框架就是复杂的留给自己,简单的留给码农,像写hello world一样简单
早年开发Spring AOP程序时,都是xml文件配置aop(现在不流行xml了,注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy大行其道),然后框架解析,
例如:
看下文,可以先参考我的博文bean创建过程一个Spring Bean从无到有的过程,
xml元素解析就不具体说了,感兴趣自己研究
由于我用的tag是<aop:config>,那么解析类就是ConfigBeanDefinitionParser,解析时会注册一个AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,一个高高高级的BeanPostProcessor
然后解析aop:config子元素,由于方法众多,我只写了大块
参照https://blog.csdn.net/dong19891210/article/details/105697175创建bean的createBeanInstance(产出原生对象)和initializeBean阶段,对应文件org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
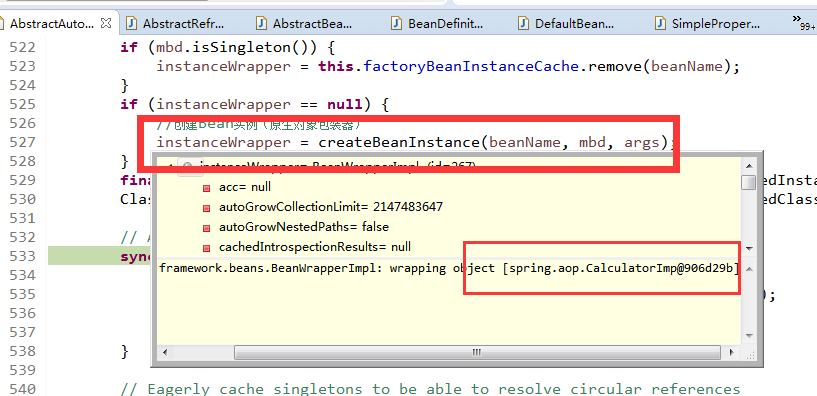
在for之前输出:
获取所有的BeanPostProcessor,
进入for阶段后,留意一个org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 的处理
处理方式可以细看,由于代码超多,只展示大方面的代码
还记得上面说过的注册的一个bean:AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,它继承自org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
在创建代理对象前,会拿到通知或拦截方法
1. 拿拦截方式org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource)
2. 创建代理 Object org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator.createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource)
文件org.springframework.aop.framework.proxyFactory.java
由于我用的是接口,那么代理实现类是JdkDynamicAopProxy.java
此时已是代理对象
然后一层层返回:
代理对象执行业务方法,顺便加些其他操作
总结:Spring AOP的处理由它AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator对bean的处理,还是对bean的生命周期的把控,在哪个阶段生成,initializeBean阶段,然后再去看怎么生成的代理对象,需要什么原材料(拦截器,通知,切面,切入点等),哪种方式(两种方式)
好了,细节慢慢深入,相信吗,Spring aop为创建代理对象,方法嵌套调用上百个,还有不少新概念,不过还好,对于开发人员用起aop来像helloword一样简单。
附图两张:

参考:
0. https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#xsd-schemas-aop
1. https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
3. https://github.com/seaswalker/spring-analysis/blob/master/note/spring-aop.md
4. Spring 框架的设计理念与设计模式分析 https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring-principle/index.html
5. Understanding Spring AOP https://www.codejava.net/frameworks/spring/understanding-spring-aop
6. Spring 源码学习(八) AOP 使用和实现原理
http://www.justdojava.com/2019/07/17/spring-analysis-note-8/
7. Spring AOP 源码初窥(三)扫描Advice与Bean匹配 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016054658
8. Spring AOP 使用介绍,从前世到今生 https://www.javadoop.com/post/spring-aop-intro
9. spring源码解析之AOP原理 https://www.cnblogs.com/liuyk-code/p/9886033.html

















