React源码看过几次,每次都没有坚持下来,索性学习一下PReact部分,网上讲解源码的不少,但是基本已经过时,所以自己来梳理下
render.js部分
import { EMPTY_OBJ, EMPTY_ARR } from './constants';
import { commitRoot, diff } from './diff/index';
import { createElement, Fragment } from './create-element';
import options from './options';
/**
* Render a Preact virtual node into a DOM element
* @param {import('./internal').ComponentChild} vnode The virtual node to render
* @param {import('./internal').PreactElement} parentDom The DOM element to
* render into
* @param {import('./internal').PreactElement | object} [replaceNode] Optional: Attempt to re-use an
* existing DOM tree rooted at `replaceNode`
*/
export function render(vnode, parentDom, replaceNode) {
if (options._root) options._root(vnode, parentDom);
// We abuse the `replaceNode` parameter in `hydrate()` to signal if we are in
// hydration mode or not by passing the `hydrate` function instead of a DOM
// element..
let isHydrating = typeof replaceNode === 'function';
// To be able to support calling `render()` multiple times on the same
// DOM node, we need to obtain a reference to the previous tree. We do
// this by assigning a new `_children` property to DOM nodes which points
// to the last rendered tree. By default this property is not present, which
// means that we are mounting a new tree for the first time.
// 为了支持多次在一个dom节点上调用render函数,需要在dom节点上添加一个饮用,用来获取指向上一次渲染的虚拟dom树。
// 这个属性默认是指向空的,也意味着我们第一次正在装备一颗新的树
// 所以开始时这里的oldVNode是空(不论isHydrating的值),但是如果重复在这个节点上调用render那oldVNode是有值的
let oldVNode = isHydrating
? null
: (replaceNode && replaceNode._children) || parentDom._children;
// 用Fragment包裹一下vnode,同时给replaceNode和parentDom的_children赋值
vnode = (
(!isHydrating && replaceNode) ||
parentDom
)._children = createElement(Fragment, null, [vnode]);
// List of effects that need to be called after diffing.
// 用来放置diff之后需要进行各种生命周期处理的Component,比如cdm、cdu;componentWillUnmount在diffChildren的unmount函数中执行不在commitRoot时执行
let commitQueue = [];
diff(
parentDom, // 这个使用parentDom的_children属性已经指向[vnode]了
// Determine the new vnode tree and store it on the DOM element on
// our custom `_children` property.
vnode,
oldVNode || EMPTY_OBJ, // 旧的树
EMPTY_OBJ,
parentDom.ownerSVGElement !== undefined,
// excessDomChildren,这个参数用来做dom复用的作用
!isHydrating && replaceNode
? [replaceNode]
: oldVNode
? null
: parentDom.firstChild // 如果parentDom有子节点就会把整个子节点作为待复用的节点使用
? EMPTY_ARR.slice.call(parentDom.childNodes)
: null,
commitQueue,
// oldDom,在后续方法中用来做标记插入位置使用
!isHydrating && replaceNode
? replaceNode
: oldVNode
? oldVNode._dom
: parentDom.firstChild,
isHydrating
);
// Flush all queued effects
// 调用所有commitQueue中的节点_renderCallbacks中的方法
commitRoot(commitQueue, vnode);
}
/**
* Update an existing DOM element with data from a Preact virtual node
* @param {import('./internal').ComponentChild} vnode The virtual node to render
* @param {import('./internal').PreactElement} parentDom The DOM element to
* update
*/
export function hydrate(vnode, parentDom) {
render(vnode, parentDom, hydrate);
}
create-context.js部分
Context的使用:
Provider的props中有value属性
Consumer中直接获取传值
import { createContext, h, render } from 'preact';
const FontContext = createContext(20);
function Child() {
return <FontContext.Consumer>
{fontSize=><div style={{fontSize:fontSize}}>child</div>}
</FontContext.Consumer>
}
function App(){
return <Child/>
}
render(
<FontContext.Provider value={26}>
<App/>
</FontContext.Provider>,
document.getElementById('app')
);
看一下源码:
import { enqueueRender } from './component';
export let i = 0;
export function createContext(defaultValue, contextId) {
contextId = '__cC' + i++; // 生成一个唯一ID
const context = {
_id: contextId,
_defaultValue: defaultValue,
/** @type {import('./internal').FunctionComponent} */
Consumer(props, contextValue) {
// return props.children(
// context[contextId] ? context[contextId].props.value : defaultValue
// );
return props.children(contextValue);
},
/** @type {import('./internal').FunctionComponent} */
Provider(props) {
if (!this.getChildContext) { // 第一次调用时进行一些初始化操作
let subs = [];
let ctx = {};
ctx[contextId] = this;
// 在diff操作用,如果判断一个组件在Comsumer中,会调用sub进行订阅;
// 同时这个节点后续所有diff的地方都会带上这个context,调用sub方法进行调用
// context具有层级优先级,组件会先加入最近的context中
this.getChildContext = () => ctx;
this.shouldComponentUpdate = function(_props) {
if (this.props.value !== _props.value) {
// I think the forced value propagation here was only needed when `options.debounceRendering` was being bypassed:
// https://github.com/preactjs/preact/commit/4d339fb803bea09e9f198abf38ca1bf8ea4b7771#diff-54682ce380935a717e41b8bfc54737f6R358
// In those cases though, even with the value corrected, we're double-rendering all nodes.
