在进入源码分析前,我们先来点基础知识。下面这张图画的是元素的盒式模型,这个没有兼容性问题,有问题的是元素的宽高怎么算。以宽度为例,ff中 元素宽度=content宽度,而在ie中 元素宽度=content宽度+border宽度+padding宽度。IE8中加入了box-sizzing,该css属性有两个值:border-box、content-box分别对应ie和ff中元素宽度的工作方式。
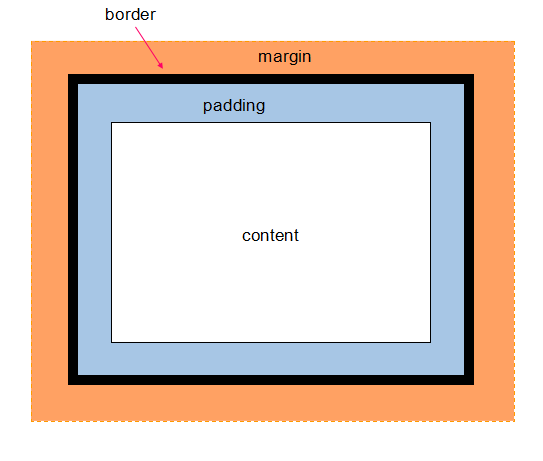
偏移量:offsetLeft、offsetTop、offsetWidth、offsetHeight
offsetLeft:包含元素的左内边框到元素的左外边框之间的像素距离。
offsetTop:包含元素的上内边框到元素的上外边框之间的相续距离。
offsetWidth:包括元素的内容区宽度、左右内边距宽度、左右边框宽度、垂直方向滚动条的宽度之和。
offsetHeight:包括元素内容区高度、左右内边距高度、左右边框高度、水平方向滚动条的高度之和。
包含元素的引用在offsetParent属性中,offsetParent属性不一定与parentNode属性相同,比如<td>的offsetParent是<table>而不是<tr>.
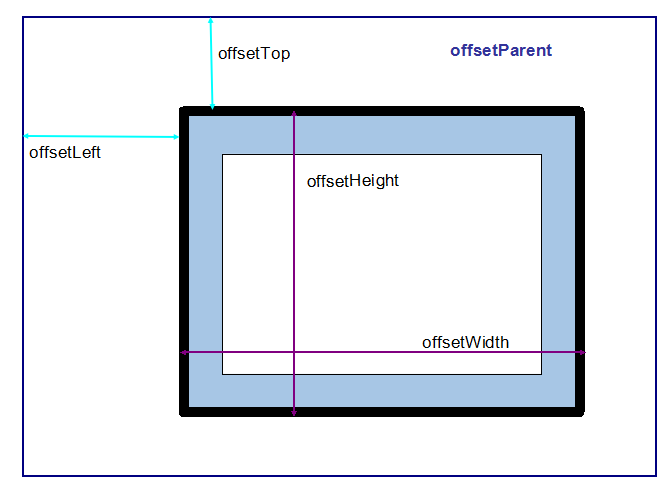
客户区大小:clientWidth、clientHeight
clientWidth:元素的内容区宽度+内边距宽度
clientHeight:元素的内容区高度+内边距高度
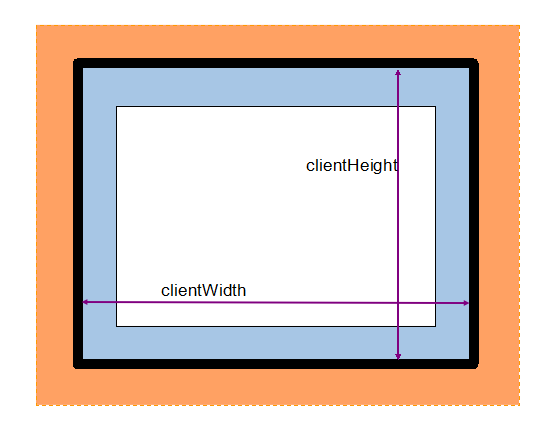
滚动大小:scrollTop、scrollLeft、scrollWidth、scrollHeight。滚动大小指的是包含滚动内容的元素大小。
scrollTop:被隐藏在内容区域上方的像素数。
scrollLeft:被隐藏在内容区域左侧的像素数。
通过设置以上两个属性可以改变元素的滚动位置。
scrollWidth:在没有滚动条情况下,元素的内容的宽度。
scrollHeight:在没有滚动条情况下,元素内容的高度。
以上基础知识,对我们分析dom-geometry模块的代码会有不少帮助。下面我们进入源码学习阶段。
dom-geometry模块封装了许多跟盒式模型相关的函数,主要涉及:content、padding、border、margin四方面。在前面的几篇文章中我们多次提到,前端js库中对dom操作的封装最终都是要用到DOM原生的API。在此模块中,最常用的原生方法就是elemet.ownerDocument.defaultView.getComputedStyle和element.getBoundingClientRect。尽管这两个方法都存在着兼容性问题,但我们都有适当的方法来解决。
getComputedStyle方法已经在dom-style模块中介绍过(ie中使用element.currentStyle其他浏览器利用原生的getComputedStyle,在webkit中对于不在正常文档流中的元素先改变display),这里简单看一下:

