1. 需求
开发封闭原则:虽然在这个原则是用的面向对象开发,但是也适用于函数式编程,简单来说,它规定已经实现的功能代码不允许被修改,但可以被拓展,即:
- 封闭:已实现的功能代码块
- 开发:对拓展开发

2. 使用装饰器
2.1 未使用装饰器(原理)
def w1(func): def inner(): # 验证1 # 验证2 # 验证3 print("----正在验证权限----") func() return inner def f1(): print("---f1----") def f2(): print("---f2----") f1 = w1(f1) f1()
----正在验证权限----
---f1----
2.2 使用装饰器
def w1(func): def inner(): # 验证1 # 验证2 # 验证3 print("----正在验证权限----") func() return inner @w1 def f1(): print("---f1----") @w1 def f2(): print("---f2----") f1() f2()
----正在验证权限----
---f1----
----正在验证权限----
---f2----
3. 再议装饰器
# 定义函数:完成包裹数据 def makeBold(fn): def wrapped(): print("-----1------") return "<b>" + fn() + "</b>" return wrapped # 定义函数:完成包裹数据 def makeItalic(fn): def wrapped(): print("-----2------") return "<i>" + fn() + "</i>" return wrapped @makeBold @makeItalic def test3(): print("-----3-----") return "hello world" s = test3() print(s)
-----1------
-----2------
-----3-----
<b><i>hello world</i></b>
4. 装饰器执行时间
@w1 def f1(): print("---f1----")
只要Python解释器执行到了这个代码 ,那么就会自动的进行装饰,而不是等到调用的时候才装饰
5. 装饰器对有参数、无参数函数进行装饰
5.1 无参数
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(): print("---func_in----1----") functionName() print("---func_in----2----") print("-----func----2-----") return func_in @func def test(): print("----test------") test()
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
---func_in----1----
----test------
---func_in----2----
5.2 函数有参数
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(aa, bb): print("---func_in----1----") functionName(aa, bb) print("---func_in----2----") print("-----func----2-----") return func_in @func def test(a, b): print("----test---a=%d---b=%d---" %(a, b)) test(11, 22)
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
---func_in----1----
----test---a=11---b=22---
---func_in----2----
5.3 函数有不定参数
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(*args, **kargs): print("---func_in----1----") functionName(*args, **kargs) print("---func_in----2----") print("-----func----2-----") return func_in @func def test(a, b, c): print("----test---a=%d---b=%d---c=%d-------" %(a, b, c)) test(11, 22, 33)
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
---func_in----1----
----test---a=11---b=22---c=33-------
---func_in----2----
5.4 函数有返回值
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(*args, **kargs): print("---func_in----1----") res = functionName(*args, **kargs) print("---func_in----2----") return res print("-----func----2-----") return func_in @func def test(a, b, c): print("----test---a=%d---b=%d---c=%d-------" %(a, b, c)) return "hahaha" res = test(11, 22, 33) print("res: ", res)
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
---func_in----1----
----test---a=11---b=22---c=33-------
---func_in----2----
res: hahaha
6. 通用的装饰器
核心代码:
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(*args, **kargs): print("---func_in----1----") res = functionName(*args, **kargs) print("---func_in----2----") return res print("-----func----2-----") return func_in
验证:
def func(functionName): print("-----func----1-----") def func_in(*args, **kargs): print("---func_in----1----") res = functionName(*args, **kargs) print("---func_in----2----") return res print("-----func----2-----") return func_in @func def test(a, b, c): print("----test---a=%d---b=%d---c=%d-------" %(a, b, c)) return "hahaha" @func def test2(a): print("-----test2---%d---"%a) res = test(11, 22, 33) print("res: ", res) test2(3)
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
-----func----1-----
-----func----2-----
---func_in----1----
----test---a=11---b=22---c=33-------
---func_in----2----
res: hahaha
---func_in----1----
-----test2---3---
---func_in----2----
7. 装饰器有参数
from time import ctime, sleep def timefun_arg(pre="hello"): def timefun(func): def wrappedfunc(): print("%s called at %s %s" %(func.__name__, ctime(), pre)) return func() return wrappedfunc return timefun @timefun_arg("douzi") def foo(): print("I am foo") @timefun_arg("python") def too(): print("I am too") foo() sleep(2) too()
foo called at Thu May 9 00:57:58 2019 douzi
I am foo
too called at Thu May 9 00:58:00 2019 python
I am too

8. 综合
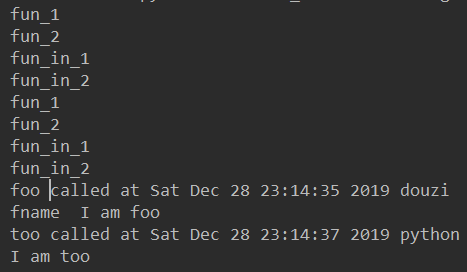
from time import ctime, sleep def timefun_arg(pre="hello"): print("fun_1") def timefun(func): print("fun_in_1") def wrappedfunc(*args, **kwargs): print("%s called at %s %s" %(func.__name__, ctime(), pre)) return func(*args, **kwargs) print("fun_in_2") return wrappedfunc print("fun_2") return timefun @timefun_arg("douzi") def foo(fname): print(fname, "I am foo") @timefun_arg("python") def too(): print("I am too") foo("fname ") sleep(2) too()