// It might be better to just tell folks not to use force-sync mode.
// Currently, using `useContext()` in a class component will overwrite its `this.context` value.
// subs.some(c => {
// c.context = _props.value;
// enqueueRender(c);
// });
// subs.some(c => {
// c.context[contextId] = _props.value;
// enqueueRender(c);
// });
// enqueueRender最终会进入renderComponent函数,进行diff、commitRoot、updateParentDomPointers等操作
subs.some(enqueueRender);
}
};
this.sub = c => {
subs.push(c);// 进入订阅数组,
let old = c.componentWillUnmount;
c.componentWillUnmount = () => { // 重写componentWillUnmount
subs.splice(subs.indexOf(c), 1);
if (old) old.call(c);
};
};
}
return props.children;
}
};
// Devtools needs access to the context object when it
// encounters a Provider. This is necessary to support
// setting `displayName` on the context object instead
// of on the component itself. See:
// https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html#contextdisplayname
// createContext最终返回的是一个context对象,带着Provider和Consumer两个函数
// 同时Consumber函数的contextType和Provider函数的_contextRef属性都指向context
return (context.Provider._contextRef = context.Consumer.contextType = context);
}
所以对于Provider组件,在渲染时会判断有没有getChildContext方法,如果有的话调用得到globalContext并一直向下传递下去
if (c.getChildContext != null) { globalContext = assign(assign({}, globalContext), c.getChildContext()); } if (!isNew && c.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate != null) { snapshot = c.