1 if(has("webkit")){ 2 getComputedStyle = function(/*DomNode*/ node){ 3 var s; 4 if(node.nodeType == 1){ 5 var dv = node.ownerDocument.defaultView; 6 s = dv.getComputedStyle(node, null); 7 if(!s && node.style){ 8 node.style.display = ""; 9 s = dv.getComputedStyle(node, null); 10 } 11 } 12 return s || {}; 13 }; 14 }else if(has("ie") && (has("ie") < 9 || has("quirks"))){ 15 getComputedStyle = function(node){ 16 // IE (as of 7) doesn't expose Element like sane browsers 17 // currentStyle can be null on IE8! 18 return node.nodeType == 1 /* ELEMENT_NODE*/ && node.currentStyle ? node.currentStyle : {}; 19 }; 20 }else{ 21 getComputedStyle = function(node){ 22 return node.nodeType == 1 /* ELEMENT_NODE*/ ? 23 node.ownerDocument.defaultView.getComputedStyle(node, null) : {}; 24 }; 25 } 26 style.getComputedStyle = getComputedStyle;
getComputedStyle得到的某些计算后样式是带有单位的,我们要把单位去掉。这里依赖dom-style中的toPixelValue方法:

1 var toPixel; 2 if(!has("ie")){ 3 toPixel = function(element, value){ 4 // style values can be floats, client code may want 5 // to round for integer pixels. 6 return parseFloat(value) || 0; 7 }; 8 }else{ 9 toPixel = function(element, avalue){ 10 if(!avalue){ return 0; } 11 // on IE7, medium is usually 4 pixels 12 if(avalue == "medium"){ return 4; } 13 // style values can be floats, client code may 14 // want to round this value for integer pixels. 15 if(avalue.slice && avalue.slice(-2) == 'px'){ return parseFloat(avalue); } 16 var s = element.style, rs = element.runtimeStyle, cs = element.currentStyle, 17 sLeft = s.left, rsLeft = rs.left; 18 rs.left = cs.left; 19 try{ 20 // 'avalue' may be incompatible with style.left, which can cause IE to throw 21 // this has been observed for border widths using "thin", "medium", "thick" constants 22 // those particular constants could be trapped by a lookup 23 // but perhaps there are more 24 s.left = avalue; 25 avalue = s.pixelLeft; 26 }catch(e){ 27 avalue = 0; 28 } 29 s.left = sLeft; 30 rs.left = rsLeft; 31 return avalue; 32 }; 33 } 34 style.toPixelValue = toPixel;
函数有点复杂,对于ie浏览器只要看懂这句就行:if(avalue.slice && avalue.slice(-2) == 'px'){ return parseFloat(avalue); }
回到dom-geometry的源码,geom.boxModel变量代表当前浏览器中对元素使用的盒式模型,默认为content-box,同时判断了ie浏览器下的情况:
var geom = { // summary: // This module defines the core dojo DOM geometry API. }; // can be either: // "border-box" // "content-box" (default) geom.boxModel = "content-box"; if(has("ie") /*|| has("opera")*/){ // client code may have to adjust if compatMode varies across iframes geom.boxModel = document.compatMode == "BackCompat" ? "border-box" : "content-box"; }
接下来的几个函数比较简单、基础,通过getComputedStyle都能直接拿到相应属性:
getPadExtents():getComputedStyle后得到paddingLeft、paddingRight、paddingTop、paddingBottom

