本文从HashMap.KeySet对象的交集和差集看HashMap相关源码。
1. 下面例子的错误操作
package com.mingo.exp.verify.set;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* HashMap KeySet
*/
public class MapKeySetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> mapOne = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put("A", 98);
put("B", 98);
put("C", 98);
}};
Map<String, Integer> mapTwo = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put("K", 99);
put("B", 99);
put("P", 99);
put("C", 99);
}};
// 下面三行是错误代码
// 交集
Set<String> intersectSet = mapOne.keySet();
// mapOne - mapTwo
Set<String> diffSetOne = mapOne.keySet();
// mapTwo - mapOne
Set<String> diffSetTwo = mapTwo.keySet();
intersectSet.retainAll(mapTwo.keySet());
diffSetOne.removeAll(mapTwo.keySet());
diffSetTwo.removeAll(mapOne.keySet());
System.out.println("交集:" + intersectSet);
System.out.println("mapOne - mapTwo:" + diffSetOne);
System.out.println("mapTwo - mapOne:" + diffSetTwo);
}
}
运行结果如下
交集:[]
mapOne - mapTwo:[]
mapTwo - mapOne:[P, B, C, K]
结果明显不正确,下面我用这个例子看下相关源码。
2. HashMap.keySet()
源码
// keySet对象初始未设置值
transient Set<K> keySet;
// keySet()方法对keySet设值
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
if (ks == null) {
ks = new KeySet();
keySet = ks;
}
return ks;
}
初次调用keySet()方法时才设置keySet字段值,也可看出代码线程不安全。也就是说测试例子中的mapOne.keySet()和mapTwo.keySet()返回的是同一个对象,做retainAll()和removeAll()操作都是在同一个对象上操作。这就造成结果不正确,并且例子中mapOne和mapTwo对象的key也被修改了。
下面先看HashMap.KeySet类的源码。
3. HashMap.KeySet类
类图
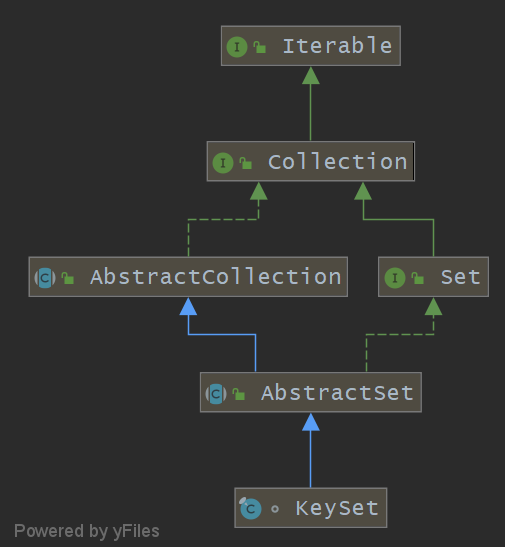
源码如下
final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
// 迭代器实现
public final Iterator<K> iterator() { return new KeyIterator(); }
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); }
public final boolean remove(Object key) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;
}
public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
return new KeySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
// 两重循环,先数元素,再遍历每个数组元素的next
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
// HashMap对象的key作为lamda表达式入参
action.accept(e.key);
}
// 比如非正常删除了元素,这里会抛异常
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
HasMap.containsKey(Object key)
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the
* specified key.
*
* @param key The key whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified
* key.
*/
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// 先判断是否存在该key,(n - 1) & hash 定位下标
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 先比较第一个元素
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 检查该节点下next
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 红黑树
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 链表
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
HasMap.removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,boolean matchValue, boolean movable)
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
// index记录下标
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
// 比较第一个值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
// 数组元素next指向不为空时
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
// 红黑树结构
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
// 链表结构
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
// p最终指向node元素的上一个节点,便于删除操作
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
// 即在第一个值时就相等,直接赋值next
tab[index] = node.next;
else
// 链表非首元素时,指向被删除元素的next
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
可看到clear()、remove(Object key)和forEach(Consumer<? super K> action)等方法都是和外部类HashMap关联。
下面先给出相关的内部类。
4. HashMap.Node类
HashMap的底层就是这样一个数组,数组中每一个元素就是hash值一样的Node的集合,排列的数据结构是链表或红黑树。
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
Node类源码
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
// 计算规则: (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
// 链表或红黑树
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
// 旧值
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
5. HashMap.KeyIterator类
abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return
Node<K,V> current; // current entry
int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail
int index; // current slot
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
Node<K,V>[] t = table;
current = next = null;
index = 0;
if (t != null && size > 0) {
// advance to first entry
// 如注释所说 剔除前面的空值,next指向数组第一个Node,index是下标
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
// 要返回的值
Node<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 设置current值为当前next值
// (next = (current = e).next) == null 用于判断该Node有无挂节点,true时且 (t = table) != null则查找下一个数组元素
//
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
// HashIterator.hasNext()
final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
// 返回key
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
}
下面看下AbstractCollection.retainAll(Collection c)和AbstractSet.removeAll(Collection c)
6. AbstractCollection.retainAll(Collection<?> c)
源码如下
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
boolean modified = false;
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// c集合不包含的元素就删除
if (!c.contains(it.next())) {
// 见HashMap.removeNode(...)方法
it.remove();
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
7. AbstractSet.removeAll(Collection<?> c)
源码如下
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
boolean modified = false;
// 这里将长度较小的集合遍历
if (size() > c.size()) {
for (Iterator<?> i = c.iterator(); i.hasNext(); )
modified |= remove(i.next());
} else {
for (Iterator<?> i = iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
if (c.contains(i.next())) {
i.remove();
modified = true;
}
}
}
return modified;
}
上面的分析可看出对HashMap.keySet()的操作会体现到HashMap对象本身上,文章开始的例子可做如下处理即可得到正确结果。
8. 正确的例子
package com.mingo.exp.verify.set;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* HashMap KeySet
*/
public class MapKeySetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> mapOne = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put("A", 98);
put("B", 98);
put("C", 98);
}};
Map<String, Integer> mapTwo = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put("K", 99);
put("B", 99);
put("P", 99);
put("C", 99);
}};
// 用new HashSet()处理
// 交集
Set<String> intersectSet = new HashSet<>(mapOne.keySet());
// mapOne - mapTwo
Set<String> diffSetOne = new HashSet<>(mapOne.keySet());
// mapTwo - mapOne
Set<String> diffSetTwo = new HashSet<>(mapTwo.keySet());
intersectSet.retainAll(mapTwo.keySet());
diffSetOne.removeAll(mapTwo.keySet());
diffSetTwo.removeAll(mapOne.keySet());
System.out.println("交集:" + intersectSet);
System.out.println("mapOne - mapTwo:" + diffSetOne);
System.out.println("mapTwo - mapOne:" + diffSetTwo);
}
}
运行结果
交集:[B, C]
mapOne - mapTwo:[A]
mapTwo - mapOne:[P, K]
new HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c)源码
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c)
if (add(e))
modified = true;
return modified;
}
new一个HashSet对象,对入参集合元素做复制操作,生成了新的集合对象。