dojo/aspect模块是dojo框架中对于AOP的实现。关于AOP的详细解释请读者另行查看其它资料,这里简单复习一下AOP中的基本概念:
- 切面(Aspect):其实就是共有功能的实现。如日志切面、权限切面、事务切面等。
- 通知(Advice):是切面的具体实现。以目标方法为参照点,根据放置的地方不同,可分为前置通知(Before)、后置通知(After)与环绕通知(Around)。
- 连接点(Joinpoint):就是程序在运行过程中能够插入切面的地点。
- 目标对象(Target):就是那些即将切入切面的对象,也就是那些被通知的对象。这些对象中已经只剩下干干净净的核心业务逻辑代码了,所有的共有功能代码等待AOP容器的切入。
- 代理对象(Proxy):将通知应用到目标对象之后被动态创建的对象。可以简单地理解为,代理对象的功能等于目标对象的核心业务逻辑功能加上共有功能。代理对象对于使用者而言是透明的,是程序运行过程中的产物。
- 织入(Weaving):将切面应用到目标对象从而创建一个新的代理对象的过程。这个过程可以发生在编译期、类装载期及运行期,当然不同的发生点有着不同的前提条件。譬如发生在编译期的话,就要求有一个支持这种AOP实现的特殊编译器;发生在类装载期,就要求有一个支持AOP实现的特殊类装载器;只有发生在运行期,则可直接通过Java语言的反射机制与动态代理机制来动态实现。
生成代理对象的过程可以按照下图理解:

dojo/aspect模块代码主要分为两部分:
- advise方法,通过使用闭包跟链式模型来构造“通知”链。
 View Code
View Code"use strict"; var undefined, nextId = 0; function advise(dispatcher, type, advice, receiveArguments){ var previous = dispatcher[type]; var around = type == "around"; var signal; if(around){ var advised = advice(function(){ return previous.advice(this, arguments); }); signal = { remove: function(){ if(advised){ advised = dispatcher = advice = null; } }, advice: function(target, args){ return advised ? advised.apply(target, args) : // called the advised function previous.advice(target, args); // cancelled, skip to next one } }; }else{ // create the remove handler signal = { remove: function(){ if(signal.advice){ var previous = signal.previous; var next = signal.next; if(!next && !previous){ delete dispatcher[type]; }else{ if(previous){ previous.next = next; }else{ dispatcher[type] = next; } if(next){ next.previous = previous; } } // remove the advice to signal that this signal has been removed dispatcher = advice = signal.advice = null; } }, id: nextId++, advice: advice, receiveArguments: receiveArguments }; } if(previous && !around){ if(type == "after"){ // add the listener to the end of the list // note that we had to change this loop a little bit to workaround a bizarre IE10 JIT bug while(previous.next && (previous = previous.next)){} previous.next = signal; signal.previous = previous; }else if(type == "before"){ // add to beginning dispatcher[type] = signal; signal.next = previous; previous.previous = signal; } }else{ // around or first one just replaces dispatcher[type] = signal; } return signal; }
- aspect方法,这个函数返回一个闭包。闭包的作用是将“通知”方法织入到目标函数中,java中运行时通过反射的方式来织入,而js中通过动态更改目标函数来实现织入过程,这时调用该方法可以使切面函数与业务逻辑同时进行。
 View Code
View Codefunction aspect(type){ return function(target, methodName, advice, receiveArguments){ var existing = target[methodName], dispatcher; if(!existing || existing.target != target){ // no dispatcher in place target[methodName] = dispatcher = function(){ var executionId = nextId; // before advice var args = arguments; var before = dispatcher.before; while(before){ args = before.advice.apply(this, args) || args; before = before.next; } // around advice if(dispatcher.around){ var results = dispatcher.around.advice(this, args); } // after advice var after = dispatcher.after; while(after && after.id < executionId){ if(after.receiveArguments){ var newResults = after.advice.apply(this, args); // change the return value only if a new value was returned results = newResults === undefined ? results : newResults; }else{ results = after.advice.call(this, results, args); } after = after.next; } return results; }; if(existing){ dispatcher.around = {advice: function(target, args){ return existing.apply(target, args); }}; } dispatcher.target = target; } var results = advise((dispatcher || existing), type, advice, receiveArguments); advice = null; return results; }; }
注意:dojo的处理过程中并不生成代理对象,而是直接更改原有的对象的方法。
关于aspect.after方法(before方法与其类似)的解释请看这篇文章:Javascript事件机制兼容性解决方案;aspect.around的由来在这篇文章Javascript aop(面向切面编程)之around(环绕)里有其一步步的演化过程。
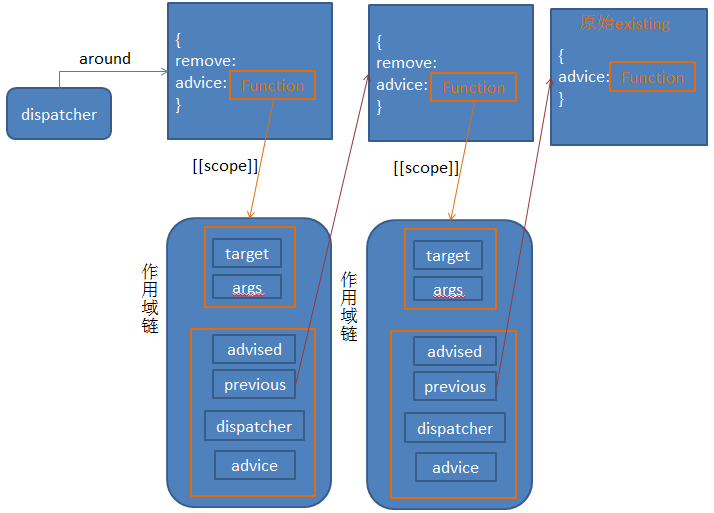
本文给出aspect模块调用后的示意图:
before与after函数:

around函数:
var advised = advice(function(){ return previous.advice(this, arguments); }); signal = { remove: function(){ if(advised){ advised = dispatcher = advice = null; } }, advice: function(target, args){ return advised ? //一旦调用remove,adviced变为空,便会跳过本次环绕通知,进入上一层的advice方法。 advised.apply(target, args) : // called the advised function previous.advice(target, args); // cancelled, skip to next one } };
可以看到around函数中借用闭包形成环绕函数链。这里调用remove方法后并没有像before跟after中将通知方法彻底移除,注册过的环绕方法仍然会存在内存中,所以这个方法无法移除环绕通知,仅仅是避免了在函数链中执行它而已。内存无法释放,不建议使用太多。
