教材学习内容总结
教材学习内容总结
5.1 队列概述
- 队列的元素是按照FIFO方式处理的:第一个进入的元素,也就是第一个退出的元素。
- 队列的处理方式与栈相反,栈的处理方式是LIFO。
- 队列中的方法有enqueue,dequeue,first等同于栈中的push,pop,peek
5.2 java API中的队列
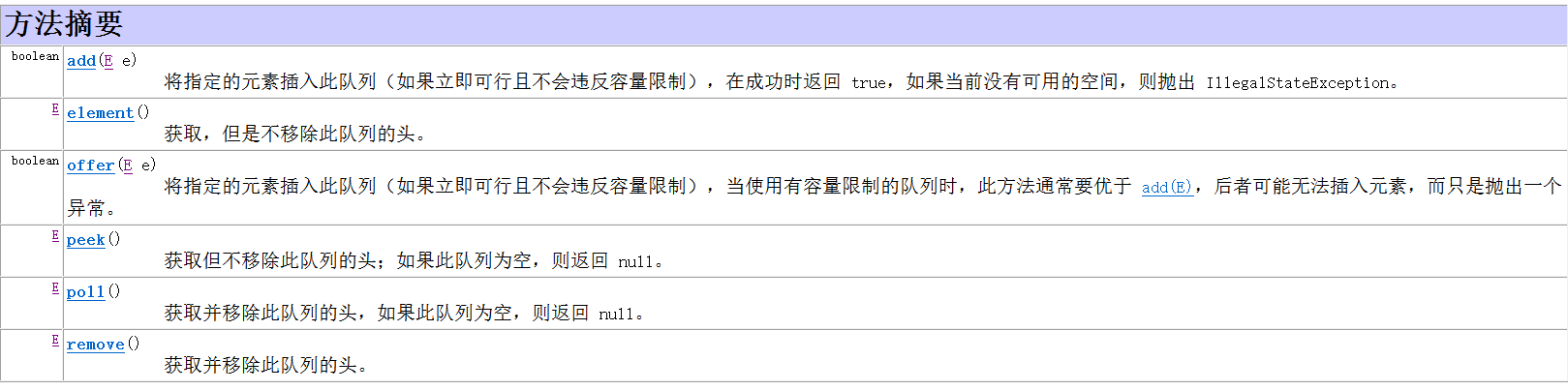
- java集合API提供了java.util.Stack类,他实现了栈集合。但他并没有提供队列类,而是提供了一个Queue接口。
- java.util.Stack类提供了push,pop和peek等操作,queue接口提供了两个方法add和offer。
- queue中的方法:
5.3 使用队列:代码秘钥和售票口模拟。
- 队列是一种可储存重复编码秘钥的遍历集合。
- 通常用表示排队的队列来实现模拟。
5.4 队列ADT
- 就像栈一样,我们也定义一个泛型QueueADT接口,表示队列的操作,把操作的一般目标与各种实现方式分开。
5.5 实现队列
5.5.1 用链表实现对列
- 两个分别指向链表首元素、链表末元素的引用方便队列的链表实现。
- 对于单向链表,可选择从末端入列,从前段出列。双向链表可以解决需要遍历链表的问题,因此在双向链表实现中,无所谓从哪端入列和出列。
- 代码:
public class CircularArrayQueue<T> implements QueueADT<T>
{
private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 100;
private int front, rear, count;
private T[] queue;
/**
* Creates an empty queue using the specified capacity.
* @param initialCapacity the initial size of the circular array queue
*/
public CircularArrayQueue (int initialCapacity)
{
front = rear = count = 0;
queue = (T[]) (new Object[initialCapacity]);
}
/**
* Creates an empty queue using the default capacity.
*/
public CircularArrayQueue()
{
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
/**
* Adds the specified element to the rear of this queue, expanding
* the capacity of the queue array if necessary.
* @param element the element to add to the rear of the queue
*/
public void enqueue(T element)
{
if (size() == queue.length)
expandCapacity();
queue[rear] = element;
rear = (rear+1) % queue.length;
count++;
}
/**
* Creates a new array to store the contents of this queue with
* twice the capacity of the old one.
