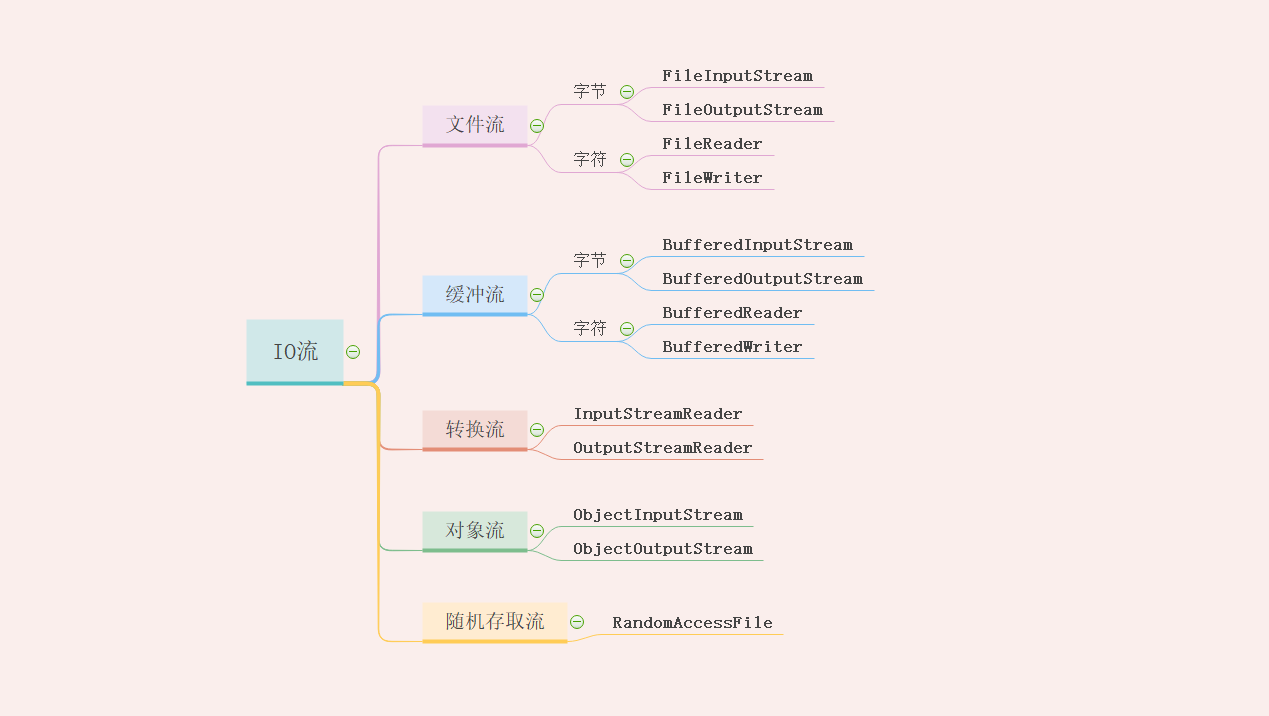
图片梳理
理解
对于文件流来说是io流的基础,牵扯到缓冲流,缓冲流是在内存中使用io流的各类操作,转换流顾名思义,是字节与字符流之间的转换 ,要先有字节流和字符流,对象流,最主要的是类的序列化与反序列化,相当于一个封装转化,随机存取流,也是在有字节流和字符流的基础上。
File类
- 能新建,删除,重命名文件和目录,但不能访问文件内容,访问文件内容要通过输入/输出流
图片梳理

File操作
package day12;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("D:\test\abc\tt.txt");//这个时候对象f就是tt.txt文件
File f4 = new File("D:\test\abc");//这个目录
<!-- File f2 = new File("D:/test/abc/tt.txt");
File f3 = new File("D:" + File.separator + "test\abc\tt.txt");
File f1 = new File("D:\test","abc\tt.txt");//这个f1也是tt.txt文件,这种实验相对比较少 -->
//注意,在文件中是路径的分隔符,但是在java编程中一个的意思是转移符,在java中\或者/才是文件的分隔符
//也可以File.separator作为文件分隔符
System.out.println(f.getName());//获取文件名
System.out.println(f4.getName());//获取文当前的文件名称
File f5 = new File("src/day12/Test.java");//使用相对路径来创建file对象
System.out.println(f5.getPath());//获取文件或者文件夹的路径,就是new file时候写的路径
System.out.println(f5.getAbsolutePath());//获取当前文件的绝对路径
System.out.println(f5);
System.out.println(f5.getAbsoluteFile());//返回一个用当前的文件的绝对路径构建的file对象
System.out.println(f5.getParent());//返回当前文件或者文件夹的父级路径
f.renameTo(new File("D:\test\abc\tt1.txt"));//给文件或文件夹重命名
File f6 = new File("D:\test\abc1");
System.out.println(f6.exists());//判断文件或者文件夹是否存在
File f7 = new File("D:\test\abc\tt1.txt");
System.out.println(f7.canWrite());//判断文件是否可写
System.out.println(f7.canRead());//判断文件是否可读
System.out.println(f7.isFile());//判断当前的file对象是不是文件
System.out.println(f7.isDirectory());//判断当前的file对象是不是文件夹或者目录
System.out.println(f7.lastModified());//获取文件的最后修改时间,返回的是一个毫秒数
System.out.println(f7.length());//返回文件的长度,单位是字节数
File f8 = new File("D:\test\abc\tt2.txt");
System.out.println(f8.exists());//判断文件是否存在
if(!f8.exists()){
try {
f8.createNewFile();//创建新的文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
<!-- f8.delete();//删除文件
File f9 = new File("D:\test\abc\cc");
File f9 = new File("D:\test\abc\cc\dd");
f9.mkdir();//创建单层目录,如果使用这一方法来创建多层目录,就得一层一层的执行mkdir()
File f10 = new File("D:\test\abc\a\b\c");
f10.mkdirs();//这个方法是直接用来创建多层目录 -->
File f11 = new File("D:\test");
String[] fl = f11.list();//返回的是当前文件夹的子集的名称,包括目录和文件
for(String s : fl){
System.out.println(s);
}
File[] fs = f11.listFiles();//返回的是当前文件夹的子集的file对象,包括目录和文件
for(File ff : fs){
System.out.println(ff);
}
}
递归遍历文件
public void test(File file){
if(file.isFile()){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件");
}else{
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件夹");
//如果是文件夹,这个文件夹里就可能有子文件夹或者文件
File[] fs = file.listFiles();//获取当前文件夹下的子文件夹或者文件的file对象
if(fs != null && fs.length > 0){
for(File ff : fs){
test(ff);//递归
if(ff.isFile()){
System.out.println(ff.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件");
}else{
System.out.println(ff.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件夹");
File[] fs1 = ff.listFiles();
if(fs1 != null && fs1.length > 0){
for(File ff1 : fs1){
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
文件流:数据流的读写都是基于文件的操作
- 字节流非常通用,可以用来操作字符的文档,还可以操作然后的其他类型文件,都是使用二进制转换
FileInputStream:字节输入流
public static void testFileInputStream(){
