1.简介
其实今天介绍也讲解的也是一种等待的方法,有些童鞋或者小伙伴们会问宏哥,这也是一种等待方法,为什么不在上一篇文章中竹筒倒豆子一股脑的全部说完,反而又在这里单独写了一篇。那是因为这个比较重要,所以宏哥专门为她量身定制了一篇。
FluentWait是Selenium中功能强大的一种等待方式,翻译成中文是流畅等待的意思。在介绍FluentWait之前,我们来讨论下为什么需要设置等待,我们前面介绍了隐式等待和显式等待。在现在很多软件产品为了加强前端的效果,采取了大量的AJAX 和Jquery技术,很多窗体内的数据,需要等待一会,才能加载完数据,才能出现一些元素,driver才能操作这些元素做一些事情。还有就是我们做一些操作,本身可能也需要等待一会才有数据显示。所以在自动化脚本开发过程,合理的设置时间等待是非常必要的,可以说百分之90以上的自动化测试用例执行失败,基本上是很时间等待有关系,造成元素没有及时在界面上显示,而报no such element子类的错误。
2.FluentWait的定义
简单来说,FluentWait就是一个普通的类,我们使用这个类能支持一直等待直到特定的条件出现。
1)是一个类而且是包org.openqa.selenium.support.ui的一部分
2)是Wait接口的一种实现
3)每个Fluent wait,我们可以设置等待最大时间,而且可以做设置等待的频率去检查一些特定的条件。
FluentWait 和 Explicit Wait的区别:简单来说就是Explicit Wait里有一些设定好了的前置条件的等待方式,而Fluent wait你可以设置自己的方法去处理各种等待的问题。
3.核心代码
3.1源码
宏哥先看一下FluentWait的源码,如何查看宏哥这里就不做赘述了。源码如下:
// Licensed to the Software Freedom Conservancy (SFC) under one
// or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
// distributed with this work for additional information
// regarding copyright ownership. The SFC licenses this file
// to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
// "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
// with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
// software distributed under the License is distributed on an
// "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
// KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
// specific language governing permissions and limitations
// under the License.
package org.openqa.selenium.support.ui;
import com.google.common.base.Throwables;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import org.openqa.selenium.TimeoutException;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriverException;
import org.openqa.selenium.internal.Require;
import java.time.Clock;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* An implementation of the {@link Wait} interface that may have its timeout and polling interval
* configured on the fly.
*
* <p>
* Each FluentWait instance defines the maximum amount of time to wait for a condition, as well as
* the frequency with which to check the condition. Furthermore, the user may configure the wait to
* ignore specific types of exceptions whilst waiting, such as
* {@link org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException NoSuchElementExceptions} when searching for an
* element on the page.
*
* <p>
* Sample usage: <pre>
* // Waiting 30 seconds for an element to be present on the page, checking
* // for its presence once every 5 seconds.
* Wait<WebDriver> wait = new FluentWait<WebDriver>(driver)
* .withTimeout(30, SECONDS)
* .pollingEvery(5, SECONDS)
* .ignoring(NoSuchElementException.class);
*
* WebElement foo = wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() {
* public WebElement apply(WebDriver driver) {
* return driver.findElement(By.id("foo"));
* }
* });
* </pre>
*
* <p>
* <em>This class makes no thread safety guarantees.</em>
*
* @param <T> The input type for each condition used with this instance.
*/
public class FluentWait<T> implements Wait<T> {
protected static final long DEFAULT_SLEEP_TIMEOUT = 500;
private static final Duration DEFAULT_WAIT_DURATION = Duration.ofMillis(DEFAULT_SLEEP_TIMEOUT);
private final T input;
private final java.time.Clock clock;
private final Sleeper sleeper;
private Duration timeout = DEFAULT_WAIT_DURATION;
private Duration interval = DEFAULT_WAIT_DURATION;
private Supplier<String> messageSupplier = () -> null;
private List<Class<? extends Throwable>> ignoredExceptions = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @param input The input value to pass to the evaluated conditions.
