功能:
- 创建两个线程,一个动态线程和一个静态线程;
- 一个线程运行完毕后自动被系统删除;另一个线程一直打印计数。
#include <rtthread.h> /* 创建两个线程,一个动态线程,一个静态线程; 一个线程运行完毕自动被系统删除,另一个线程一直打印计数 */ static rt_thread_t tid1 = RT_NULL; #define THREAD_PRIORITY 25 #define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 512 #define THREAD_TIMESLICE 5 /* 线程1的入口函数 */ static void thread1_entry(void * param) { rt_uint32_t count = 0; while(1) { /* 线程1采用低优先级运行,一直打印计数值 */ rt_kprintf("thread1 count:%d ",count++); rt_thread_mdelay(500); } } ALIGN(RT_ALIGN_SIZE) static char thread2_stack[512]={0}; static struct rt_thread thread2; /* 线程2的入口函数 */ static void thread2_entry(void *param) { rt_uint32_t count = 0; /* 线程2拥有较高优先级,以抢占线程1而获得运行 */ for(count = 0;count <10;count++) { rt_kprintf("thread2 count2 :%d ",count); rt_thread_mdelay(500); } /* 线程2运行结束后将自动被系统删除;线程控制块和线程栈在idle线程中释放 */ rt_kprintf("thread2 exit "); } /* 线程示例初始化函数 */ int test_thread_sample(void) { /* 创建线程1,名称是thread1,线程入口函数是thread1_entry */ tid1 = rt_thread_create("thread1", thread1_entry, RT_NULL, THREAD_STACK_SIZE, THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE); /* 如果获得线程控制块,启动这个线程 */ if(tid1 != RT_NULL) { rt_thread_startup(tid1); } /* 初始化线程2,名称是thread2,线程入口函数是thread2_entry */ rt_thread_init( &thread2, "thread2", thread2_entry, RT_NULL, &thread2_stack[0], sizeof(thread2_stack), THREAD_PRIORITY-1, THREAD_TIMESLICE); rt_thread_startup(&thread2); return 0; } /* 导入 msh 命令列表中 */ MSH_CMD_EXPORT(test_thread_sample,test01 thread sample);
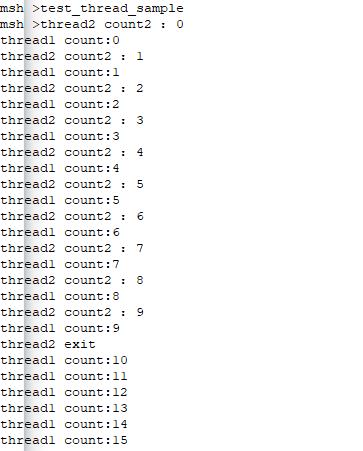
运行结果: