剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
//法一:
// if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
// ListNode *pre = nullptr, *cur = head;
// while (cur)
// {
// ListNode *t = cur->next;
// cur->next = pre; pre = cur;
// cur = t;
// }
// return pre;
//法二
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode *pre = new ListNode(head->val); head = head->next;
while (head)
{
ListNode *t = new ListNode(head->val);
t->next = pre; pre = t;
head = head->next;
}
return pre;
// if (!head || !head->next) return head;
// ListNode *newHead = reverseList(head->next);
// head->next->next = head;
// head->next = NULL;
// return newHead;
}
};

剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 3 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head;
while (fast && k--)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast && slow)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
O(N)
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
返回删除后的链表的头节点。注意:此题对比原题有改动
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 1
输出: [4,5,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
说明:
题目保证链表中节点的值互不相同
若使用 C 或 C++ 语言,你不需要 free 或 delete 被删除的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
if (head->val == val) return head->next;
ListNode *cur = head->next, *pre = head;
while (cur && cur->val != val)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur) {
pre->next = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
};

剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
// Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
// if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
// Node *cur = head;
// unordered_map<Node*, Node*> dic;
// while (cur)
// {
// dic[cur] = new Node(cur->val);
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// cur = head;
// while(cur)
// {
// dic[cur]->next = dic[cur->next];
// dic[cur]->random = dic[cur->random];
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// return dic[head];
// }
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head)
{
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
Node *cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node *tmp = new Node(cur->val);
//插入新节点 tmp (tmp == cur)
tmp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp;
cur = tmp->next;
}
//2. 构建各个新节点的random指向
cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->random != nullptr) {
//cur->next是cur的新节点
//cur->random->next是cur->random的新节点
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
//cur真正next是 cur->next->next
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//3. 拆分两个链表
//新节点头节点
cur = head->next;
Node *pre = head, *res = head->next;
while (cur->next != nullptr)
{
//建立原始结点链表
pre->next = pre->next->next;
//新节点链表
cur->next = cur->next->next;
pre = pre->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
//如果这条不写,相当于修改了原始链表最后一个元素的指针
pre->next = nullptr;
//返回新链表头节点
return res;
}
};

剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。为了让您更好地理解问题,以下面的二叉搜索树为例:

我们希望将这个二叉搜索树转化为双向循环链表。链表中的每个节点都有一个前驱和后继指针。对于双向循环链表,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
下图展示了上面的二叉搜索树转化成的链表。“head” 表示指向链表中有最小元素的节点。
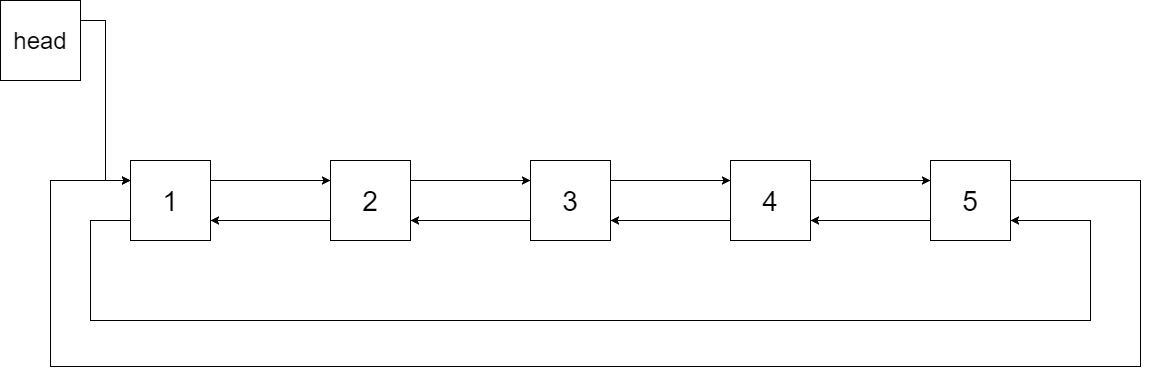
特别地,我们希望可以就地完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
Node *pre, *head;
void dfs(Node *cur)
{
if (cur == nullptr) return;
dfs(cur->left);
if (pre == nullptr) {
head = cur; //记录头指针
} else {
pre->right = cur;
}
cur->left = pre;
pre = cur;
dfs(cur->right);
}
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
dfs(root);
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
};

141. 环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
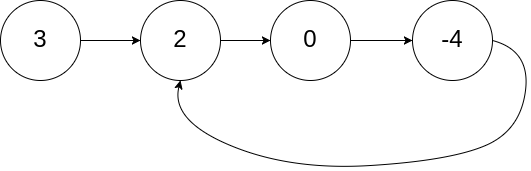
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false;
// ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
// while (fast->next && fast->next->next)
// {
// slow = slow->next;
// fast = fast->next->next;
// if (slow == fast) {
// return true;
// }
// }
// return false;
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head->next;
while (slow != fast)
{
if (!fast->next || !fast->next->next) {
return false;
} else {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
}
return true;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n);空间复杂度:O(1)
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
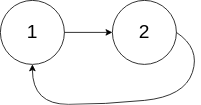
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围在范围 [0, 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 的值为 -1 或者链表中的一个有效索引
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return NULL;
unordered_set<ListNode*> st;
while (head && st.count(head) == 0)
{
st.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
if (head) {
return head;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
};
法二:快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return NULL;
// unordered_set<ListNode*> st;
// while (head && st.count(head) == 0)
// {
// st.insert(head);
// head = head->next;
// }
// if (head) {
// return head;
// } else {
// return NULL;
// }
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
//链表长度为 a + b, a为入口前长度,b为环长度
//相遇时,f=2s, f=s+nb => f=2nb, s=nb,f,s分别走2n,n个环长度
//统计k步,slow走到环入口,k=a+nb
//让slow先走nb步
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
//slow已走过nb步,让slow再走a步,到环入口;若从head开始走a步,也可以到环入口,相遇;
fast = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