*/
public FluentWait(T input) {
this(input, Clock.systemDefaultZone(), Sleeper.SYSTEM_SLEEPER);
}
/**
* @param input The input value to pass to the evaluated conditions.
* @param clock The clock to use when measuring the timeout.
* @param sleeper Used to put the thread to sleep between evaluation loops.
*/
public FluentWait(T input, java.time.Clock clock, Sleeper sleeper) {
this.input = Require.nonNull("Input", input);
this.clock = Require.nonNull("Clock", clock);
this.sleeper = Require.nonNull("Sleeper", sleeper);
}
/**
* Sets how long to wait for the evaluated condition to be true. The default timeout is
* {@link #DEFAULT_WAIT_DURATION}.
*
* @param timeout The timeout duration.
* @return A self reference.
*/
public FluentWait<T> withTimeout(Duration timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
return this;
}
/**
* Sets the message to be displayed when time expires.
*
* @param message to be appended to default.
* @return A self reference.
*/
public FluentWait<T> withMessage(final String message) {
this.messageSupplier = () -> message;
return this;
}
/**
* Sets the message to be evaluated and displayed when time expires.
*
* @param messageSupplier to be evaluated on failure and appended to default.
* @return A self reference.
*/
public FluentWait<T> withMessage(Supplier<String> messageSupplier) {
this.messageSupplier = messageSupplier;
return this;
}
/**
* Sets how often the condition should be evaluated.
*
* <p>
* In reality, the interval may be greater as the cost of actually evaluating a condition function
* is not factored in. The default polling interval is {@link #DEFAULT_WAIT_DURATION}.
*
* @param interval The timeout duration.
* @return A self reference.
*/
public FluentWait<T> pollingEvery(Duration interval) {
this.interval = interval;
return this;
}
/**
* Configures this instance to ignore specific types of exceptions while waiting for a condition.
* Any exceptions not whitelisted will be allowed to propagate, terminating the wait.
*
* @param types The types of exceptions to ignore.
* @param <K> an Exception that extends Throwable
* @return A self reference.
*/
public <K extends Throwable> FluentWait<T> ignoreAll(Collection<Class<? extends K>> types) {
ignoredExceptions.addAll(types);
return this;
}
/**
* @param exceptionType exception to ignore
* @return a self reference
* @see #ignoreAll(Collection)
*/
public FluentWait<T> ignoring(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType) {
return this.ignoreAll(ImmutableList.<Class<? extends Throwable>>of(exceptionType));
}
/**
* @param firstType exception to ignore
* @param secondType another exception to ignore
* @return a self reference
* @see #ignoreAll(Collection)
*/
public FluentWait<T> ignoring(Class<? extends Throwable> firstType,
Class<? extends Throwable> secondType) {
return this.ignoreAll(ImmutableList.of(firstType, secondType));
}
/**
* Repeatedly applies this instance's input value to the given function until one of the following
* occurs:
* <ol>
* <li>the function returns neither null nor false</li>
* <li>the function throws an unignored exception</li>
* <li>the timeout expires</li>
* <li>the current thread is interrupted</li>
* </ol>
*
* @param isTrue the parameter to pass to the {@link ExpectedCondition}
* @param <V> The function's expected return type.
* @return The function's return value if the function returned something different
* from null or false before the timeout expired.
* @throws TimeoutException If the timeout expires.
*/
@Override
public <V> V until(Function<? super T, V> isTrue) {
Instant end = clock.instant().plus(timeout);
Throwable lastException;
while (true) {
try {
V value = isTrue.apply(input);
if (value != null && (Boolean.class != value.getClass() || Boolean.TRUE.equals(value))) {
return value;
}
// Clear the last exception; if another retry or timeout exception would
// be caused by a false or null value, the last exception is not the
// cause of the timeout.
lastException = null;
} catch (Throwable e) {
lastException = propagateIfNotIgnored(e);
}
// Check the timeout after evaluating the function to ensure conditions
// with a zero timeout can succeed.
if (end.isBefore(clock.instant())) {
String message = messageSupplier != null ?
messageSupplier.get() : null;
String timeoutMessage = String.format(
"Expected condition failed: %s (tried for %d second(s) with %d milliseconds interval)",
message == null ? "waiting for " + isTrue : message,
timeout.getSeconds(), interval.toMillis());
throw timeoutException(timeoutMessage, lastException);
}
try {
sleeper.sleep(interval);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new WebDriverException(e);
}
}
}
private Throwable propagateIfNotIgnored(Throwable e) {
for (Class<? extends Throwable> ignoredException : ignoredExceptions) {
if (ignoredException.isInstance(e)) {
return e;
}
}
Throwables.throwIfUnchecked(e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
/**
* Throws a timeout exception. This method may be overridden to throw an exception that is
* idiomatic for a particular test infrastructure, such as an AssertionError in JUnit4.
*
* @param message The timeout message.
* @param lastException The last exception to be thrown and subsequently suppressed while waiting
* on a function.
* @return Nothing will ever be returned; this return type is only specified as a convenience.
*/
protected RuntimeException timeoutException(String message, Throwable lastException) {
throw new TimeoutException(message, lastException);
}
}
3.2语法
宏哥从源码中的Sample usage提取FluentWait的使用语法如下:
Wait wait = new FluentWait(WebDriver reference)
.withTimeout(timeout, SECONDS)
.pollingEvery(timeout, SECONDS)
.ignoring(Exception.class);
WebElement foo=wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() {
public WebElement applyy(WebDriver driver) {
return driver.findElement(By.id("foo"));
}
});
3.3例子
有了语法,按照语法写一个简单例子,如下:
Wait wait = new FluentWait<WebDriver>(driver)
.withTimeout(45, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.pollingevery(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.ignoring(NoSuchElementException.class);
FluentWait主要使用两个参数–超时值(withTimeout)和轮询频率(pollingevery)。在上面的语法中,我们将超时值设置为45秒,轮询频率设置为5秒。等待条件的最长时间(45秒)和检查指定条件成功或失败的频率(5秒)。如果元素在此时间范围内可以查找到,它将执行下一步操作,否则它将抛出“ElementNotVisibleException”。
3.4完整代码
简单例子的完整代码如下:
package lessons;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.FluentWait;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.Wait;
import com.google.common.base.Function;
public class FluentWait {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", ".\Tools\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("www.test.com");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
Wait<WebDriver> wait = new FluentWait<WebDriver>(driver)
.withTimeout(45, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.pollingEvery(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.ignoring(NoSuchElementException.class);
WebElement ele1 = wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() {
public WebElement apply(WebDriver driver) {
return driver.findElement(By.id("xxxxxxx"));
}
});
}
}
4.项目实战
由于没有现成的网页或者网站以供宏哥进行演示,因此宏哥自己简单写了一个demo以便演示使用。
4.1测试网页代码
宏哥这个网页主要思想就是点击按钮后10s倒计时,倒计时结束出现元素(一段英文文字)。
测试网页test.html,参考代码如下所示:
<html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title>北京-宏哥</title> </head> <style> #click { background-color: #4CAF50; border: none; color: white; padding: 15px 32px; text-align: center; text-decoration: none; display: inline-block; font-size: 16px; margin: 4px 2px; cursor: pointer; } .button { background-color: #f44336; border: none; color: white; padding: 15px 32px; text-align: center; text-decoration: none; display: inline-block; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 100px; } #myAnchor { text-decoration:none; color: white; } </style> <body> <div style=" text-align:center;"> <div style="height: 100px;margin-top: 200px;"> <button class="button"><a id="myAnchor" href="https://www.cnblogs.com/du-hong/">北京-宏哥</a></button></br> <input type="button" value="Click Me - Fluent Wait" id="click" onclick="foo(this, 10000);"/> <p style='color:red; font-family: verdana; font-size: 20;align="center";' id="demo">Click and Wait for <b>10 seconds</b> to view a message - "Software Testing Material - DEMO PAGE"</p> </div> </div> </body> <script> function foo(obj, time) { obj.disabled = true; setTimeout(function() { var x = setInterval(function(){ time= time - 1000; //reduce each second obj.value = (time/1000)%60; if(time==0){ clearInterval(x); obj.value = document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Software Testing Material - DEMO PAGE"; obj.disabled = false; } }, 1000); }, time-10000); } </script> </html>
下边宏哥编写java测试脚本。
4.2代码设计
设计思路:打开网页后,点击按钮开始5s频率的轮训查找元素,第一次没有找到,第二次10s刚好出现,代码也轮训查找也刚结束,没有找到,等到第三次英文文字出现了,代码也查找到,结束轮训,继续下一步操作。代码设计如下图所示:
4.3Java参考代码
宏哥首页用单元测试Junit测试一下写的方法有没有问题,没有问题,然后再调用。
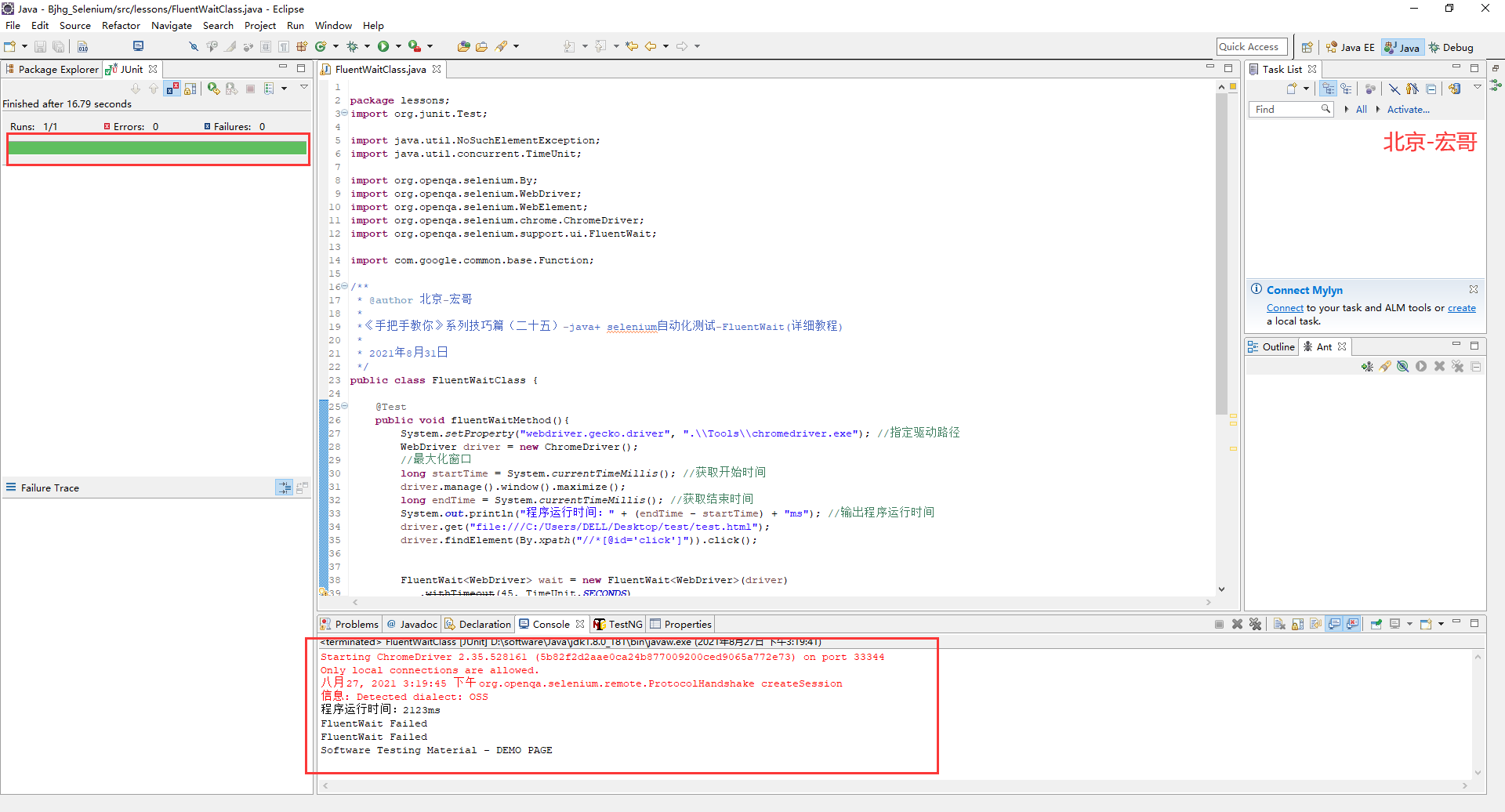
4.3.1运行代码
1.运行代码,右键Run AS->JUnit Test,控制台输出,绿色的进度条证明写的方法没有问题,而且控制台也循环了2次(每次5s,一共10s),等待到了元素的出现并将其打印出来。如下图所示:
2.运行代码后电脑端的浏览器的动作,如下小视频所示:
4.4Java优化参考代码
通过上边的单元测试我们知道写的方法没有问题,那么下边我们直接调用该方法即可。优化后代码如下:
package lessons; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.openqa.selenium.By; import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement; import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.FluentWait; import com.google.common.base.Function; /** * @author 北京-宏哥 * *《手把手教你》系列技巧篇(二十五)-java+ selenium自动化测试-FluentWait(详细教程) * * 2021年8月31日 */ public class FluentWaitClass { @Test public static void fluentWaitMethod(){ System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver", ".\Tools\chromedriver.exe"); //指定驱动路径 WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); //最大化窗口 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间 driver.manage().window().maximize(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间 System.out.println("程序运行时间1:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间 driver.get("file:///C:/Users/DELL/Desktop/test/test.html"); driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='click']")).click(); FluentWait<WebDriver> wait = new FluentWait<WebDriver>(driver) .withTimeout(45, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .pollingEvery(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .ignoring(NoSuchElementException.class); long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间 WebElement element = wait.until(new Function<WebDriver, WebElement>() { public WebElement apply(WebDriver driver) { WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='demo']")); String getTextOnPage = element.getText(); if(getTextOnPage.equals("Software Testing Material - DEMO PAGE")){ System.out.println(getTextOnPage); return element; }else{ System.out.println("FluentWait Failed"); return null; } } }); long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间 System.out.println("程序运行时间3:" + (endTime1 - startTime1) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间 //driver.close(); } public static void main(String [] args){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间 fluentWaitMethod(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间 System.out.println("程序运行时间2:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间 } }
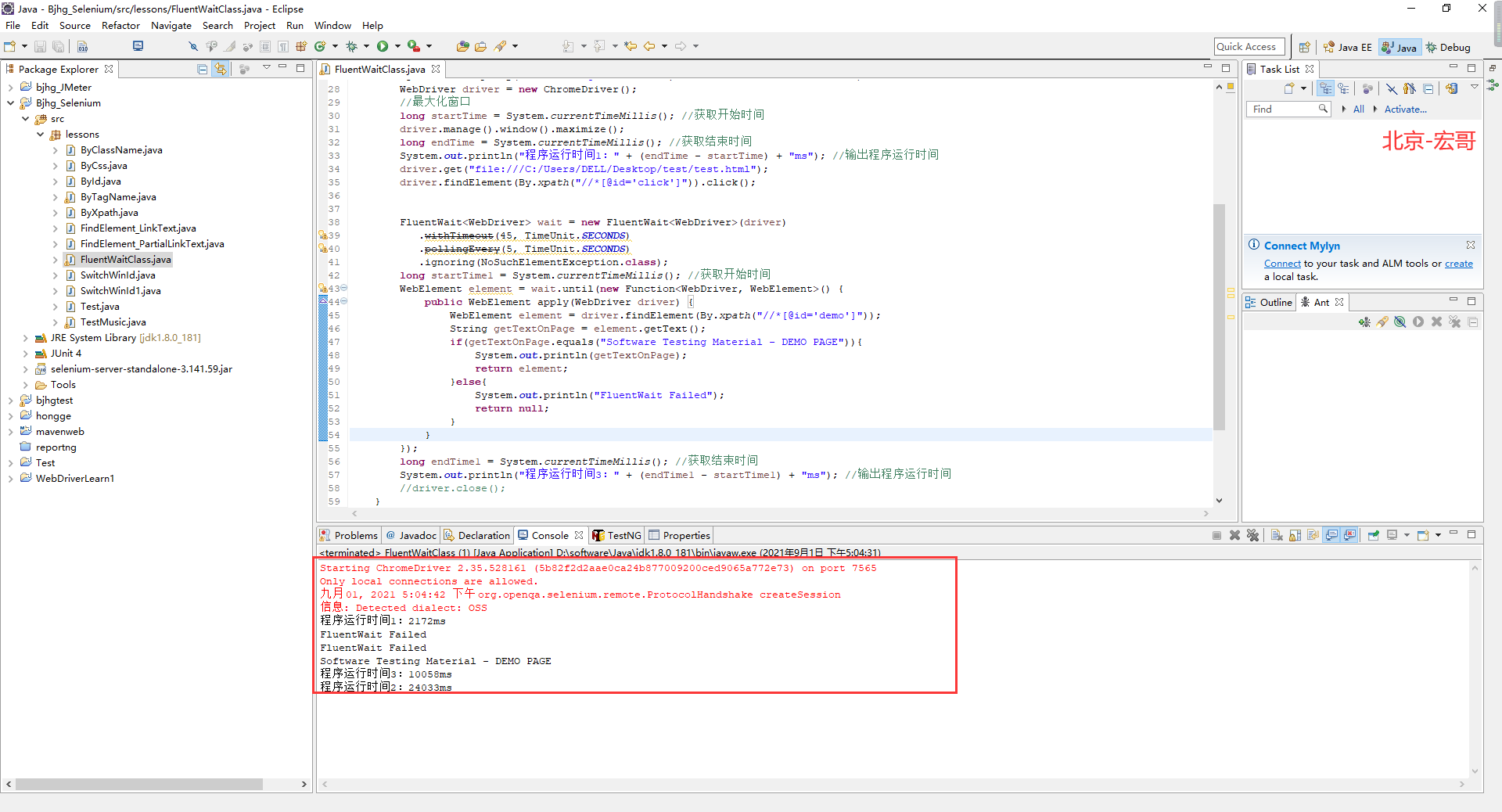
4.4.1运行代码
1.运行代码,右键Run AS->java Application,控制台输出,如下图所示:
2.运行代码后电脑端的浏览器的动作,如下小视频所示:
5.小结
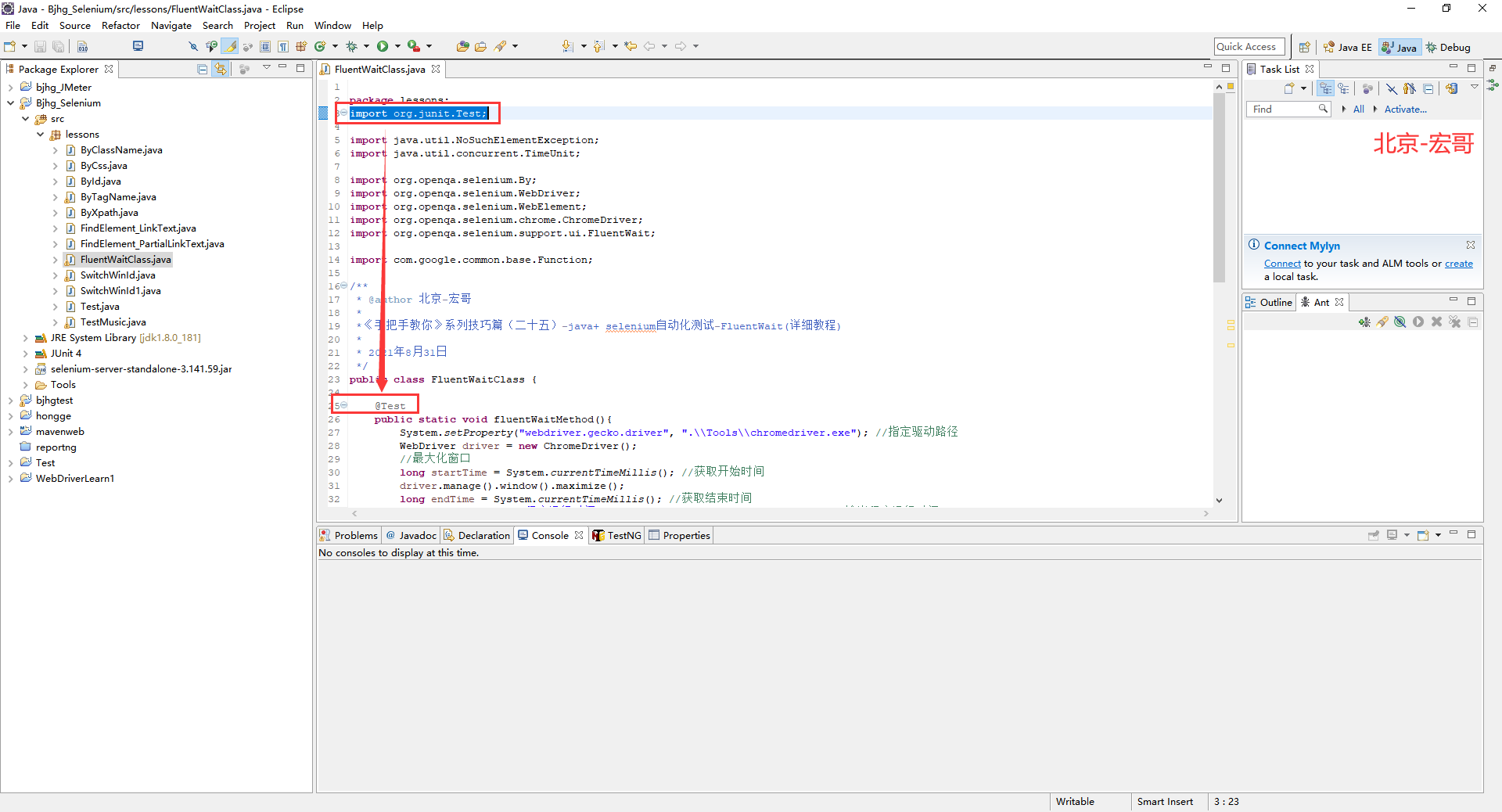
1.在设计代码过程中会报错:Type mismatch: cannot convert from Test to Annotation 如下图所示:

查了好多都说是:类名不能和注解名称相同的原因。后来宏哥检查了一下,不相同啊,但是宏哥为啥这里还会报这个错了。原来是宏哥没有导入单元测试的包,但是也没有提示导入包,因此宏哥将包导入,代码错误消失。如下图所示:
好了,今天就分享到这里了,感谢你耐心的阅读!

