概述
控制反转IoC(Inversion of Control)是说创建对象的控制权进行转移,以前创建对象的主动权和创建时机是由自己把控的,而现在这种权力转移到第三方,比如转移交给了IoC容器,它就是一个专门用来创建对象的工厂,你要什么对象,它就给你什么对象,有了 IoC容器,依赖关系就变了,原先的依赖关系就没了,它们都依赖IoC容器了,通过IoC容器来建立它们之间的关系。
1.IoC加载
2.注入
从SpringAOP源码的入口一节,我们可以定位加载bean的源码到doLoadBeanDefinitions:
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); // 取得XML文件的Document对象, 这个解析过程由DefaultDocumentLoader完成,包括验证Document等 return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); //解析Document } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } ....... }
doLoadDocument
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); }
XML比如 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> //XSD方式,用于验证XML文件的正确性 <bean id="..">...</bean> </beans> //常用的XML文件验证方法有两种:DTD和XSD,DTD现在基本不用了,而上图中的spring-beans-4.0.xsd对应在源码中的org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.spring-beans-4.0.xsd。
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) { //获取XML的验证方式 int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode(); //获取检测模式 if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) { return validationModeToUse; } int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource);//如果没有启动,则自动检测 if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) { return detectedMode; } // Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD, // since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until // detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag). return VALIDATION_XSD; }
XML的Document对象就到这里,接下来是registerBeanDefinitions了,启动对beanDefinition的解析
registerBeanDefinitions
BeanDefinition载入过程其实就是把定义的BeanDefinition在IoC容器中转化为一个Spring内部表示的数据结构的过程。IoC容器对Bean的管理和依赖注入的实现,
都是通过对其持有的BeanDefinition进行各种相关的操作来完成的。这些BeanDefinition数据在IoC容器中通过一个HashMap来维护。
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 得到BeanDefinitionDocumentReader来对XML的BeanDefinition进行解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 具体的解析过程在BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法中完成
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createDelegate(this.readerContext, root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { Assert.state(this.environment != null, "Environment must be set for evaluating profiles"); String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { return; } } } preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {//获取Document对象根元素的所有子节点并循环解析 NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);//解析spring bean规则默认节点 } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); //解析自定义节点(之前的AOP就是在这里解析的) } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } } private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { //import元素 importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { //alias元素 processAliasRegistration(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { //bean元素 processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {内嵌beans元素,作为根节点递归解析 // recurse doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); } }
直接从代码就可以看出,Spring首先获取Document的根元素(一般为<beans/>),然后取得根元素所有的子节点并循环解析这些子节点;如果子节点在Spring默认的命名空间内,则按照Spring Bean定义规则来解析,否则按照自定义的节点解析。在按照Spring Bean定义规则进行解析的parseDefaultElement方法中,完成了对<import/>、<alias/>、<bean/>、<beans/>等元素的解析。
这里只关注bean的解析
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 具体的解析委托给BeanDefinitionParserDelegate来完成
// BeanDefinitionHolder是BeanDefinition的封装类, 封装了BeanDefinition、Bean的名字和别名, 用它来完成向IoC容器注册.
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//解析<bean>元素,获取id和name属性 String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();//处理bean中的alias属性 if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) { String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); } String beanName = id; if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {//如果bean没有配置id,将别名中的第一个名赋值给beanName beanName = aliases.remove(0); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName + "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); } } if (containingBean == null) { //检查name是否唯一 checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); } AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); if (beanDefinition != null) {//对bean元素进行详细解析 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { try { if (containingBean != null) { beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); } else { beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); if (beanClassName != null && beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { aliases.add(beanClassName); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); } } catch (Exception ex) { error(ex.getMessage(), ele); return null; } } String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); } return null; }
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement( Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) { this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName)); String className = null; if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) { //获取class属性值,载入到beanDefinition中,此时并不实例化 className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim(); } try { String parent = null; if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) { parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE); } AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent); //根据class名称及parent属性创建BeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); // 对当前<Bean>元素中配置的一些属性进行解析, 如singleton、abstract等 bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 对<Bean>元素的meta(元数据)、lookup-method、replaced-method等子元素进行解析 parseMetaElements(ele, bd); parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); //解析构造方法参数 parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); //解析property设置 parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource()); bd.setSource(extractSource(ele)); return bd; } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex); } catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) { error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err); } catch (Throwable ex) { error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex); } finally { this.parseState.pop(); } return null; }
<bean>元素解析已经完了,而<bean>元素属性及其子元素的解析顺序为:1,解析<bean>元素的属性。2,解析<description>子元素。3,解析<meta>子元素。4,解析<lookup-method/>子元素。5,解析<replaced-method>子元素。6,解析<constructor-arg>子元素。7,解析<property>子元素。8,解析<qualifier>子元素。解析过程中像<meta>、<qualifier>等子元素都很少使用,而下面就直接解析最常用的子元素<property>子元素。
/** * Parse property sub-elements of the given bean element. */ public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) { NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();//获取所有子元素 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {//如果是property元素,则进行解析 parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd); } } } /** * Parse a property element. */ public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) { String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);//property的name属性 if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) { error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele); return; } this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName)); try { if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {//如果一个bean下存在相同的property,则直接返回 error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele); return; } // 解析<property>元素, 返回的对象对应<property>元素的解析结果, 最终封装到PropertyValue中, 并设置到BeanDefinitionHolder中 Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName); PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val); parseMetaElements(ele, pv); pv.setSource(extractSource(ele)); bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv); } finally { this.parseState.pop(); } } public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) { String elementName = (propertyName != null) ? "<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" : "<constructor-arg> element"; // Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.property子元素只能是这几个 NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes(); Element subElement = null; for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) && !nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) { // Child element is what we're looking for. if (subElement != null) { error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele); } else { subElement = (Element) node; } } } // 判断property元素是否含有ref和value属性, 不允许既有ref又有value属性. // 同时也不允许ref和value属性其中一个与子元素共存. boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE); boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE); if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) || ((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) { error(elementName + " is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele); } if (hasRefAttribute) { String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE); if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) { error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele); } RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName); ref.setSource(extractSource(ele)); return ref; } else if (hasValueAttribute) { TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE)); valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele)); return valueHolder; } else if (subElement != null) { return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd); } else { // Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found. error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele); return null; } }
就这样beanDefinition加载好了
再经过其他的一些初始化,已经可以getBean来获取bean 了
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); ac.getBean("iUserDao");
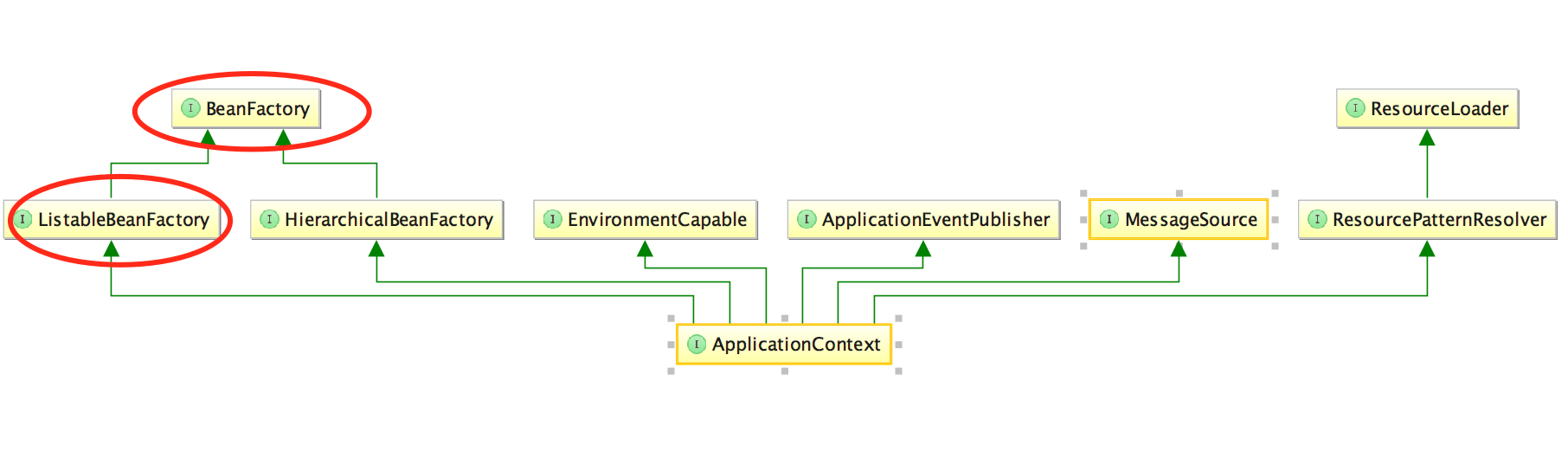
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中的getBean方法哪来的呢?看一下继承关系就知道了
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); //beanFactory来源,最终loadBeanDefinitions为DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
再看下继承关系图
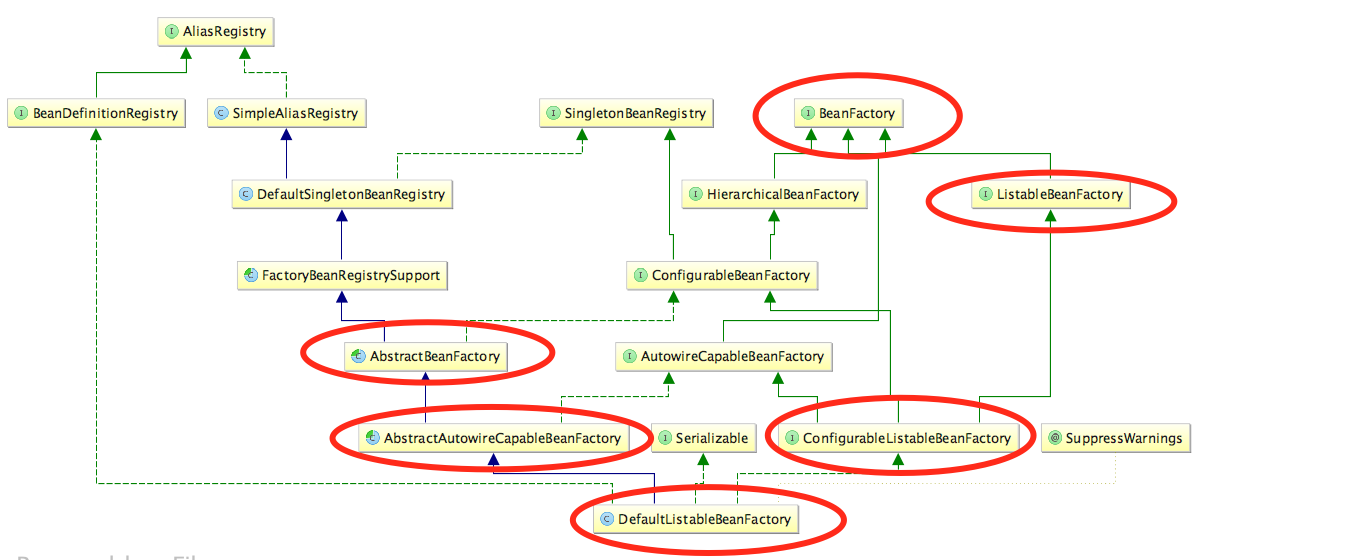
现在来看下getBean的实现
AbstractBeanFactory.java
protected <T> T doGetBean( final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { //指定名称获取被管理的bean名称 final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. //单例模式 Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {//如果单例模式已经存在 logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } //这里完成FactoryBean的相关处理,对于FactoryBean,BeanFactory已经有所提及,在后面会详细分析 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. //对容器中的BeanDefinition进行检查,检查能否在当前的BeanFactory中取得Bean. //如果在当前的工厂中取不到,则到父类的BeanFactory中去取 //如果在父类中取不到,则到父类的父类中取 BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } } if (!typeCheckOnly) { markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } try { final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) { if (isDependent(beanName, dependsOnBean)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dependsOnBean + "'"); } registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName); getBean(dependsOnBean); } } // Create bean instance.单例模式 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance.创建新的实例 Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " + "consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } } // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) { try { return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } } return (T) bean; }
从上面,可以看出doGetBean,是依赖注入的实际入口,他定义了Bean的定义模式,单例模式(Singleton)和原型模式(Prototype),而依赖注入触发的前提是BeanDefinition数据已经建立好的前提下。其实对于Ioc容器的使用,Spring提供了许多的参数配置,每一个参数配置实际上代表了一个Ioc实现特性,而这些特性的实现很多都需要在依赖注入的过程中或者对Bean进行生命周期管理的过程中完成。Spring Ioc容器作为一个产品,其真正的价值体现在一系列产品特征上,而这些特征都是以依赖反转模式作为核心,他们为控制反转提供了很多便利,从而实现了完整的Ioc容器。
