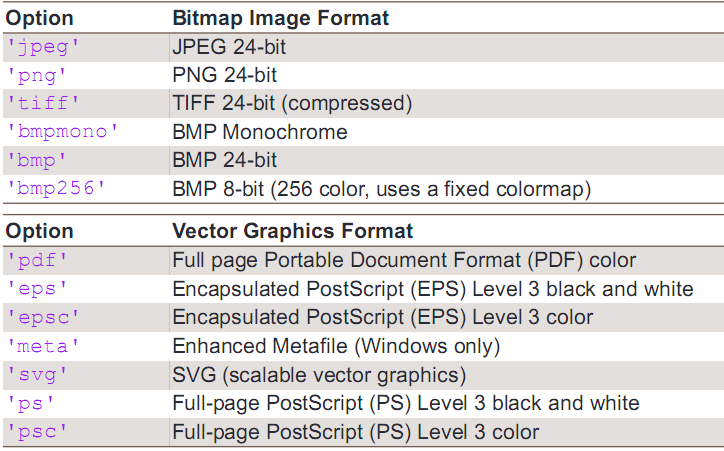
matlab 初级画图
1.plot()
plot(x,y) plots each vector pairs (x,y)
画图函数画出每个点 每组变量
plot (y) plots each vector pairs(x,y),where x=[1...n],n=length(y)
仅有一个变量时 仅画出 当x=整数点时的对应y值得点
example:
plot (cos(0:pi/20:2*pi));
从0-2π 间隔为pi/20的 那些cos值
x=0:1/1000:2*pi; 1/1000为步进值 越小越光滑
y=sin(x);
plot(x,y);
保持当前图的基础上再另加其他的图 需要用到指令 hold on
关闭功能为hold off
例如 hold on
plot(sin(0:2pi));
plot(cos(0:2pi));
hold off
plot style
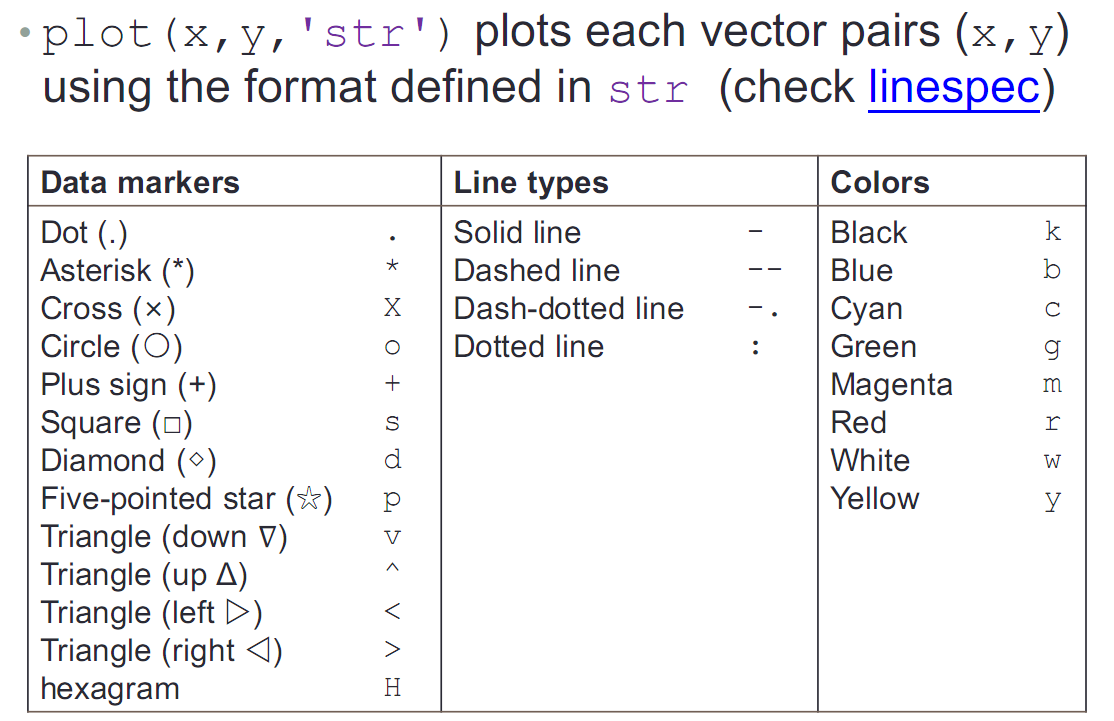
hold on
plot (cos(0:pi/20:2*pi),'or'); 对照上表中 or表示红色的圆圈
plot(sin(0:pi/20:2*pi).'xg'); xg 表示绿色的XX
hold off
如下图所示
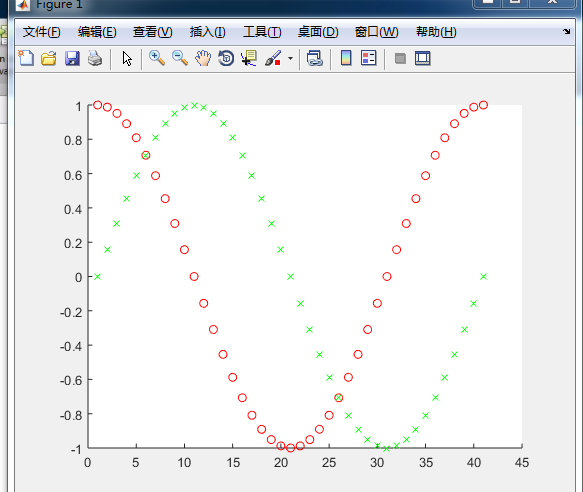
legend() 图例
1.add legend to graph
legend('L1',....)