1 geom.getPadExtents = function getPadExtents(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 3 node = dom.byId(node); 4 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), px = style.toPixelValue, 5 l = px(node, s.paddingLeft), t = px(node, s.paddingTop), r = px(node, s.paddingRight), b = px(node, s.paddingBottom); 6 return {l: l, t: t, r: r, b: b, w: l + r, h: t + b}; 7 };
getBorderExtents():getComputedStyle后得到borderLeftWidth、borderRightWidth、borderTopWidth、borderBottomWidth;同时如果border-style设置为none,border宽度为零

1 geom.getBorderExtents = function getBorderExtents(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 node = dom.byId(node); 3 var px = style.toPixelValue, s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), 4 l = s.borderLeftStyle != none ? px(node, s.borderLeftWidth) : 0, 5 t = s.borderTopStyle != none ? px(node, s.borderTopWidth) : 0, 6 r = s.borderRightStyle != none ? px(node, s.borderRightWidth) : 0, 7 b = s.borderBottomStyle != none ? px(node, s.borderBottomWidth) : 0; 8 return {l: l, t: t, r: r, b: b, w: l + r, h: t + b}; 9 };
getPadBorderExtents():通过上两个方法,pad+border

1 geom.getPadBorderExtents = function getPadBorderExtents(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 node = dom.byId(node); 3 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), 4 p = geom.getPadExtents(node, s), 5 b = geom.getBorderExtents(node, s); 6 return { 7 l: p.l + b.l, 8 t: p.t + b.t, 9 r: p.r + b.r, 10 b: p.b + b.b, 11 w: p.w + b.w, 12 h: p.h + b.h 13 }; 14 };
getMarginExtents():getComputedStyle后得到marginLeft、marginRight、marginTop、marginBottom

1 geom.getMarginExtents = function getMarginExtents(node, computedStyle){ 2 node = dom.byId(node); 3 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), px = style.toPixelValue, 4 l = px(node, s.marginLeft), t = px(node, s.marginTop), r = px(node, s.marginRight), b = px(node, s.marginBottom); 5 return {l: l, t: t, r: r, b: b, w: l + r, h: t + b}; 6 };
下面的几个函数稍微有点复杂
getMarginBox()这个方法返回一个对象
{
t: 父元素上内边框到元素上外边距的距离,
l: 父元素左内边框到元素左外边距的距离,
w: 元素左外边距到右外边距的距离,
h: 元素上外边距到下外边距的距离
}
这个函数中主要用到上文提到的偏移量,正常情况下:
t = offsetTop,
l = offsetLeft,
w = offsetWidth + marginExtents.w,
h = offsetHeight + marginExtents.h
在这个函数中有几个兼容性问题:
1、在firefox中,如果元素的overflow样子的计算值不为visible,那么offsetLeft/offsetTop得到的值是减去borderLeftStyle/borderTopStyle后的值。这应该是firefox的bug,所以我们要对此进行修复。如果getComputedStyle中能够得到left和top那就用这两个属性代替offsetLeft和offsetTop,否则计算parentNode的border宽度,手动加上这部分值

1 if(has("mozilla")){ 2 // Mozilla: 3 // If offsetParent has a computed overflow != visible, the offsetLeft is decreased 4 // by the parent's border. 5 // We don't want to compute the parent's style, so instead we examine node's 6 // computed left/top which is more stable. 7 var sl = parseFloat(s.left), st = parseFloat(s.top); 8 if(!isNaN(sl) && !isNaN(st)){ 9 l = sl; 10 t = st; 11 }else{ 12 // If child's computed left/top are not parseable as a number (e.g. "auto"), we 13 // have no choice but to examine the parent's computed style. 14 if(p && p.style){ 15 pcs = style.getComputedStyle(p); 16 if(pcs.overflow != "visible"){ 17 l += pcs.borderLeftStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderLeftWidth) : 0; 18 t += pcs.borderTopStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderTopWidth) : 0; 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }
2、在IE8和opera中情况正好相反,offsetLeft/offsetTop包含了父元素的边框,这里我们需要把他们减去

1 if(has("opera") || (has("ie") == 8 && !has("quirks"))){ 2 // On Opera and IE 8, offsetLeft/Top includes the parent's border 3 if(p){ 4 pcs = style.getComputedStyle(p); 5 l -= pcs.borderLeftStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderLeftWidth) : 0; 6 t -= pcs.borderTopStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderTopWidth) : 0; 7 } 8 }
真个函数代码如下:

1 geom.getMarginBox = function getMarginBox(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 node = dom.byId(node); 3 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), me = geom.getMarginExtents(node, s), 4 l = node.offsetLeft - me.l, t = node.offsetTop - me.t, p = node.parentNode, px = style.toPixelValue, pcs; 5 if(has("mozilla")){ 6 var sl = parseFloat(s.left), st = parseFloat(s.top); 7 if(!isNaN(sl) && !isNaN(st)){ 8 l = sl; 9 t = st; 10 }else{ 11 if(p && p.style){ 12 pcs = style.getComputedStyle(p); 13 if(pcs.overflow != "visible"){ 14 l += pcs.borderLeftStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderLeftWidth) : 0; 15 t += pcs.borderTopStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderTopWidth) : 0; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }else if(has("opera") || (has("ie") == 8 && !has("quirks"))){ 20 if(p){ 21 pcs = style.getComputedStyle(p); 22 l -= pcs.borderLeftStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderLeftWidth) : 0; 23 t -= pcs.borderTopStyle != none ? px(node, pcs.borderTopWidth) : 0; 24 } 25 } 26 return {l: l, t: t, w: node.offsetWidth + me.w, h: node.offsetHeight + me.h}; 27 };
getContentBox()函数返回如下对象:
{
l: 元素左内边距,
t: 元素上内边距,
w: 元素内容区的宽度,
h: 元素内容区的高度
}
对象中的w和h与元素的盒式模型无关。以内容区的宽高都有两套方案:clientWidth-padingWidth或者offsetWidth-paddingWidth-borderWidth,下面是函数的源码:

1 geom.getContentBox = function getContentBox(node, computedStyle){ 2 // summary: 3 // Returns an object that encodes the width, height, left and top 4 // positions of the node's content box, irrespective of the 5 // current box model. 6 // node: DOMNode 7 // computedStyle: Object? 8 // This parameter accepts computed styles object. 9 // If this parameter is omitted, the functions will call 10 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle to get one. It is a better way, calling 11 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle once, and then pass the reference to this 12 // computedStyle parameter. Wherever possible, reuse the returned 13 // object of dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle(). 14 15 // clientWidth/Height are important since the automatically account for scrollbars 16 // fallback to offsetWidth/Height for special cases (see #3378) 17 node = dom.byId(node); 18 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), w = node.clientWidth, h, 19 pe = geom.getPadExtents(node, s), be = geom.getBorderExtents(node, s); 20 if(!w){ 21 w = node.offsetWidth; 22 h = node.offsetHeight; 23 }else{ 24 h = node.clientHeight; 25 be.w = be.h = 0; 26 } 27 // On Opera, offsetLeft includes the parent's border 28 if(has("opera")){ 29 pe.l += be.l; 30 pe.t += be.t; 31 } 32 return {l: pe.l, t: pe.t, w: w - pe.w - be.w, h: h - pe.h - be.h}; 33 };
接下来有三个私有函数setBox、isButtonTag、usersBorderBox。
setBox忽略盒式模型,直接对元素样式的width、height、left、top进行设置

1 function setBox(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Number?*/ l, /*Number?*/ t, /*Number?*/ w, /*Number?*/ h, /*String?*/ u){ 2 // summary: 3 // sets width/height/left/top in the current (native) box-model 4 // dimensions. Uses the unit passed in u. 5 // node: 6 // DOM Node reference. Id string not supported for performance 7 // reasons. 8 // l: 9 // left offset from parent. 10 // t: 11 // top offset from parent. 12 // w: 13 // width in current box model. 14 // h: 15 // width in current box model. 16 // u: 17 // unit measure to use for other measures. Defaults to "px". 18 u = u || "px"; 19 var s = node.style; 20 if(!isNaN(l)){ 21 s.left = l + u; 22 } 23 if(!isNaN(t)){ 24 s.top = t + u; 25 } 26 if(w >= 0){ 27 s.width = w + u; 28 } 29 if(h >= 0){ 30 s.height = h + u; 31 } 32 }
isButtonTag函数用来判断元素是否是button按钮,button元素可能是直接的<button>标签,也可能是<input type="button">,所以要对着两方面进行判断

1 function isButtonTag(/*DomNode*/ node){ 2 // summary: 3 // True if the node is BUTTON or INPUT.type="button". 4 return node.tagName.toLowerCase() == "button" || 5 node.tagName.toLowerCase() == "input" && (node.getAttribute("type") || "").toLowerCase() == "button"; // boolean 6 }
usersBorderBox判断元素的盒式模型是否为border-box,三个方面:geom的boxModel是否为border-box、元素是否为table元素,元素是否为button元素

1 function usesBorderBox(/*DomNode*/ node){ 2 // summary: 3 // True if the node uses border-box layout. 4 5 // We could test the computed style of node to see if a particular box 6 // has been specified, but there are details and we choose not to bother. 7 8 // TABLE and BUTTON (and INPUT type=button) are always border-box by default. 9 // If you have assigned a different box to either one via CSS then 10 // box functions will break. 11 12 return geom.boxModel == "border-box" || node.tagName.toLowerCase() == "table" || isButtonTag(node); // boolean 13 }
setContentSize方法,设置元素内容区的大小。如果元素盒式模式是border-box,则需要在参数传入的width基础上加上padding与border的宽度,否则直接设置width、height样式。

1 geom.setContentSize = function setContentSize(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ box, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 // summary: 3 // Sets the size of the node's contents, irrespective of margins, 4 // padding, or borders. 5 // node: DOMNode 6 // box: Object 7 // hash with optional "w", and "h" properties for "width", and "height" 8 // respectively. All specified properties should have numeric values in whole pixels. 9 // computedStyle: Object? 10 // This parameter accepts computed styles object. 11 // If this parameter is omitted, the functions will call 12 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle to get one. It is a better way, calling 13 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle once, and then pass the reference to this 14 // computedStyle parameter. Wherever possible, reuse the returned 15 // object of dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle(). 16 17 node = dom.byId(node); 18 var w = box.w, h = box.h; 19 if(usesBorderBox(node)){ 20 var pb = geom.getPadBorderExtents(node, computedStyle); 21 if(w >= 0){ 22 w += pb.w; 23 } 24 if(h >= 0){ 25 h += pb.h; 26 } 27 } 28 setBox(node, NaN, NaN, w, h); 29 };
setMarginBox方法,设置marginBox的宽度。该方法中不去判断元素的盒式模型,width = w-padding - border -margin。通过这种方式直接设置元素的width或height属性。这里涉及的兼容性问题,主要对于低版本浏览器,所以不去分析他。

1 geom.setMarginBox = function setMarginBox(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Object*/ box, /*Object*/ computedStyle){ 2 // summary: 3 // sets the size of the node's margin box and placement 4 // (left/top), irrespective of box model. Think of it as a 5 // passthrough to setBox that handles box-model vagaries for 6 // you. 7 // node: DOMNode 8 // box: Object 9 // hash with optional "l", "t", "w", and "h" properties for "left", "right", "width", and "height" 10 // respectively. All specified properties should have numeric values in whole pixels. 11 // computedStyle: Object? 12 // This parameter accepts computed styles object. 13 // If this parameter is omitted, the functions will call 14 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle to get one. It is a better way, calling 15 // dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle once, and then pass the reference to this 16 // computedStyle parameter. Wherever possible, reuse the returned 17 // object of dojo/dom-style.getComputedStyle(). 18 19 node = dom.byId(node); 20 var s = computedStyle || style.getComputedStyle(node), w = box.w, h = box.h, 21 // Some elements have special padding, margin, and box-model settings. 22 // To use box functions you may need to set padding, margin explicitly. 23 // Controlling box-model is harder, in a pinch you might set dojo/dom-geometry.boxModel. 24 pb = usesBorderBox(node) ? nilExtents : geom.getPadBorderExtents(node, s), 25 mb = geom.getMarginExtents(node, s); 26 if(has("webkit")){ 27 // on Safari (3.1.2), button nodes with no explicit size have a default margin 28 // setting an explicit size eliminates the margin. 29 // We have to swizzle the width to get correct margin reading. 30 if(isButtonTag(node)){ 31 var ns = node.style; 32 if(w >= 0 && !ns.width){ 33 ns.width = "4px"; 34 } 35 if(h >= 0 && !ns.height){ 36 ns.height = "4px"; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 if(w >= 0){ 41 w = Math.max(w - pb.w - mb.w, 0); 42 } 43 if(h >= 0){ 44 h = Math.max(h - pb.h - mb.h, 0); 45 } 46 setBox(node, box.l, box.t, w, h); 47 };
position()方法,主要使用node.getBoundingClientRect() ,这个方法得到left、right、top、bottom。在老版本ie下,这个方法的基准点并不是从(0,0)开始计算的,而是以(2,2)位基准点。所以ie中这个方法得到的位置信息比实际位置多了两个像素,我们要把这两个像素减掉。基准点位置偏移两个像素,所以dcument.documentElement即<html>标签的位置也不是0;所以我们可以利用document.documentElement.getBoundingClientRect().left/top得到偏移量。减去偏移量就得到了真正的位置。(偏移量问题在IE9已经修复了,而IE8标准模式是没有这个问题,所以具体获取偏移量的细节不讨论)

