
# 当在函数中使用未认证的变量名时,Python搜索4个作用域:
# [本地作用域(L-local)(函数内部声明但没有使用global的变量),
# 之后是上一层结构def或者lambda的本地作用域(E-enclosure),
# 之后是全局作用域(G-global)(函数中使用global声明的变量或在模块层声明的变量),
# 最后是内置作用域(B)(即python的内置类和函数等)]
# 并且在第一处能够找到这个变量名的地方停下来。
# 如果变量名在整个的搜索过程中都没有找到,Python就会报错。
#
# 补:上面的变量规则只适用于简单对象,当出现引用对象的属性时,则有另一套搜索规则:
# 属性引用搜索一个或多个对象,而不是作用域,并且有可能涉及到所谓的"继承"
# 补2:global修饰符在python里的一个独特现象:
# 在模块层面定义的变量(无需global修饰),
# 如果在函数中没有再定义同名变量,可以在函数中当做全局变量使用.
# 如果在函数中要对它重新赋值的话, 则必须在本函数中事先声明为全局变量, 否则会抛出异常.
#
# #先声明全局本函数里用到的全局变量: 图表, 上下文, 股票对象
# #使用global语句可以清楚地表明变量是在外面的块定义的, 而且在本函数内
# #可以使用或者修改这些变量(前提是必须先声明为全局变量, 以便告诉python
# #解释器这些变量是全局的(主块和函数块共有的)已经是在外部--主代码块里--定义好了的,
# # 或者是本代码块要传递到主代码块里的变量).
#==============================================================================
global fig, ax1, ax2, ax3 # 模块级变量名, 分别代表: 整个图表, 子图1/2/3
global context, stk, subset # 模块级变量名
global candle_colors, length
ax2=ax3=None #初始化 ax2/ax3 子图实例为None,
#fig和ax1可以不用初始化, 因为调用layout()后总是要返回fig和ax1的
ptype_dict={
'lday':u'日',
'lc5':u'五分钟'} # 这里声明的变量, 不用加global修饰符, 也是全局变量
def layout(volume_bars=True):
u'''
'''
global fig, ax1, ax2, ax3
if volume_bars:
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, gridspec_kw={'height_ratios': [3,1]} )
res = fig, (ax1,ax2)
else:
fig,ax1 = plt.subplots(1,1)
res = fig, ax1
return res
def candles(
#subset=None,
col_func=None):
u'''
subset:
slice object, slice(start,stop,step)
that is:
slice(100)
slice(-100,None)
slice(100,200)
slice(-200,-100,2)
'2011-09'
'2017'
'''
global context, stk, subset
global candle_colors # 可能会被以后的函数所用到(比如画成交量柱子)
global length
def default_col_func(index, open1, close, low, high):
return 'black' if open1[index] > close[index] else 'white' # r g b cyan black white
col_func= col_func or default_col_func
ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
open1,high,low,close = ohlc.open, ohlc.high, ohlc.low, ohlc.close
length = len(close)
x = np.arange(length)
candle_colors = [col_func(i, open1, close, low, high) for i in x]
# 计算出 每日的开盘价/收盘价里的最大值和最小值
oc_min = pd.concat([open1, close], axis=1).min(axis=1)
oc_max = pd.concat([open1, close], axis=1).max(axis=1)
#candles = ax1.bar(x, oc_max-oc_min, bottom=oc_min, color=candle_colors, linewidth=0)
#lines = ax1.vlines(x + 0.4, low, high, color=candle_colors, linewidth=1)
candles = ax1.bar(x-0.4, oc_max-oc_min, bottom=oc_min, color=candle_colors, linewidth=0.2, edgecolor='black')
shadlines_up = ax1.vlines(x, oc_max, high, color=['black']* length, linewidth=0.3)
shadlines_dn = ax1.vlines(x, low, oc_min, color=['black']* length, linewidth=0.3)
#print candles.__class__, shadlines_up.__class__, shadlines_dn.__class__
isinstance(candles, matplotlib.container.BarContainer) == True
isinstance(shadlines_dn, matplotlib.collections.LineCollection)
isinstance(shadlines_up, matplotlib.collections.LineCollection)
custom_figure()
custom_yaxis()
pass
def primary_curves(): #subset=None):
#ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
#close = ohlc.close
if (isinstance(stk.ma20, pd.Series) and isinstance(stk.cyc61, pd.Series)):
ma20 = stk.ma20[subset] if subset else stk.ma20
cyc61 = stk.cyc61[subset] if subset else stk.cyc61
length = len(ma20)
x = np.arange(length)
indicators = [ma20, cyc61]
for ind in indicators:
ax1.plot(x, ind, 'o-', lw=0.1, markersize=0.7, markeredgewidth=0.1, label=ind.name) #带圆圈标记的实线
ax1.legend()
custom_xaxis(ax=ax1)
def secondary_curves(ax,subset=None):
# ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
pass
def vol_bars():
u'''
'''
global stk, subset
ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
volume = ohlc['volume']
#open1,high,low,close = ohlc.open, ohlc.high, ohlc.low, ohlc.close
x = np.arange(length)
volume_scale = None
scaled_volume = volume
if volume.max() > 1000*1000:
volume_scale = u'百万股' #'M'
scaled_volume = volume / 1000.0/1000.0
elif volume.max() > 1000:
volume_scale = u'千股'
scaled_volume = volume / 1000.0
ax2.bar(x-0.4, scaled_volume, color=candle_colors, linewidth=0.2, edgecolor='black')
volume_title = 'Volume'
if volume_scale:
volume_title = 'Volume (%s)' % volume_scale
ax2.set_title(volume_title)
ax2.xaxis.grid(False)
#plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), fontsize=6)
