1.查询记录
select*from 表名 [where 条件];
eg:select*from students;//查询 students 表中所有记录,所有字段的值都显示出来
select field1,field2,...fieldn... from 表名 [where 条件];
eg:select id,name,age from students;//查询 students 表中所有记录, 只显示出 id,name,age三个字段的值
1.“*”表示将所有的字段都显示出来
2.用逗号分割,列出需要显示的字段
2.查询不重复的记录
select distinct 字段 from 表名;
eg: select distinct name from students;//查询名字不相同的学生;
select distinct name,age from students;//查询名字和年龄同时不同的学生
1.distinct必须放在最开头
2.distinct只能使用需要去重的字段进行操作。 ----也就是说我sidtinct了name,age两个字段,我后面想根据id进行排序,是不可以的,因为只能name,age两个字段进行操作.
3.distinct去重多个字段时,含义是:几个字段 同时重复 时才会被 过滤。
3.条件查询
select 字段 from 表名 where 条件; eg:select * from student where sex='男' and age>20; //查询性别是男,并且年龄大于20岁的人。
where后面的条件可以用>、<、>=、<=、!=等多种比较运算符,多个条件之间可以用or、and等逻辑运算符
4.排序和限制
排序
select * from 表名 [where 条件] [ order by field1 [desc/asc],field2 [desc/asc]... ];
eg:select *from student order by age desc;//查询学生表并按年龄降序排列。
1.desc 降序排列,asc 升序排列
2.order by 后面可以跟多个不同的排序字段,每个排序字段都可以有不同的排序顺序。
3.如果排序字段的值一样,则相同的字段按照第二个排序字段进行排序。
4.如果只有一个排序字段,则字段相同的记录将会无序排列。
限制 select ... [limit 起始偏移量,行数];
eg:select * from student order by mark desc limit 5;//取出成绩前五名的学生(省略了起始偏移量,此时默认为0)
1.默认情况下,起始偏移量为0,只写记录行数就可以。
5.聚合
select 字段 fun_name from 表名 [where 条件] [group by field1,field2...] [with rollup] [having 条件];
eg:
1.fun_name 表示要做的聚合操作,也就是说聚合函数,常用的有 : sum(求和)、count(*)(记录数)、max(最大值)、min(最小值)。
2.group by关键字 表示要进行分类聚合的字段。比如要按照部门分类统计员工数量,部门就应该写在group by 后面。
3.with rollup 是可选语法,表明是否对分类聚合后的结果进行再汇总
4.having 关键字表示对分类后的结果再进行条件过滤。
公司员工表A如下 (编号,姓,名,薪水) :
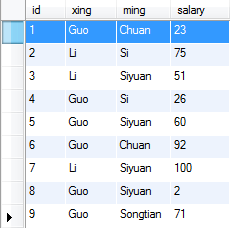
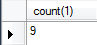
统计总人数 select count(1) from A;
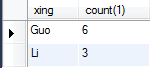
统计各个姓的人数 select xing,count(1) from A group by xing;
既要统计各个姓的人数,又统计总人数 select xing,count(1) from A group by xing with rollup;
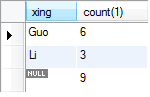
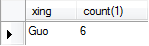
统计人数大4的姓 select xing,count(1) from A group by xing having count(1)>4;
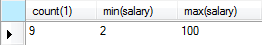
统计薪水总额,最低薪资,最高薪资 select count(1),min(salary),max(salary) from A;
6.表连接
表连接分为内连接和外连接。
他们之间最主要的区别:内连接仅选出两张表中互相匹配的记录,外连接会选出其他不匹配的记录。
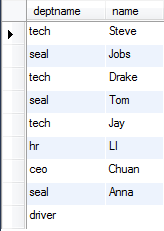
以下是员工表staff和职位表deptno:
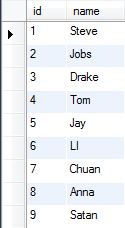
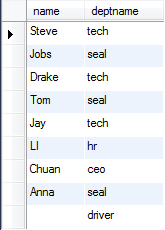
内连接 select staff.name,deptname from staff,deptno where staff.name=deptno.name;
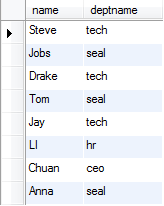
外连接 分为左连接和右连接
左连接:包含所有左边表中的记录,甚至是右边表中没有和他匹配的记录。
右连接:包含所有右边表中的记录,甚至是右边表中没有和他匹配的记录。
外连接(左连接): select staff.name,deptname from staff left join deptno on staff.name=deptno.name;
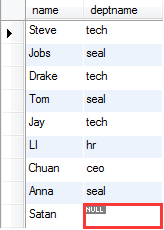
外连接(右连接): select deptname,deptno.name from staff right join deptno on deptno.name=staff.name;