*/
private void expandCapacity()
{
T[] larger = (T[]) (new Object[queue.length *2]);
for (int scan = 0; scan < count; scan++)
{
larger[scan] = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % queue.length;
}
front = 0;
rear = count;
queue = larger;
}
/**
* Removes the element at the front of this queue and returns a
* reference to it.
* @return the element removed from the front of the queue
* @throws EmptyCollectionException if the queue is empty
*/
public T dequeue() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
T result = queue[front];
queue[front] = null;
front = (front+1) % queue.length;
count--;
return result;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to the element at the front of this queue.
* The element is not removed from the queue.
* @return the first element in the queue
* @throws EmptyCollectionException if the queue is empty
*/
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
}
else
return queue[front];
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns true if this queue is empty and false otherwise.
* @return true if this queue is empty
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return count==0;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements currently in this queue.
* @return the size of the queue
*/
public int size()
{
return count;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this queue.
* @return the string representation of the queue
*/
public String toString()
{
String result = "";
int a =front;
for (int i = 0 ;i< count;i++){
result += queue[a]+" ";
a++;
}
return result;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
}
5.5.2 用数组实现队列
- 由于队列操作会修改集合的两端,因此将一段固定于索引0处要求移动元素。
- 非环形数组实现元素的移位,将产生O(n)的复杂度。
- 将数组看作是环形的,可以去除在队列的数组实现中把元素移位的需要
- 代码:
public class LinkedQueue<T> implements QueueADT<T>
{
private int count;
private LinearNode<T> head, tail;
/**
* Creates an empty queue.
*/
public LinkedQueue()
{
count = 0;
head = tail = null;
}
/**
* Adds the specified element to the tail of this queue.
* @param element the element to be added to the tail of the queue
*/
public void enqueue(T element)
{
LinearNode<T> node = new LinearNode<T>(element);