custom_xaxis(ax2)
pass
def custom_yaxis():
u'''
# 设定 Y 轴上的刻度
#==================================================================================================================================================
python - Matplotlib log scale tick label number formatting - Stack Overflow
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21920233/matplotlib-log-scale-tick-label-number-formatting
'''
#use_expo=True;
expbase=1.1 # 2 e 10
yaxis= ax1.get_yaxis()
isinstance(yaxis, matplotlib.axis.YAxis)
ax1.set_yscale(value='log', basey=expbase)
pass
def custom_figure():
u''' '''
# 依据绘图数据的长度和时间轴的比例尺(比如1:16)确定图表的长度:
#fig = plt.gcf()
#fig.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
fig.set_size_inches(length/16.0, 6) # /18 /20 /16 diff time-scales
title = u'%s(%s)%s周期蜡烛图'%(context.name, context.symbol, ptype_dict[context.ptype])
ax1.set_title(title)
pass
def custom_xaxis(ax):
u'''
'''
global ax1, ax2, ax3
ohlc = stk.ohlc[subset] if subset else stk.ohlc
close = ohlc.close
#length = len(close)
ax.set_xlim(-2, length+10)
xaxis= ax.get_xaxis()
yaxis= ax.get_yaxis()
# 设定 X 轴上的主刻度/次刻度位置
#==================================================================================================================================================
mdindex, wdindex, sdindex= ohlc_find_idx_fdim(close)
xMajorLocator= FixedLocator(np.array(mdindex)) # 针对主刻度,实例化一个"固定式刻度定位"
xMinorLocator= FixedLocator(np.array(wdindex)) # 确定 X 轴的 MinorLocator
# 确定 X 轴的 MajorFormatter 和 MinorFormatter
# 自定义的刻度格式(应该是一个function)
datelist = close.index.date.tolist()
def x_major_formatter_1(idx, pos=None):
u'''
格式函数的功能: idx 是位置location, 依据位置, 返回对应的日期刻度标签
'''
#return datelist[idx].strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
return datelist[idx].strftime('%m
%Y')
def x_major_formatter_2(idx, pos=None):
return datelist[idx].strftime('
%m
%Y')
def x_minor_formatter_1(idx, pos=None):
#return datelist[idx].strftime(u'一
%d') # 周一
return datelist[idx].strftime(u'M
%d') # 周一
def x_minor_formatter_2(idx, pos=None):
return datelist[idx].strftime('%m-%d')
xMajorFormatter_1 = FuncFormatter(x_major_formatter_1)
xMajorFormatter_2 = FuncFormatter(x_major_formatter_2)
xMinorFormatter_1 = FuncFormatter(x_minor_formatter_1)
# 设定 X 轴的 Locator 和 Formatter
xaxis.set_major_locator(xMajorLocator)
xaxis.set_minor_locator(xMinorLocator)
xaxis.set_major_formatter(xMajorFormatter_1)
if ax2 is None:
xaxis.set_major_formatter(xMajorFormatter_2)
xaxis.set_minor_formatter(xMinorFormatter_1)
if ax2 is None: # 仅绘制主图
# 设定不显示的刻度标签:
if ax==ax1:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), visible=True) #主刻度标签 可见
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True), visible=True) #次刻度标签 可见
elif ((ax1 != None) and (ax2 != None)): # case of 主图+成交量图
if ax==ax2:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True), visible=False) #次刻度标签 隐藏
elif ax==ax1:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False), visible=False) #主刻度标签 隐藏
# 设定 X 轴主刻度和次刻度标签的样式(字体大小)
for malabel in ax.get_xticklabels(minor=False):
malabel.set_fontsize(12) # 6号也太小了
#malabel.set_horizontalalignment('right')
#malabel.set_rotation('45')
# if ax == ax1 or ax2:
for milabel in ax.get_xticklabels(minor=True):
milabel.set_fontsize(12) # 5 太小了
#milabel.set_horizontalalignment('right')
#milabel.set_rotation('45')
#milabel.set_fontdict=myfont
#milabel.set_fontproperties=myfont
#milabel.set_prop=myfont
# 设置两个坐标轴上的 grid
#==================================================================================================================================================
#xaxis_2.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='solid', linewidth=0.2)
xaxis.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.3)
xaxis.grid(True, 'minor', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
#yaxis_2.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=0.2)
yaxis.grid(True, 'major', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
yaxis.grid(True, 'minor', color='0.3', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=0.1)
def ohlc_find_idx_fdim(ohlc):
u'''
功能: index of first trading-day in month
------
- 获取每个月的第一个交易日的下标(又称0轴索引).