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:/test/abc/tt1.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[10];//设置一个byte数组接收读取的文件的内容
int len = 0;//设置一个读取数据的长度
//in.read(b);//in.read方法有一个返回值,返回值是读取的数据的长度,如果读取到最后一个数据,还会向后读一个,这个时候返回值就是-1
//也就意味着当in.read的返回值是-1的时候整个文件就读取完毕了
while((len = in.read(b)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
//new String(b,0,len),参数1是缓冲数据的数组,参数2是从数组的那个位置开始转化字符串,参数3是总共转化几个字节
}
in.close();//注意。流在使用完毕之后一段要关闭
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
FileOutputStream:字节输出流
public static void testFileOutputStream(){
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:/test/abc/tt4.txt");//指定行tt4输出数据
String str = "knsasjadkajsdkjsa";
out.write(str.getBytes());//把数据写到内存
out.flush();//把内存中的数据刷写到硬盘
out.close();//关闭流
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
复制文件到指定位置
public static void copyFile(String inPath, String outPanth){
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(inPath);//读取的源文件
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outPanth);//复制到哪里
byte[] b = new byte[100];
int len = 0;
while((len = in.read(b)) != -1){
out.write(b, 0, len);//参数1是写的缓冲数组,参数2是从数组的那个位置开始,参数3是获取的数组的总长度
}
out.flush();//把写到内存的数据刷到硬盘
out.close();
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
FileReader:字符输入流
public static void testFileReader(String inPath){
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(inPath);//创建文件字符输入流的对象
char[] c = new char[10];//创建临时存数据的字符数组
int len = 0;//定义一个输入流的读取长度
while((len = fr.read(c)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, len));
}
fr.close();//关闭流
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
FileWriter:字符输出流
public static void testFileWriter(String text,String outPath){
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outPath);
fw.write(text);//写到内存中
fw.flush();//把内存的数据刷到硬盘
fw.close();//关闭流
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
复制文件到指定位置(字符流只适合操作内容是字符文件)
public static void copyFile(String inPaht, String outPath){
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(inPaht);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outPath);
char[] c = new char[100];
int len = 0;
while((len = fr.read(c)) != -1){//读取数据
fw.write(c,0,len);//写数据到内存
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
fr.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
缓冲流:数据流的读写都是基于内存的操作
- 缓冲流要套接在相应的节点流之上,对读写的数据提供了缓冲的功能,提高了读写的效率,同时增加了一些新的方法,对于输出的缓冲流,写出的数据会先在内存中缓存,使用flush()将会使内存中的数据立刻写出
- 简单来说就是先把数据缓存到内存里,在内存中做io操作
BufferedInputStream:缓冲字节输入流
public static void testBufferedInputStream() throws Exception {
// 文件字节输入流对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt.txt");
// 把文件字节输入流放到缓冲字节输入流对象
BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] b = new byte[10];
int len = 0;
while ((len = br.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
}
// 关闭流的时候,本着一个最晚开的最早关,依次关
br.close();
in.close();
}
BufferedOutputStream:缓冲字节输入流
public static void testBufferedOutputStream() throws Exception {
// 创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt1.txt");
// 把字节输出流对象放到缓冲字节输出流中
BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