1 geom.position = function(/*DomNode*/ node, /*Boolean?*/ includeScroll){ 2 // summary: 3 // Gets the position and size of the passed element relative to 4 // the viewport (if includeScroll==false), or relative to the 5 // document root (if includeScroll==true). 6 // 7 // description: 8 // Returns an object of the form: 9 // `{ x: 100, y: 300, w: 20, h: 15 }`. 10 // If includeScroll==true, the x and y values will include any 11 // document offsets that may affect the position relative to the 12 // viewport. 13 // Uses the border-box model (inclusive of border and padding but 14 // not margin). Does not act as a setter. 15 // node: DOMNode|String 16 // includeScroll: Boolean? 17 // returns: Object 18 19 node = dom.byId(node); 20 var db = win.body(node.ownerDocument), 21 ret = node.getBoundingClientRect(); 22 ret = {x: ret.left, y: ret.top, w: ret.right - ret.left, h: ret.bottom - ret.top}; 23 24 if(has("ie") < 9){ 25 // On IE<9 there's a 2px offset that we need to adjust for, see dojo.getIeDocumentElementOffset() 26 var offset = geom.getIeDocumentElementOffset(node.ownerDocument); 27 28 // fixes the position in IE, quirks mode 29 ret.x -= offset.x + (has("quirks") ? db.clientLeft + db.offsetLeft : 0); 30 ret.y -= offset.y + (has("quirks") ? db.clientTop + db.offsetTop : 0); 31 } 32 33 // account for document scrolling 34 // if offsetParent is used, ret value already includes scroll position 35 // so we may have to actually remove that value if !includeScroll 36 if(includeScroll){ 37 var scroll = geom.docScroll(node.ownerDocument); 38 ret.x += scroll.x; 39 ret.y += scroll.y; 40 } 41 42 return ret; // Object 43 };
normalizeEvent()方法主要针对鼠标位置信息layerX/layerY、pageX/pageY做修正;前者利用ie中的offsetX/offsetY即可,后者利用clientX+documentElement/body.scrollLeft - offset和clientY+documentElement/body.scrollTop - offset,offset即是上文提到的在ie中偏移量。

geom.normalizeEvent = function(event){ // summary: // Normalizes the geometry of a DOM event, normalizing the pageX, pageY, // offsetX, offsetY, layerX, and layerX properties // event: Object if(!("layerX" in event)){ event.layerX = event.offsetX; event.layerY = event.offsetY; } if(!has("dom-addeventlistener")){ // old IE version // FIXME: scroll position query is duped from dojo/_base/html to // avoid dependency on that entire module. Now that HTML is in // Base, we should convert back to something similar there. var se = event.target; var doc = (se && se.ownerDocument) || document; // DO NOT replace the following to use dojo/_base/window.body(), in IE, document.documentElement should be used // here rather than document.body var docBody = has("quirks") ? doc.body : doc.documentElement; var offset = geom.getIeDocumentElementOffset(doc); event.pageX = event.clientX + geom.fixIeBiDiScrollLeft(docBody.scrollLeft || 0, doc) - offset.x; event.pageY = event.clientY + (docBody.scrollTop || 0) - offset.y; } };
一个周的学习研究结束,如果您觉得这篇文章对您有帮助,请不吝点击下方推荐