1.position adjustment 位置调节
例如:
x=0:0.05:4*pi;
y=sin(x);
h=cos(x);
w=1./(1+exp(-x));
g=(1/(2*pi*2)^0.5).*exp((-1.*(x-2*pi).^2)./(2*2^2));
plot(x,y,'bd-',x,h,'gp:',x,w,'ro-',x,g,'c^-');
legend('sin(x)','cos(x)','Sigmoid','Gauss function');
如下图所示
title() and ?label() 标题和坐标轴
title() xlabel() ylabel() zlabel()
xlabel('str');
ylabel('str');
title('str');
str中的转义字符 例如pi 表示成π 则需要 输入pi
表示e的-x次方 需要输入 e^{-x} 大括号表示特殊的字元
text() and annotation()
text with mathematical expression using LaTex
x=linspace(0,3);
y=x.^2.*sin(x);
plot(x,y);
line([2,2],[0,2^2*sin(2)]);
str='$$ int_{0}^{2} x^2sin(x) dx $$';
text(0.25,2.5,str,'Interpreter','latex');
annotation('arrow','X',[0.32,0.5],'Y',[0.6,0.4]);
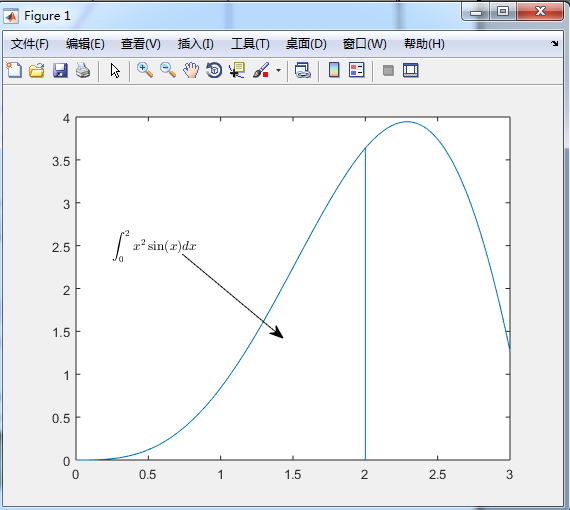
1.
linspace是Matlab中的均分计算指令,用于产生x1,x2之间的N点行线性的矢量。其中x1、x2、N分别为起始值、终止值、元素个数。若默认N,默认点数为100。 X=linspace(1,100)
3.int 就是积分符号 _{0}为下标 ^{2} 表示上标 ,x^2sin(x)dx 为内容为x的平方sin(x)dx ,$$为语法格式
4.'arrow','X',[0.32,0.5],'Y',[0.6,0.4] 其中的0.32和0.5为箭头的坐标
练习
plot f as a black line and g as aseries of red circles for the range t=1 to 2 in on figure
f=t^2 and g=sin(2πt)
Label each axis, and add title and legend
hold on
t=linspace(1,2);
f=t.^2;
g=sin(2*pi*t);
plot(t,f,'k-',t,g,'ro');
xlabel('Time(ms)');
ylabel('f(t)');
title('Mini Assignment #1');
legend('t^{2}','sin(2pit)');
hold off
图示如下

Figure Adjustment
several properties:
font font size line width axis limit tick position tick label
字体 大小 线条宽度 轴的极限 步进位置 步进标签
first step what kinds of objects in the graph?
a figure is composed of many objects?
figure object axes object line object
层级关系
hierarchy--》figure--》axes----》(line;text;surface;....) 对象的层级关系 分别是 图形 坐标轴 (线 文本 表面...)