String s = "hello world";
bo.write(s.getBytes());// 写到内存中
bo.flush();// 刷到硬盘上
// 关闭流的时候,本着一个最晚开的最早关,依次关
bo.close();
out.close();
}
缓冲流实现文件的复制
public static void copyFile() throws Exception {
// 缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt1.txt"));
// 缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt2.txt"));
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;// 设置一个没出读取到的数据的长度,直到br.read方法执行到最后(比如说文件中只有hello
// world,执行到最后一个就读取d的后面,这个时候返回值就是-1)
while ((len = br.read(b)) != -1) {
bo.write(b, 0, len);// 写到内存
}
bo.flush();// 刷到硬盘
bo.close();
br.close();
}
BufferedReader:缓冲字符输入流
public static void testBufferedReader() throws Exception {
FileReader r = new FileReader("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(r);
char[] c = new char[100];
int len = 0;
while ((len = br.read(c)) != -1) {// br.read(c)读到文件的最后一个字符的下一位,返回值就是-1
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, len));
}
br.close();
r.close();
}
BufferedWriter:缓冲字符输出流
public static void testBufferedWriter() throws Exception {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt3.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
String s = "hello world!!!!";
bw.write(s);
bw.flush();
bw.close();
fw.close();
}
缓冲字符流复制文件
public static void copyFile() throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt3.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt4.txt"));
char[] c = new char[100];
int len = 0;
while ((len = br.read(c)) != -1) {
bw.write(c, 0, len);
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
转换流
- 转换字节输入流为字符输入流 注意,在转换字符流的时候,设置的字符集编码要与读取的文件的数据的编码一致 不然就会出现乱码 InputStreamReader
- 所有的文件都是有编码格式,对于我们来说,TXT和java文件一般来讲有三种编码,ISO8859-1,西欧编码,是纯粹英文编码,不适应汉字,GBK和UTF-8,这两编码是适用于重要和英文,我们一般使用UTF-8编码
InputStreamReader:转换字节输入流为字符输入流
public static void testInputStreamReader() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt5.txt");
// 把字节流转换为字符流
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(fs, "GBK");// 参数1是字节流,参数2是编码
//InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(fs,"UTF-8");//参数1是字节流,参数2是编码
char[] c = new char[100];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read(c)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, len));
}
in.close();
fs.close();
}
OutputStreamReader:转换字节输出流为字符输出流
public static void testOutputStreamWriter() throws Exception {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt6.txt");
//OutputStreamWriter os = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "UTF-8");
OutputStreamWriter os = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "GBK");
os.write("你好你好");
os.flush();
os.close();
out.close();
}
标准输入输出流
- System.in(默认输入键盘):类型是InputStream
- System.out(默认输出显示器):类型是PrintStream,是OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream的子类
标准的输入流
public static void testSystemIn() throws Exception {
// 创建一个接收键盘输入数据的输入流
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
// 把输入流放到缓冲流里
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(is);
String str = "";// 定义一个临时接收数据的字符串
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
is.close();
}
把控制台输入的内容写到指定的TXT文件中,当接收到字符串over,就结束程序的运行
public static void write2TXT() throws Exception {
// 创建一个接收键盘输入数据的输入流
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
// 把输入流放到缓冲流里
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(is);
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\testdemo\demo\src\day13\tt7.txt"));
String line = "";
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if (line.equals("over")) {
break;
}
// 读取的每一行都写到指定的TXT文件
out.write(line);
}
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
is.close();
}
打印流(了解)
PrintStream/PrintWriter:System.out.println等
数据流(了解):专门用来做基本数据类型的读写的
DataInputStream:数据输出流
用数据输出流写到文件的中的基本数据类型的数据,是乱码的,不能直接辨认出来,需要数据输入流来读取 DataOutputStream
public static void testDataOutputStream() throws Exception {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt8.txt"));
//out.writeBoolean(true);
out.writeDouble(1.35d);
//out.writeInt(100);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
DataOutputStream:数据输入流
如果写的时候是writeDouble,读的时候就得是readDouble DataInputStream
public static void testDataInputStream() throws Exception {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt8.txt"));
System.out.println(in.readDouble());
in.close();
}
对象流(序列化与反序列化):把一个对象转化为一个数据流进行读写
ObjectInputStream:对象的序列化
public static void testSerialize() throws Exception {
// 定义对象的输出流,把对象的序列化之后的流放到指定的文件中
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt9.txt"));
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "zhangsan";
p.age = 11;
out.writeObject(p);
out.flush();// 刷写数据到硬盘
out.close();
}
ObjectOutputStream:对象的反序列化
public static void testDeserialize() throws Exception {
// 创建对象输入流对象,从指定的文件中把对象序列化后的流读取出来
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt9.txt"));
Object obj = in.readObject();
Person p = (Person) obj;
// 这个时候序列化与反序列化使用的类不是一个类分别是day13.Person和day13.test.Person
// 这个时候反序列化就有异常day13.Person cannot be cast to day13.test.Person
//day13.test.Person p = (day13.test.Person)obj;
System.out.println(p.name);
System.out.println(p.age);
in.close();
}
RandomAccessFile:随意存取文件流:插入位置,读取位置,存储位置随意
- RandomAccessFile的构造有两个参数,参数1是读写的文件的路径
- 参数2是指定 RandomAccessFile 的访问模式
- r: 以只读方式打开
- rw:打开以便读取和写入
- rwd:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容的更新
- rws:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容和元数据的更新
- 最常用是r和rw
随意读文件
public static void testRandomAccessFileRead() throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile ra = new RandomAccessFile("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt10.txt", "r");
//ra.seek(0);//设置读取文件内容的起始点
ra.seek(8);// 通过设置读取文件内容的起始点,来达到从文件的任意位置读取
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = ra.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
}
ra.close();
}
随意存文件
public static void testRandomAccessFileWrite() throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile ra = new RandomAccessFile("D:/testdemo/demo/src/day13/tt10.txt", "rw");
//ra.seek(0);//设置写的起始点,0代表从开头写
// 注意:如果是在文件开头或者中间的某个位置开始写的话,就会用写的内容覆盖掉等长度的原内容
ra.seek(ra.length());// 设置写的起始点,ra.length()代表从文件的最后结尾写,也就是文件的追加
ra.write("你好".getBytes());
ra.close();
}