再看核心createBean方法
getBean是依赖注入的起点,之后就会调用createBean,createBean可以生成需要的Bean以及对Bean进行初始化,但对createBean进行跟踪,发现他在AbstractBeanFactory中仅仅是声明,而具体实现是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类里。
直接定位到createBeanInstance
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); //创建bean } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); } }); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //依赖注入 if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.// 确认需要创建的Bean实例的类可以实例化 Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
//这里使用工厂方法对Bean进行实例化 if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); } if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } // Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...//使用容器自动装配方法进行实例化 boolean resolved = false; boolean autowireNecessary = false; if (args == null) { synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) { resolved = true; autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; } } } if (resolved) { if (autowireNecessary) {//配置自动装配属性,使用容器自动实例化 return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null); } else {//无参构造方法实例化 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } } // Need to determine the constructor... Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);//使用容器自动装配,调用构造方法实例化 } // No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.//使用默认构造函数对Bean进行实例化 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); }
看个默认的实例化方式instantiateBean
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) { try { Object beanInstance; final BeanFactory parent = this; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent); } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent); } BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance); initBeanWrapper(bw); return bw; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex); } }
/** * Return the instantiation strategy to use for creating bean instances. */ protected InstantiationStrategy getInstantiationStrategy() { return this.instantiationStrategy; } private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy(); //这里用到了cglib,但是一定用到了cglib吗?
Object instantiate(Constructor<?> ctor, Object[] args) { Class<?> subclass = createEnhancedSubclass(this.beanDefinition); Object instance; if (ctor == null) { instance = BeanUtils.instantiate(subclass); } else { try { Constructor<?> enhancedSubclassConstructor = subclass.getConstructor(ctor.getParameterTypes()); instance = enhancedSubclassConstructor.newInstance(args); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(this.beanDefinition.getBeanClass(), String.format( "Failed to invoke constructor for CGLIB enhanced subclass [%s]", subclass.getName()), ex); } } // SPR-10785: set callbacks directly on the instance instead of in the // enhanced class (via the Enhancer) in order to avoid memory leaks. Factory factory = (Factory) instance; factory.setCallbacks(new Callback[] {NoOp.INSTANCE, new LookupOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner), new ReplaceOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner)}); return instance; }
SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java
@Override public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName, BeanFactory owner) { // Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides. if (beanDefinition.getMethodOverrides().isEmpty()) { Constructor<?> constructorToUse; synchronized (beanDefinition.constructorArgumentLock) { constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) beanDefinition.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod; if (constructorToUse == null) { final Class<?> clazz = beanDefinition.getBeanClass(); if (clazz.isInterface()) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface"); } try { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>() { @Override public Constructor<?> run() throws Exception { return clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null); } }); } else { constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null); } beanDefinition.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex); } } } return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse); } else { // Must generate CGLIB subclass. return instantiateWithMethodInjection(beanDefinition, beanName, owner); } }
