打算修改zxing 源码应用到其它方面,所以最近花了点时间阅读其源码,无意中找到这篇博客,条码扫描二维码扫描——ZXing android 简化源码分析 对过程的分析还是可以参考的.原作者给出的一个基本的UML序列图:
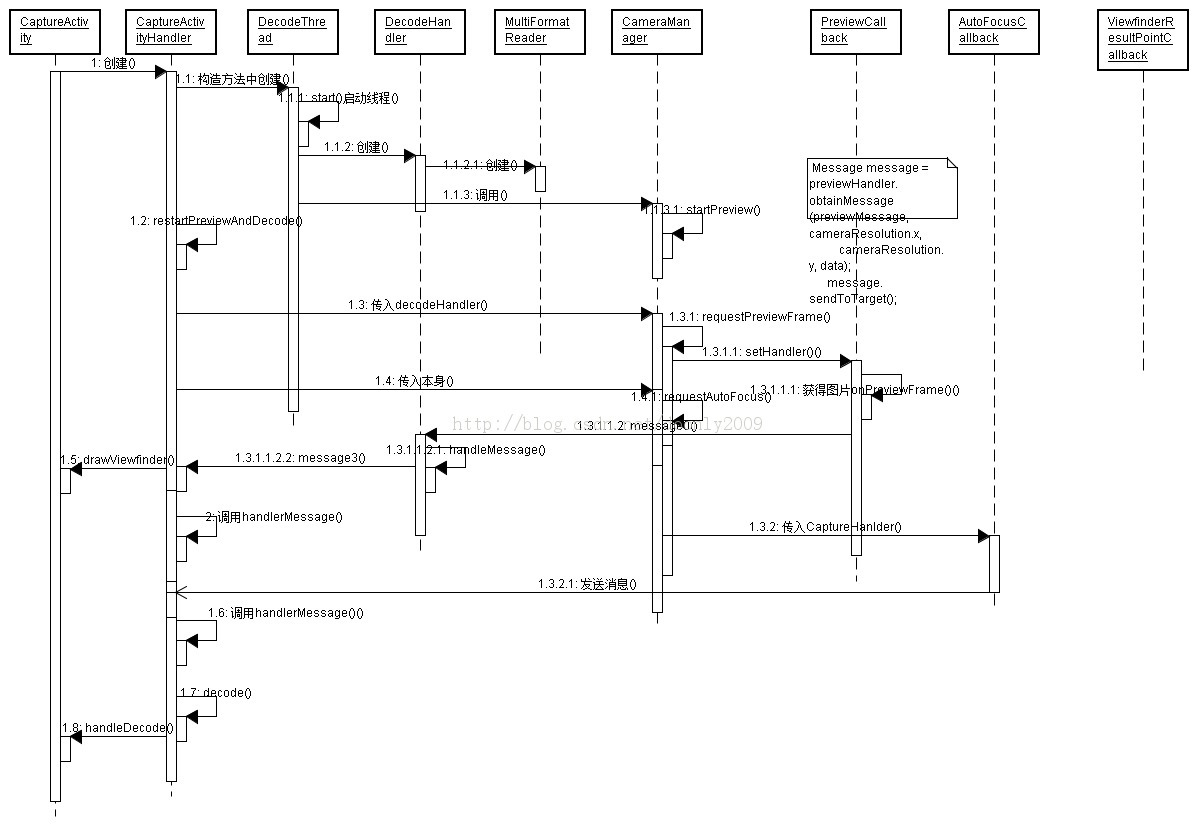
(图像引用自http://blog.csdn.net/doonly2009/article/details/12175997)
结合上面的序列图,本文将本zxing 一维码部分的源码进行解析,有不对的地方忘大家给予指正,所有内容仅供大家参考.更正上图的一个小错误,DecodeThead 是被CaptureActivityHandler 调用 decodeThread.start()方法启动的,而不是在构造方法中触发的.
部分一 ,环境搭建 2014.1.14
从这里下载工程文件,导入到Eclipse中(我的环境,windows,eclipse).这个工程文件是把一些代码打包成了jar文件,这反而不利于文件的分析.我们这里利用从官网下载的源码重新建立一个库工程文件,方便我们的代码分析.
1,core.jar 文件打包过程 .
这里的core.jar 和网上的zxing.jar core.jar 类似 ,不过网上下载的都是简化过的.过程如下:
①,新建android 工程 ,不需要勾选 Create activty
②,右键工程中的src -->new-->packages 命名为 com.google.zxing
③,右键 com.google.zxing --> import --> File System -->找到 zxing 源码 .. javacomgooglezxing 即可.
④,右键工程 选择 android 标签,勾选 Is Library 如图.
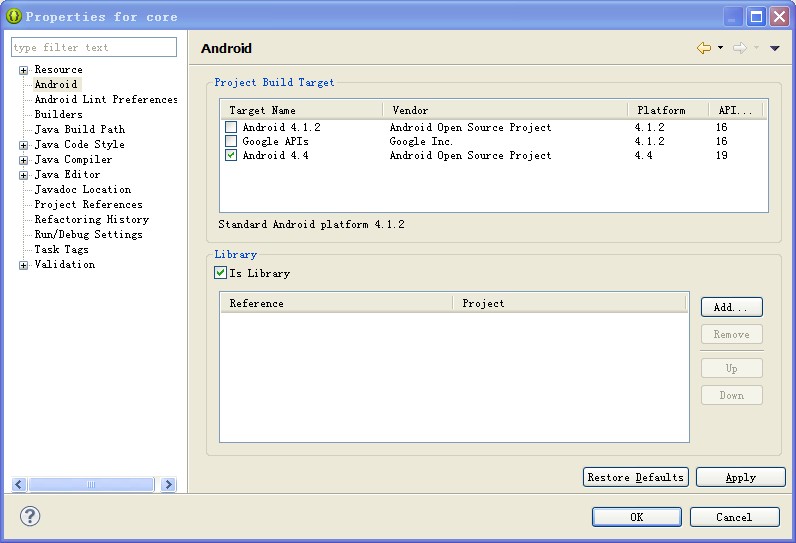
打开你的工程文件,可以看到生成的jar文件了.如图:
2,使用自己的 core.jar文件
打开之前下载的工程文件(已经导入到eclipse)删除之前引用的 zxing.jar 文件 .右键BarCodeTest 工程文件-->Properties-->Android 选项 -->在Libarary 选项中添加 . 这里会自动找到刚创建的包工程文件.
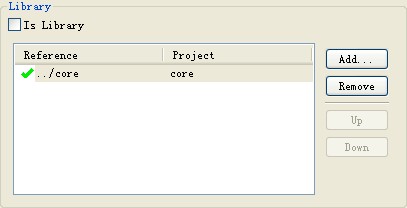
强调一点,若其它工程文件引用这个jar工程文件,则这个jar工程文件必须是打开状态.经过测试 zxing 2.3 和 1.6 版本的 core 文件都可以在上面下载到的简化工程使用.环境配置完成 ,下面将进行核心代码的分析.
部分二,源码分析 2014.1.21
经过一段时间阅读和分析源码,下面以程序执行的大体顺序进行源码的分析.我们从获取一帧数据开始分析,流程图如下:
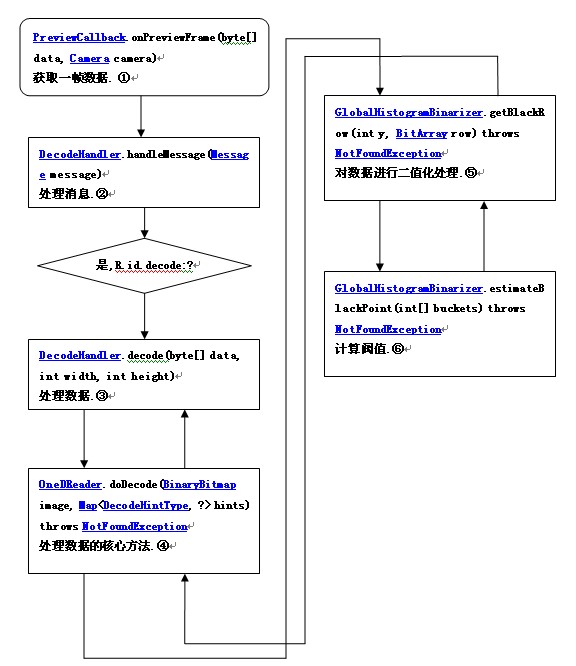
这里按这个流程图进行代码的分析.
1 ,过程①,获取最原始的数据,数据存储在 byte[] data 中.
2,过程②,通过传递 handler, 当有消息时,会自动跳转到 public void handleMessage(Message message) {}处执行.
DecodeHandler.handleMessage(Message message) 在restartPreviewAndDecode()方法中被传递,其过程如下图:

zxing中主要采用 Message 来传递消息 ,这里有两个继承handler 的类,分别为CaptureActivityHandler和DecodeHandler.消息实例的 创建分别在:
1 public void onPreviewFrame(byte[] data, Camera camera) { 2 Point cameraResolution = configManager.getCameraResolution(); 3 if (!useOneShotPreviewCallback) { 4 camera.setPreviewCallback(null); 5 } 6 if (previewHandler != null) { 7 //从这里传递 message 参数 ,创建Message对象,其Handler.obtainMessage可以调用Message.obtain来创建消息。 8 Message message = previewHandler.obtainMessage(previewMessage, cameraResolution.x, 9 cameraResolution.y, data); 10 //Sends this Message to the Handler specified by getTarget(). 11 //Throws a null pointer exception if this field has not been set. 12 //who use the getTarget() function? 13 //通过Message.sendToTarget向消息队列插入消息; 14 message.sendToTarget(); 15 previewHandler = null; 16 } else { 17 Log.d(TAG, "Got preview callback, but no handler for it"); 18 } 19 }
和,位于 com.zxing.decoding.DecodeHandler 类中的方法
1 private void decode(byte[] data, int width, int height) { 2 3 ......... 4 Message message = Message.obtain(activity.getHandler(), R.id.decode_succeeded, rawResult); 5 ......... 6 }
这样当有message 到来时便会自动调用 相应类中的handleMessage() 方法,实现对消息的处理.
3,过程③,这里实现对数据的解码,如果解码不成功,则进行下次解码,否则将会发送消息给CaptureActivityHandler 对象.
4,过程④,这里是实现解码的核心方法,包括数据的二值化和最内层的解码方法 Result result = decodeRow(rowNumber, row, hints),因为我这里只分析一维码的部分,所以预先设定的解码类型,这里会跳转到 这个类MultiFormatUPCEANReader中的decodeRow 方法.
OneDReader.doDecode(BinaryBitmap image, Map<DecodeHintType, ?> hints) throws NotFoundException 对每一次获取的帧进行最大15次的解码,这里的解码只是针对一行数据.从中间区域开始,分别对上下依次获取的行数据进行解码,如果解码成功则返回.
强调一点,zxing 不对获取的图片数据进行旋转,虽然支持旋转.但是支持对转动180 的一维码的解码,代码如下:
1 if (attempt == 1) { // trying again? 2 row.reverse(); // reverse the row and continue 3 // This means we will only ever draw result points *once* in the life of this method 4 // since we want to avoid drawing the wrong points after flipping the row, and, 5 // don't want to clutter with noise from every single row scan -- just the scans 6 // that start on the center line. 7 if (hints != null && hints.containsKey(DecodeHintType.NEED_RESULT_POINT_CALLBACK)) { 8 Map<DecodeHintType,Object> newHints = new EnumMap<DecodeHintType,Object>(DecodeHintType.class); 9 newHints.putAll(hints); 10 newHints.remove(DecodeHintType.NEED_RESULT_POINT_CALLBACK); 11 hints = newHints; 12 } 13 }
这里主要的就是这句 row.reverse().
5,过程⑤,zxing 对行数据二值化的代码如:
1 public BitArray getBlackRow(int y, BitArray row) throws NotFoundException { 2 LuminanceSource source = getLuminanceSource(); 3 int width = source.getWidth(); 4 if (row == null || row.getSize() < width) { 5 row = new BitArray(width); 6 } else { 7 row.clear(); 8 } 9 10 initArrays(width); 11 //在这里 luminances 被赋值 12 //y=180; 13 byte[] localLuminances = source.getRow(y, luminances); 14 //统计并建立直方图 15 int[] localBuckets = buckets; 16 /*---------modify here ,just for analysis .--------------------*/ 17 int i_row[] = new int [width]; 18 for(int x=0;x<width;x++){ 19 i_row[x]=localLuminances[x] & 0xff; 20 } 21 /*-------------------------------------------------------------*/ 22 for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) { 23 int pixel = localLuminances[x] & 0xff; 24 localBuckets[pixel >> LUMINANCE_SHIFT]++; 25 } 26 //According to the histogram, find the threshold. 27 int blackPoint = estimateBlackPoint(localBuckets); 28 //Based on threshold ,set 1 bit. 21.1.2014 29 int left = localLuminances[0] & 0xff; 30 int center = localLuminances[1] & 0xff; 31 for (int x = 1; x < width - 1; x++) { 32 int right = localLuminances[x + 1] & 0xff; 33 // A simple -1 4 -1 box filter with a weight of 2. 34 int luminance = ((center << 2) - left - right) >> 1; 35 if (luminance < blackPoint) { 36 row.set(x); 37 } 38 left = center; 39 center = right; 40 } 41 return row; 42 }
代码的基本过程包括,统计并建立直方图-->根据直方图找到白与黑的中间阀值-->大于阀值的为白色,反之黑色.在这个方法中, int luminance = ((center << 2) - left - right) >> 1; 这句代码我起初理解为对图像进行降噪处理,后来经过数学推导不合理,所以便在zxing group 进行了提问,zxing 成员给予了热心的回复:
6,过程⑥,zxing 黑白阀值的寻找比较巧妙,其代码如下 :
1 private static int estimateBlackPoint(int[] buckets) throws NotFoundException { 2 // Find the tallest peak in the histogram. 3 int numBuckets = buckets.length; 4 int maxBucketCount = 0; 5 int firstPeak = 0; 6 int firstPeakSize = 0; 7 //找到 数组中最多像素点的个数(maxBucketCount) 和 对应的 序号,序号其实就是亮度值(区间)firstPeak. 8 //这里的 firstPeak 即可能是 黑色的区间,也可能是白色的区间. 9 for (int x = 0; x < numBuckets; x++) { 10 if (buckets[x] > firstPeakSize) { 11 firstPeak = x; 12 firstPeakSize = buckets[x]; 13 } 14 if (buckets[x] > maxBucketCount) { 15 maxBucketCount = buckets[x]; 16 } 17 } 18 19 // Find the second-tallest peak which is somewhat far from the tallest peak. 20 int secondPeak = 0; 21 int secondPeakScore = 0; 22 for (int x = 0; x < numBuckets; x++) { 23 int distanceToBiggest = x - firstPeak; 24 // Encourage more distant second peaks by multiplying by square of distance. 25 int score = buckets[x] * distanceToBiggest * distanceToBiggest; 26 if (score > secondPeakScore) { 27 secondPeak = x; 28 secondPeakScore = score; 29 } 30 } 31 32 // Make sure firstPeak corresponds to the black peak. 33 if (firstPeak > secondPeak) { 34 int temp = firstPeak; 35 firstPeak = secondPeak; 36 secondPeak = temp; 37 } 38 39 // If there is too little contrast in the image to pick a meaningful black point, throw rather 40 // than waste time trying to decode the image, and risk false positives. 41 if (secondPeak - firstPeak <= numBuckets >> 4) { 42 throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance(); 43 } 44 45 // Find a valley between them that is low and closer to the white peak. 46 int bestValley = secondPeak - 1; 47 int bestValleyScore = -1; 48 for (int x = secondPeak - 1; x > firstPeak; x--) { 49 int fromFirst = x - firstPeak; 50 //这里找 到两个峰比较远,同时又点少的区间.这里 fromFist 采用平方的形式,可以理解更接近于白色. 51 int score = fromFirst * fromFirst * (secondPeak - x) * (maxBucketCount - buckets[x]); 52 if (score > bestValleyScore) { 53 bestValley = x; 54 bestValleyScore = score; 55 } 56 } 57 58 return bestValley << LUMINANCE_SHIFT; 59 }
代码还是比较清晰的,因为对于一维码和二维码,图像的主要颜色为黑白色,所以直方图呈现双峰结构.知道这个特性,其算法思想也就明子了.基本过程:根据直方图找到最多的像素区域--->根据 int score = buckets[x] * distanceToBiggest*distanceToBiggest 这个评分,找到第二个像素区域.可以理解为距离白色(黑色)比较远且个数比较多的像素区域.--->根据 int score = fromFirst * fromFirst * (secondPeak - x) * (maxBucketCount - buckets[x]);这个评分,找到距离两个峰比较远且比较少的区域为阀值. 这里fromFist 采用平方的形式,可以理解更接近于白色.距离比重越大,其阀值便越靠近另外一个峰.
代码分析基本到这里,我这里将对zxing 原码进行修改,进行二次开发应用到其它方面.
2014.2.13
经过一段时间的程序开发,基于android 的数卡程序终于完工了,为了解化程序的开发,这里手机照的照片再打印出来,如下图:

下面的日志显示了程序的识别效果,识别左上角的卡片.
02-13 18:22:13.438: D/Correct rate(30802): Successful frequency 4.171029.
02-13 18:22:13.478: D/Correct rate(30802): The times of success 985,The times of failed 6,The correct rate 0.99394554.
02-13 18:22:13.478: D/Correct rate(30802): Successful frequency 4.174507.
02-13 18:22:13.569: D/Correct rate(30802): The times of success 986,The times of failed 6,The correct rate 0.9939516.
02-13 18:22:13.569: D/Correct rate(30802): Successful frequency 4.177081.
从日志里可以看出,识别能够得到不错的效果. 使用时要求卡片明亮清洁,扫描背景最好为黑灰色.卡片数量大于3 张小于50张.
程序算法及思想:
程序先根据二值化后的数据,先均匀先取5 行-->找总亮度值最小的前3行-->根据第2和3行号 取2行数据 -->找到这两行的起始位置
-->从起始位置找 白色卡片的数量(这里是经过二值后的数据) --> 如果最终两行计算的数据相等则返回结果 和结束位置.
本人面向对象的编程能力实在不敢恭维,android 程序写出了 c 语言风格.所以我这里便不公开源码,代码写的很乱.
这里本人上传 打包的apk 程序和图片素材.
安装包和测试文件安装包和测试图片4.rar
算法经过优化之后的安装包和测试文件5.rar
功能展示
最佳性能测试视频. 距离图片50cm ,纯黑白条件下,白色条纹宽3mm 缝隙为 0.8mm
博文为本人所写,转载请表明出处,博客园梦工厂2012.
推荐阅读
http://blog.csdn.net/doonly2009/article/details/12175997
http://kuangjianwei.blog.163.com/blog/static/190088953201361015055110/
http://www.cnblogs.com/zdwillie/p/3331250.html