figure 的属性 编辑---》图形属性 调出界面

modifying properties of an object
strategy:
1. identify the handle of an object 定义对象的句柄(变量实例);
2. fetch or modify the object 's properties 获取或修改对象的属性
example
1.upon creantion:
h=plot(x,y);
get(h);
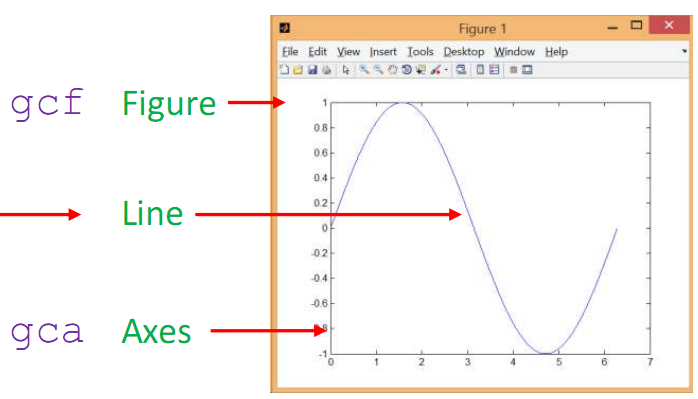
例子中的h指向line
utility functions 工具函数
gca return handle of current axes 当前的坐标轴实例句柄
gcf return handle of the current figure 当前图像的实例句柄
allchild find all children of specified objects 所有特殊指定对象的孩子
ancestor find ancestor of graphics object 图像中对象的祖先
delete delete an object
findall find all graphics objects
fetching modifying properties
to fetch properties ,
get()
to modify properties
set()
geting object properties
获取对象的属性
get(h);
get(gca);
setting axes limites
set(gca,'XLim',[0,2*pi]);
set(gca,'YLim',[-1.2,1.2]);
alternative:
xlim({0,2*pi});
ylim({-1.2,1.2});
setting font and tick of axes
set(gca,'FontSize ',25);
set(gca,'XTick',0:pi/2:2*pi); 给定范围和步进
set(gca,'XTickLabel',0:90:360); 以角度的形式替代上面的pi值
set(gca,'FontName','symbol'); 设置显示字类型 符号(字符串显示)
set(gca,'XTickLabel',{0",'p/2','p','3p/2','2p'}); 将坐标数值用字符显示 将字符列出
line specification
line style and width
set(h,'LineStyle','-.',...'LineWidth',7.0,'Color','g'); 其中 ...表示 其余的参数可以输入 如果没有其余参数 则...去掉
alternative:
plot(x,y,'-.g','LineWidth',7.0);
删除delete(h);
Marker specification
face and edge colors of the markder
x=rand(20,1); 随机生成矩阵 数值大于等于0 20个数
set(gca,'FontSize',18);
plot(x,'-md','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g','MarkerSize',10); k为黑色 markeredgecolor 黑色边框 ;markerfacecolor 边框范围内的颜色为g 绿色 如图所示
xlim([1,20]);

exercise:

图1代码如下
set(gca,'XTick',1:1/5:2);
set(gca,'YTick',-1:1/2:4);
t=linspace(1,2);
y=t.^2;
f=sin(2*pi*t);
plot(t,y,'k-',t,f,'ro');
xlabel('Time(ms)');
ylabel('f(t)');
title('Mini Assignment #1');
legend('t^2','sin(2pi t)','Location','northwest');
图2代码如下
set(gca,'XTick',1:1/5:2,'YTick',-1:1:4,'FontSize',15);
t=linspace(1,2);
y=t.^2;
f=sin(2*pi*t);
hold on
m=plot(t,y,'k-');
n=plot(t,f,'ro');
set(n,'MarkerEdgeColor','r','MarkerFaceColor','b');
set(m,'LineWidth',4);
xlabel('Time(ms)');
ylabel('f(t)');
title('Mini Assignment #1');
legend('t^2','sin(2pi t)','Location','northwest');
hold off
Multiple Figures
Create a figure windows by calling figure 调用函数 创建图像
example:
x=-10:0.1:10;
y1=x.^2-8;
y2=exp(x);
figure, plot(x,y1);
figure,plot(x,y2);
分别画出两个图像

be careful when using the gcf handle where there exists multiple figures
存在多个figure 注意 gcf函数时调用的那个句柄
Figure Position and Size
figure('Position',[left,bottom,width,height]);
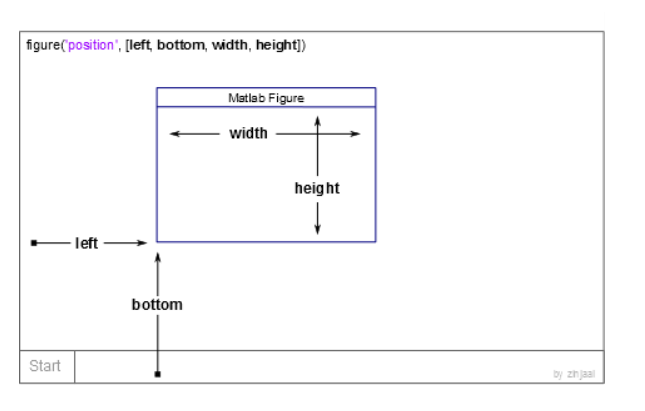
example:
x=-10:0.1:10;
y1=x.^2-8;
figure('position',[10,10,1000,700]); 窗口在屏幕中的位置会变化
plot(x,y1);
Several Plots in One Figure 一个窗口中多个图像
Several small plots "in a figure"
subplot(m,n,1); 其中的m n为矩阵中的行数和列数 1为位置

example:
t=0:0.2:2*pi;
x=3*cos(t);
y=sin(t);
subplot(2,2,1);plot(x,y);axis normal
subplot(2,2,2);plot(x,y);axis square
subplot(2,2,3);plot(x,y);axis equal
subplot(2,2,4);plot(x,y);axis equal tight
如图所示
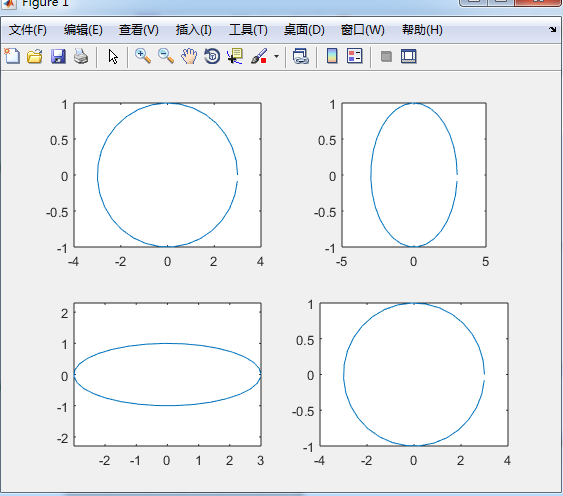
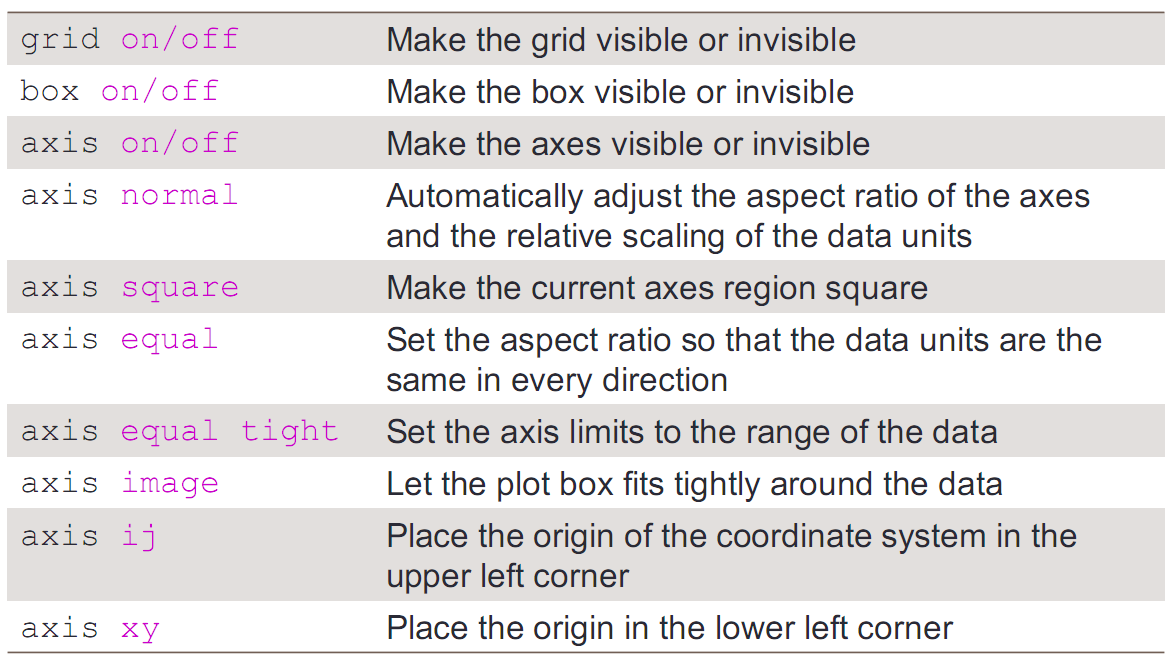
Control of Grid,Box,and Axis
Saving Figures into Files
命令:saveas(gcf,'<filename>','<formattype>');
选项