如果有需要覆盖或者动态替换的方法使用Cglib进行动态代理,如果没有需要动态改变的方法那就直接使用反射进行实例化。所谓的动态替换或覆盖的情况,就是使用了replace或者lookup的配置方法。这两个方法的作用就是在调用目标方法的时候,对调用过程进行拦截,调用实现增强功能的拦截器,返回原来实例的代理。关于拦截和代理这部分会在AOP中进行详细的分析。
接下来就是分别使用Jdk的反射和Cglib进行实例化的具体过程了。
这所以对象实例化,Spring反射不一定用的是Jdk的反射机制,有可能也会有cglib。
下面分别为jdk和cglib的方式
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException { Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null"); try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor); return ctor.newInstance(args); } catch (InstantiationException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor.getDeclaringClass(), "Is it an abstract class?", ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor.getDeclaringClass(), "Is the constructor accessible?", ex); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor.getDeclaringClass(), "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor.getDeclaringClass(), "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException()); } } Object instantiate(Constructor<?> ctor, Object[] args) { Class<?> subclass = createEnhancedSubclass(this.beanDefinition); Object instance; if (ctor == null) { instance = BeanUtils.instantiate(subclass); } else { try { Constructor<?> enhancedSubclassConstructor = subclass.getConstructor(ctor.getParameterTypes()); instance = enhancedSubclassConstructor.newInstance(args); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(this.beanDefinition.getBeanClass(), String.format( "Failed to invoke constructor for CGLIB enhanced subclass [%s]", subclass.getName()), ex); } } // SPR-10785: set callbacks directly on the instance instead of in the // enhanced class (via the Enhancer) in order to avoid memory leaks. Factory factory = (Factory) instance; factory.setCallbacks(new Callback[] {NoOp.INSTANCE, new LookupOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner), new ReplaceOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner)}); return instance; }
标准的使用Enhancer实例化对象的方法,包括设置基类,回调方法等。这个方法中出现了LookupOverrideMethodInterceptor和ReplaceOverrideMethodInterceptor两个拦截器,作用就是拦截目标方法,实现方法增强的功能。
Bean对象已经创建好了,接下来就该进行依赖注入了。回到populateBean方法
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) { //获取beanDefinition中property的值 PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); if (bw == null) {//实例对象为空 if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {//属性不为空 throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance"); } else {//实例为空,属性也为空直接返回 // Skip property population phase for null instance. return; } } // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the // state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, // to support styles of field injection. //在设置属性之前调用Bean的PostProcessor后置处理器 boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { continueWithPropertyPopulation = false; break; } } } } if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) { return; } //开始进行依赖注入过程,先处理autowire的注入 //根据bean名字或类型自动装配处理 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {//根据类型自动装配注入 autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } pvs = newPvs; } //检查日期是否持有用于单态模式Bean关闭时的后置处理器 boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(); boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE); if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) { PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); if (hasInstAwareBpps) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvs == null) { return; } } } } if (needsDepCheck) { //对要配置的属性进行依赖检查 checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs); } } //对属性进行依赖注入 applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); }
1、依赖注入发生的时间
当Spring IoC容器完成了Bean定义资源的定位、载入和解析注册以后,IoC容器中已经管理类Bean定义的相关数据,但是此时IoC容器还没有对所管理的Bean进行依赖注入,依赖注入在以下两种情况发生:
(1).用户第一次通过getBean方法向IoC容索要Bean时,IoC容器触发依赖注入。
(2).当用户在Bean定义资源中为<Bean>元素配置了lazy-init属性,即让容器在解析注册Bean定义时进行预实例化,触发依赖注入。