The "eight queens puzzle" is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other. Thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. The eight queens puzzle is an example of the more general N queens problem of placing N non-attacking queens on an N×N chessboard. (From Wikipedia - "Eight queens puzzle".)
Here you are NOT asked to solve the puzzles. Instead, you are supposed to judge whether or not a given configuration of the chessboard is a solution. To simplify the representation of a chessboard, let us assume that no two queens will be placed in the same column. Then a configuration can be represented by a simple integer sequence (, where Qi is the row number of the queen in the i-th column. For example, Figure 1 can be represented by (4, 6, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 5) and it is indeed a solution to the 8 queens puzzle; while Figure 2 can be represented by (4, 6, 7, 2, 8, 1, 9, 5, 3) and is NOT a 9 queens' solution.
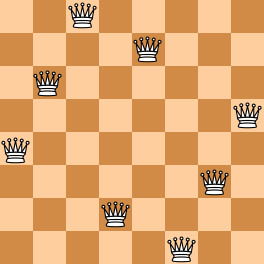 | 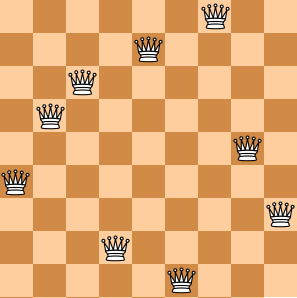 | |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives an integer K (1). Then K lines follow, each gives a configuration in the format "N Q1 Q2 ... QN", where 4 and it is guaranteed that 1 for all ,. The numbers are separated by spaces.
Output Specification:
For each configuration, if it is a solution to the N queens problem, print YES in a line; or NO if not.
Sample Input:
4
8 4 6 8 2 7 1 3 5
9 4 6 7 2 8 1 9 5 3
6 1 5 2 6 4 3
5 1 3 5 2 4Sample Output:
YES
NO
NO
YES#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn=10; main(){ int n,m; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d",&m); vector<int> v(m); bool cnt=true; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ cin>>v[j]; for(int k=0;k<j;k++){ if(v[k]==v[j]||abs(v[k]-v[j])==abs(j-k)){ cnt=false; break; } } } if(cnt==false){ printf("NO "); }else{ printf("YES "); } } return 0; }