从数据框的时间索引里提取对应的日期, 然后检索出下标.
- 另外, 也获取每个交易周的第一个交易日的下标
输入:
- ohlc: pandas数据框
返回:
- list
例子:
-------
>>> mdindex, wdindex, sdindex= ohlc_find_idx_fdim(ohlc_last60)
'''
#datelist= [ datetime.date(int(ys), int(ms), int(ds)) for ys, ms, ds in [ dstr.split('-') for dstr in pdata[u'日期'] ] ]
last60 = ohlc[-250:]
datelist = last60.index.date.tolist()
# 确定 X 轴的 MajorLocator
mdindex= [] # 每个月第一个交易日在所有日期列表中的 index, 月日期索引
years= set([d.year for d in datelist]) # 所有的交易年份
for y in sorted(years):
months= set([d.month for d in datelist if d.year == y]) # 当年所有的交易月份
for m in sorted(months):
monthday= min([dt for dt in datelist if dt.year==y and dt.month==m]) # 当月的第一个交易日
mdindex.append(datelist.index(monthday))
wdindex =[] # weekday index, 每周的第一个交易日的索引
for y in sorted(years):
weeknum= set([int(d.strftime('%U')) for d in datelist if d.year==y])
for w in sorted(weeknum):
wd= min([dt for dt in datelist if dt.year==y and int(dt.strftime('%U'))==w])
wdindex.append(datelist.index(wd))
#==============================================================================
# wdindex= [] # 每周第一个交易日在所有日期列表中的 index, 每周的第一个交易日的索引
# for d in datelist:
# if d.weekday() == 0: wdindex.append(datelist.index(d))
#
#==============================================================================
# === 检索每个季末交易日的下标: sdindex: end of season day index ===
# 对ndarray or list 进行逻辑运输时, 需要用np.logical_or()方法才是正确的方法:
#filter1= (months==3) or (months==6)
#filter1= (months==3).tolist() or (months==6).tolist()
#ValueError: The truth value of an array with more than one element is ambiguous. Use a.any() or a.all()
dt= last60.index.date # 得到ndarray of date,
# dti= last60.index # 得到pd.ts.index.DtetimeIndex of date,
months= last60.index.month #得到ndarray of month, 取值范围为: 1~12
# nextbar_m= last60.index.shift(1, freq='D').month # 当移动时间下标时, 数据的频率不能为空
# 这样做还是有问题的, pd的做法是: 引用未来1 Day的日期, 也就是当前的日期+1day的日期
# 比如: 当前的日期是 2016-12-30, 2017-01-03
# .shift(1)的日期是: 2016-12-31, 2017-01-04
# ==> 误判了4季末的日期变更线坐标位置
# 解决办法: 应该让freq= 'per index bar', 查询一下pd的doc吧...
# 变通办法: .drop first element value or .delete(0) the first location
# and then .insert one value at end, to make the same length
# 变通办法之: 用 freq='BQ', 来生成一个dtindex:
# pd.date_range(start=mi[0], end=mi[-1], freq='BQ') # BQ business quarter endfrequency
# Time Series / Date functionality — pandas 0.19.2 documentation
# http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/timeseries.html#offset-aliases
#
# === 还有更简洁的办法: 就是dti.quarter属性直接提供了第几个季节 ===
i_index= last60.index.delete(0)
i_index= i_index.insert(-1, last60.index[-1]) # -1 表示最后一个下标位置
nextbar_m= i_index.month #
endMar= np.logical_and(months==3, nextbar_m==4)
endJun= np.logical_and(months==6, nextbar_m==7)
endSep= np.logical_and(months==9, nextbar_m==10)
endDec= np.logical_and(months==12, nextbar_m==1)
tmp1= np.logical_or(endMar, endJun)
tmp2= np.logical_or(endSep, endDec)
mask= np.logical_or(tmp1, tmp2)
sdindex= [dt.tolist().index(i) for i in dt[mask] ]
#print u'
==> 季节变更坐标线:'
#print u' 每个季末的x轴的位置下标: %r' % sdindex
#print u' 每个季末的x轴的位置时间: %r' % last60.index[sdindex]
return mdindex, wdindex, sdindex
def plot_candle_only(datas):
u'''仅绘制主图
'''
global context, stk, subset
global fig, ax1, ax2, ax3
global candle_colors, length
context, stk, subset = datas
layout(volume_bars=False)
candles()
primary_curves()
#fig #在ipython console里显示整个图表
def plot_candle_vol(datas):
u'''主图+成交量图
'''
global context, stk, subset
global fig, ax1, ax2, ax3
global candle_colors, length
context, stk, subset = datas
layout(volume_bars=True)
candles()
primary_curves()
vol_bars()
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass