1、EL表达式的作用
EL表达式的作用:向浏览器输出域对象中的变量值或者表达式计算结果。
语法:${变量或者表达式}
注:
Jsp的核心语法:jsp的表达式<%= %>和jsp的脚本<% %>。
jsp的开发原则:尽量在jsp页面中少写甚至不写java代码,使用EL表达式替换掉jsp表达式。
2、EL表达式的语法
1) 输出基本的数据类型变量
1.1从四个域中获取
${name}
1.2指定域获取
${pageScope.name}
域范围:pageScope/requestScope/sessionScope/applicationScope
2) 输出对象的属性值
${Student.name} 注意:.name 相当于.getName()方法
3)输出list集合
${list[0].name} 注意:[0] 相当于get(下标)方法
4)输出map集合
${map[key].name} 注意:[key] 相当于get(key)方法
3、实例
例1:
1 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 3 <html> 4 <head> 5 <title>EL表达式语法</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <% 9 String name="rose"; 10 //放入域对象中 11 //pageContext.setAttribute("name",name); 12 pageContext.setAttribute("name",name,PageContext.PAGE_SCOPE); 13 %> 14 <%-- 打印到页面 --%> 15 <%=name %> 16 <br/> 17 18 <%--从四个域中自动搜索--%> 19 jsp表达式:<%=pageContext.findAttribute("name")%> 20 EL表达式:${name } 21 <br/> 22 23 <%-- 从指定域中获取数据 --%> 24 EL表达式:${pageScope.name } 25 <%-- 26 ${pageScope.name} 等同于 <%=pageContext.getAttribute("name",pageContext.PAGE_SCOPE)%> 27 --%> 28 </body> 29 </html>
例2
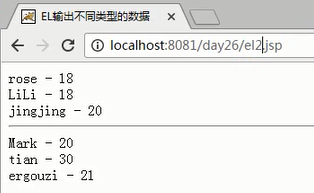
1 <%@page import="com.bw.entity.Student"%> 2 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 3 <% 4 String path = request.getContextPath(); 5 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 6 %> 7 8 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 9 <html> 10 <head> 11 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 12 13 <title>EL输出不同类型的数据</title> 14 15 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 16 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 17 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 18 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 19 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 20 <!-- 21 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> 22 --> 23 </head> 24 <body> 25 <%-- 1)EL输出对象的属性 --%> 26 <% 27 //保存数据 28 Student student=new Student("jack",20); 29 //放入域中 30 pageContext.setAttribute("student",student); 31 32 //list集合(保存数据) 33 List<Student> list=new ArrayList<Student>(); 34 list.add(new Student("rose",18)); 35 list.add(new Student("LiLi",18)); 36 list.add(new Student("jingjing",20)); 37 //放入域中 38 pageContext.setAttribute("list",list); 39 40 //Map集合(保存数据) 41 Map<String,Student> map=new HashMap<String,Student>(); 42 map.put("100", new Student("Mark",20)); 43 map.put("101", new Student("tian",30)); 44 map.put("102", new Student("ergouzi",21)); 45 //放入域中 46 pageContext.setAttribute("map", map); 47 %> 48 49 <%--使用EL表达式获取对象 --%> 50 ${list[0].name } - ${list[0].age }<br/> 51 ${list[1].name } - ${list[1].age }<br/> 52 ${list[2].name } - ${list[2].age }<br/> 53 54 <%-- 55 list[0]等价于(中括号相对于调用了get(参数)方法) 56 ((list)pageContext.findAttribute("list")).get(0) 57 --%> 58 <hr/> 59 60 <%--使用EL获取Map对象--%> 61 ${map['100'].name } - ${map['100'].age }<br/> 62 ${map['101'].name } - ${map['101'].age }<br/> 63 ${map['102'].name } - ${map['102'].age }<br/> 64 </body> 65 </html>
实例结果图
例3:
1 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <% 3 String path = request.getContextPath(); 4 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 5 %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 8 <html> 9 <head> 10 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 11 12 <title>EL表达式计算</title> 13 14 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 15 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 16 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 17 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 18 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 19 <!-- 20 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> 21 --> 22 23 </head> 24 25 <body> 26 <%-- 27 1)算术的表达式 28 + - * / 29 --%> 30 加法运算:${10+5 }<br/> 31 乘法运算:${10*5 } 32 <hr/> 33 34 <%-- 35 2)比较运算符 36 > < >= <= == != 37 --%> 38 ${10>5 }<br/> 39 ${10<5 }<br/> 40 ${10!=10 }<br/> 41 <hr/> 42 43 <%-- 44 3)逻辑运算符 45 && || ! 46 --%> 47 ${true && true }<br/> 48 ${true || false }<br/> 49 ${!false }<br/> 50 <hr/> 51 52 <%-- 53 4)判断 54 null 或者 空字符串 :empty 55 --%> 56 <% 57 String name="hello"; 58 pageContext.setAttribute("name",name); 59 %> 60 判断null: ${name==null }</br> 61 判断空字符串: ${name=="" }</br> 62 判断:${name==null || name=="" }<br/> 63 另一种判断空的写法:${empty name } 64 </body> 65 </html> 66
|
原创作者:DSHORE 作者主页:http://www.cnblogs.com/dshore123/ 原文出自:https://www.cnblogs.com/dshore123/p/10163207.html 欢迎转载,转载务必说明出处。(如果本文对您有帮助,可以点击一下右下角的 推荐,或评论,谢谢!) |