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(oldProps, oldState); } let isTopLevelFragment = tmp != null && tmp.type === Fragment && tmp.key == null; let renderResult = isTopLevelFragment ? tmp.props.children : tmp; diffChildren( parentDom, Array.isArray(renderResult) ? renderResult : [renderResult], newVNode, oldVNode, globalContext, isSvg, excessDomChildren, commitQueue, oldDom, isHydrating );
当渲染遇到Consumer时,即遇到contextType属性,先从Context中拿到provider,然后拿到provider的props的value值,作为组件要获取的上下文信息。
同时这时候会调用provider的sub方法,进行订阅,当调用到Provider的shouldComponentUpdate中发现value发生变化时就会将所有的订阅者进入enqueueRender函数。
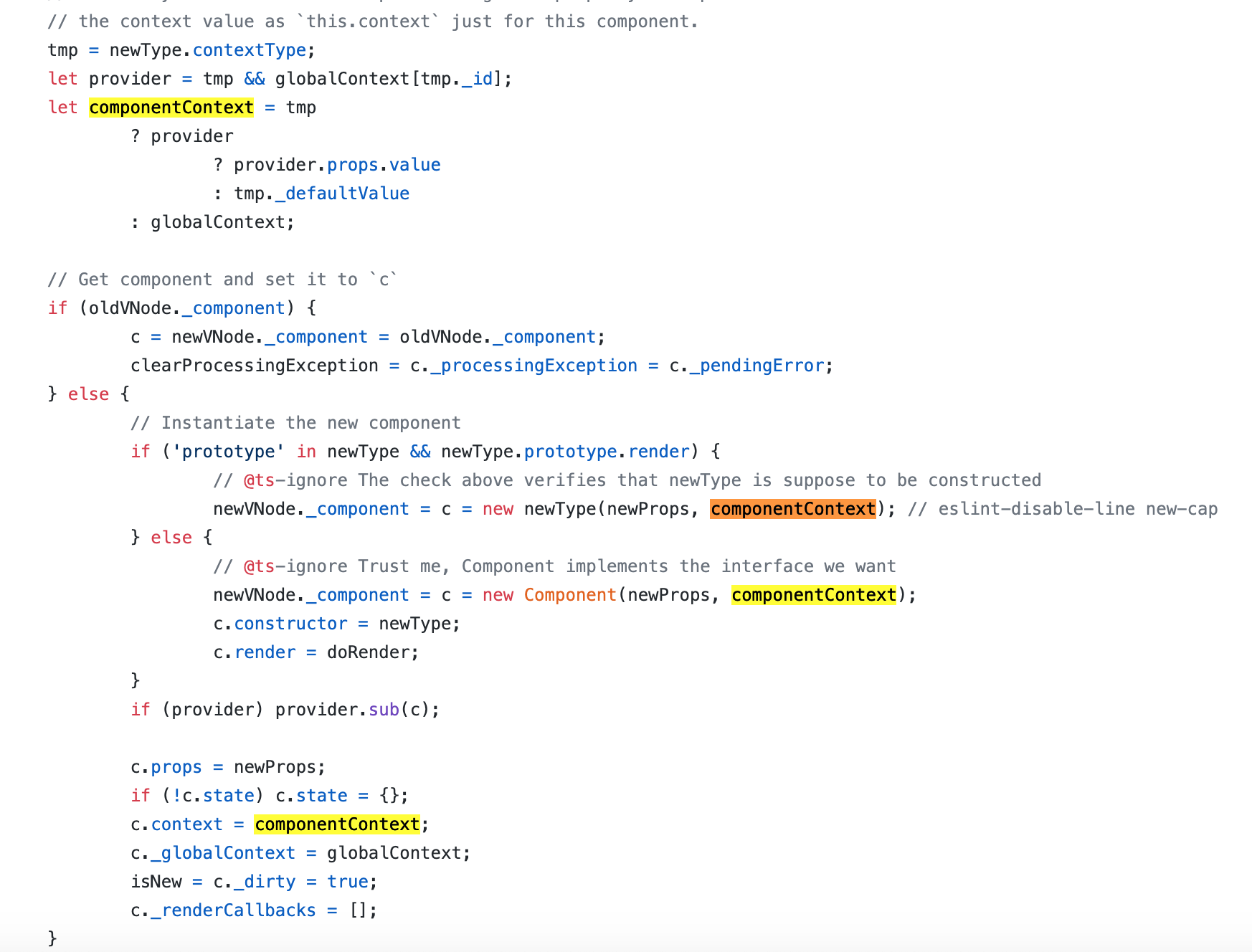
所以源码中,globalContext对象的每一个key指向一个Context.Provider;componentContext代表组件所在的Consumer传递的上下文信息即配对的Provider的props的value;
同时Provider的shouldComponentUpdate方法中用到了 ·this.props.value !== _props.value· 那么这里的this.props是哪来的?Provider中并没有相关属性。
主要是下面这个地方,当判断没有render方法时,会先用Compoent来实例化一个对象,并将render方法设置为doRender,并将constructor指向newType(当前函数),在doRender中调用this.constructor方法
// Instantiate the new component if ('prototype' in newType && newType.prototype.render) { // @ts-ignore The check above verifies that newType is suppose to be constructed newVNode._component = c = new newType(newProps, componentContext); // eslint-disable-line new-cap } else { // @ts-ignore Trust me, Component implements the interface we want newVNode._component = c = new Component(newProps, componentContext); c.constructor = newType; c.render = doRender; }
/** The `.render()` method for a PFC backing instance. */ function doRender(props, state, context) { return this.constructor(props, context); }
diff部分
diff部分比较复杂,整体整理了一张大图

真是不得不吐槽,博客园的编辑器bug太多了,尤其是mac上使用,比如第二次上传代码提交不了;赋值粘贴用不了。。。
只有情怀让我继续在这里更新
