文件描述符重定向
cat<test01 :将输入重定向到test01文件
cat>test02<test01 :将标准正确输出重定向到test02文件,输入设备重定向到test01文件。如果test02存在会覆盖内容。输出文件不存在会自动创建。
cat>>test02<test01 :输出追加到test02
cat>test02 2>error <test01 :将标准输出重定向到test02文件,错误输出重定向到error文件。均是被覆盖。2>>error是追加。
cat>test02 2>&1<test01 :&表示联合,将正确和错误信息都重定向到test02文件
cat 2>&1 1>test02<test01 :联合没有传递性,标准错误输出在当前终端,正确信息输入test02
下面的整体都没有想清楚,文件描述符怎么实现重定向的?popen的机制是什么?
重定向编程
输入重定向:关闭标准输入设备,打开或复制普通文件,使其文件描述符为0
输出重定向:关闭标准输出设备,打开或复制普通文件,使其文件描述符为1
错误重定向:关闭标准错误输入设备,打开或复制普通文件,使其文件描述符为2
int dup (int __fd):复制某打开的文件描述符,与原来的文件描述符共享同一个文件表项
下面代码将输出重定向到管道的写端
int f_des[2]; pipe(f_des); //创建无名管道 close(fileno(stdout)); //关闭标准输出设备 dup(f_des[1]); //返回一个最低的可用文件描述符,即已经关闭的标准输出设备(描述符为1)
int dup2 (int __fd, int __fd2) :如果fd2是一个已经打开的文件描述符,则首先关闭该文件,然后再复制。成功会返回新的文件描述符fd2,否则返回-1。
重定向编程的例子:
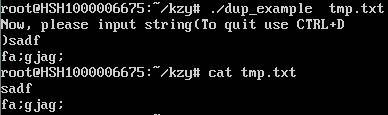
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #define BUFFER_SIZE 1024 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int fd; char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; if(argc != 2) { fprintf(stderr,"Usage:%s outfilename a", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } //打开重定向文件 if((fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR)) == - 1) { fprintf(stderr, "Open %s Error:%s a", argv[1], strerror(errno)); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if(dup2(fd, fileno(stdout)) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Redirect Standard Out Error:%s a", strerror(errno)); // a是响铃符,会出现滴的一声 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } fprintf(stderr, "Now, please input string"); fprintf(stderr, "(To quit use CTRL+D )"); while(1) { fgets(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE, stdin); if(feof(stdin)) break; write(fileno(stdout), buffer, strlen(buffer)); } exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
用重定向实现who|sort
父进程开两个子进程,分别指向who,sort 并且重定向相应的端,关闭与另一端的连接。
父进程关闭管道两个方向的连接,等待子进程退出。
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int fds[2]; if(pipe(fds) == -1) { perror("pipe"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if(fork() == 0) //执行sort的子进程 { char buf[128]; dup2(fds[0], 0); //重定向标准输入 close(fds[1]); execlp("sort", "sort", (char *)0); } else { if(fork() == 0) { dup2(fds[1], 1); //重定向标准输出 close(fds[0]); execlp("who", "who",(char *)0); } else { close(fds[0]); close(fds[1]); wait(NULL); //等待子进程退出 wait(NULL); } } return 0; }

流重定向
在POSIX2中可以实现流的重定向,通过函数popen(), pclose()
FILE *popen (__const char * __command, __const char * __modes):创建子进程, 并在子进程中执行第一个参数所指程序,同时返回一个文件指针。第二个参数表示I/O方式。
- 如果是输出重定向,需要设置第二个参数为 "r" 权限,即可以被进程读
- 如果是输入重定向,需要设置第二个参数为 "w" 权限,即可以被进程写
int pclose (FILE * __stream) :关闭相应流对象
利用流的重定向实现echo test|cat
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<limits.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { FILE * finput, * foutput; char buffer[PIPE_BUF]; int n; finput = popen("echo test!", "r"); //将echo test命令的输出与读端相连 foutput = popen("cat", "w"); //将cat的命令输入与写端相连 read(fileno(finput), buffer, strlen("test!")); //读echo test的输出结果到buf write(fileno(foutput),buffer,strlen("test")); //将管道内容读出作为cat输入 pclose(finput); pclose(foutput); printf(" "); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
