一、引用计数
引用计数是Objetive-C语言的内存管理机制,用于管理OC对象(通常指包含isa指针的结构体)的内存。
一个对象的引用计数为大于0的计数,表示这个对象被持有,不能被释放,当引用计数为0时表示这个对象需要被释放掉。
改变引用计数的方法有,retain、release、alloc、autorelease、reatinautorelease、copy、multicopy方法。其中后面的两种方法内部也是调用前面alloc的方法改变union isa_t
union isa_t
{
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
# __x86_64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x001f800000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x001d800000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t shiftcls : 44;
uintptr_t magic : 6;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 8;
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<56)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<7)
};
}
跟引用计数相关的为两个变量,一个是extra_rc 一个是has_sidetable_rc
第二个字段跟sidetable相关
struct SideTable {
spinlock_t slock;
RefcountMap refcnts;
weak_table_t weak_table;
void lock() { slock.lock(); }
void unlock() { slock.unlock(); }
void forceReset() { slock.forceReset(); }
// Address-ordered lock discipline for a pair of side tables.
static void lockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);
static void unlockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);
};
通过sidetable中的RefCountMap,应用计数hash表来查找某个对象的引用计数,对引用计数进行操作;具体的hash方法是
#if __LP64__
static inline uint32_t ptr_hash(uint64_t key)
{
key ^= key >> 4;
key *= 0x8a970be7488fda55;
key ^= __builtin_bswap64(key);
return (uint32_t)key;
}
#else
static inline uint32_t ptr_hash(uint32_t key)
{
key ^= key >> 4;
key *= 0x5052acdb;
key ^= __builtin_bswap32(key);
return key;
}
#endif
综上,引用计数存储在两个地方,优先存储到extra_rc中,存不下的时候放到sidetable中
retain的过程如下:
[NSObject retain];
- (id)retain {
return ((id)self)->rootRetain();
}
id objc_object::rootRetain()
{
return rootRetain(false, false);
}
id objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (id)this;
bool sideTableLocked = false;
bool transcribeToSideTable = false;
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
do {
transcribeToSideTable = false;
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
if (slowpath(!newisa.nonpointer)) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
if (tryRetain) return sidetable_tryRetain() ? (id)this : nil;
else return sidetable_retain();
}
if (slowpath(tryRetain && newisa.deallocating)) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return nil;
}
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry);
if (slowpath(carry)) {
if (!handleOverflow) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
return rootRetain_overflow(tryRetain);
}
if (!tryRetain && !sideTableLocked) sidetable_lock();
sideTableLocked = true;
transcribeToSideTable = true;
newisa.extra_rc = RC_HALF;
newisa.has_sidetable_rc = true;
}
} while (slowpath(!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)));
if (slowpath(transcribeToSideTable)) {
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
}
if (slowpath(!tryRetain && sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();
return (id)this;
}
那extra_rc中能存下多少呢,一个字节最大255,当大于255会发生溢出,然后extra_rc减半,一半存储到sidetable中
二、Tagged Pointer
苹果为了优化部分小对象的存储效率,没有针对这一类小对象使用引用计数的方式,比如小NSString、NSNumber
具体使用Tagged Pointer的类型有:
OBJC_TAG_NSAtom = 0, OBJC_TAG_1 = 1, OBJC_TAG_NSString = 2, OBJC_TAG_NSNumber = 3, OBJC_TAG_NSIndexPath = 4, OBJC_TAG_NSManagedObjectID = 5, OBJC_TAG_NSDate = 6, OBJC_TAG_7 = 7
比如代码:
NSString *str1 = [[NSString alloc] initWithCString:"1"
encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSString *str2 = [[NSString alloc] initWithCString:"20000xdsfdsadwd"
encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"%@", [str1 valueForKey:@"retainCount"]);
NSLog(@"%@", [str2 valueForKey:@"retainCount"]);
输出:
2018-11-09 10:37:04.591196+0800 ARCTest2[506:158351] 18446744073709551615 2018-11-09 10:37:04.591240+0800 ARCTest2[506:158351] 1
具体Tagged Pointer的内存布局
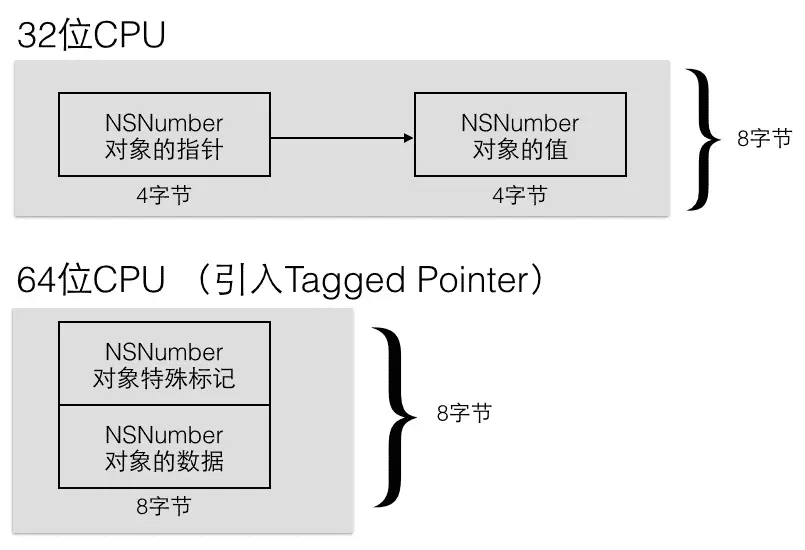
也就是,对于Tagged Pointer指向的对象,值就存在于指针的内存区域中
它的特征:
Tagged Pointer 专门用来存储小的对象,例如 NSNumber 和 NSDate(后来可以存储小字符串) Tagged Pointer 指针的值不再是地址了,而是真正的值。所以,实际上它不再是一个对象了,它只是一个披着对象皮的普通变量而已。 它的内存并不存储在堆中,也不需要 malloc 和 free,所以拥有极快的读取和创建速度。
三、附录一道相关面试题
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *target;
//.... dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("parallel", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000 ; i++) {
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
self.target = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ksddkjalkjd%d",i];
});
}
上面的变量target在多线程访问之下,其指向的对象存在多线程中被释放的问题。但是如果将后面的string 改为小数字就不会,因为小对象的内存不需要free。