if (isEmpty())
head = node;
else
tail.setNext(node);
tail = node;
count++;
}
/**
* Removes the element at the head of this queue and returns a
* reference to it.
* @return the element at the head of this queue
* @throws EmptyCollectionException if the queue is empty
*/
public T dequeue() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
T result = head.getElement();
head = head.getNext();
count--;
if (isEmpty())
tail = null;
return result;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to the element at the head of this queue.
* The element is not removed from the queue.
* @return a reference to the first element in this queue
* @throws EmptyCollectionException if the queue is empty
*/
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
}
else
return head.getElement() ;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns true if this queue is empty and false otherwise.
* @return true if this queue is empty
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return count == 0;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements currently in this queue.
* @return the number of elements in the queue
*/
public int size()
{
return count;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this queue.
* @return the string representation of the queue
*/
public String toString()
{
String result = "" ;
while(head!=null){
result+=head.getElement()+" ";
head = head.getNext();
}
return result;
// To be completed as a Programming Project
}
}
5.6 双向链表
课后作业:
代码总览:
- 代码总览
- pp5.1:LinkedQueue类
- pp5.2: ArrayQueue类
- pp5.7:deque类
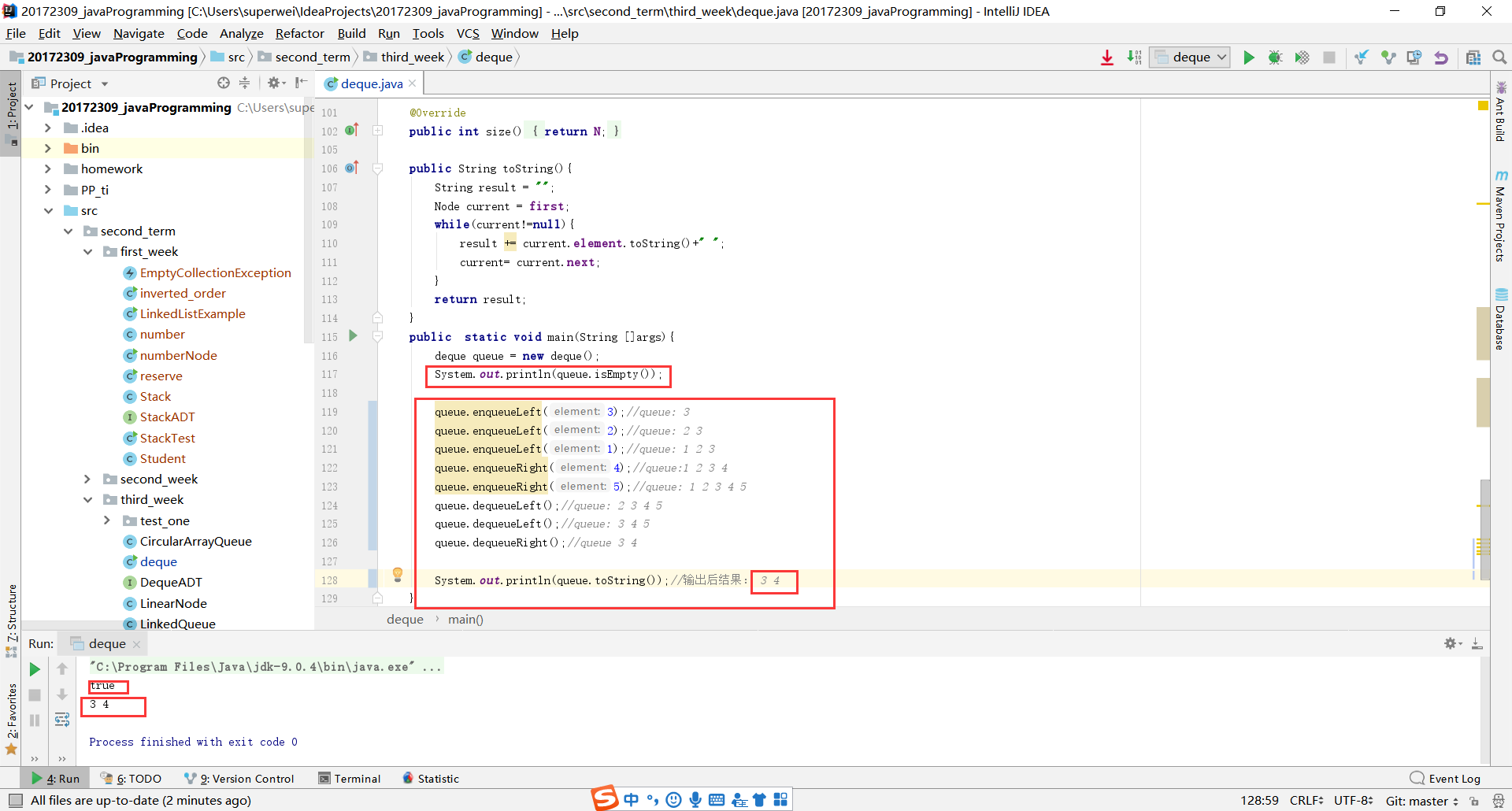
测试结果
-
pp5.1 pp5.2:

-
pp5.7:
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:课本81页说:在链表的前端实现dequeue操作,需将一个临时变量指向链表前端的元素,然后把front变量设置为第一个节点的next指针的值。 我想问为什么不可以直接
front.next = front.next.next - 问题1解决方案:个人觉得两种方法都可以。
- 问题2:如何理解
front = (front + 1 ) % queue,length? - 问题2解决方案:书上说是非环形的数组实现元素移位,将产生O(n)的复杂度,所以把数组看作是环形的,可以除去在队列的数组实现中把原始与移位的需要。
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
-
问题1:用数组实现链表时,使用两次enqueue方法,在使用一次dequeue方法,发现第一次实现的没有用为null。

-
问题1解决方案:toString方法出现错误:
修改前:
修改后:
出现这个问题的原因是:当使用dequeue方法后不知道front已经发生变化。
代码托管

上周考试错题总结
- 错题暂未公布
点评模板:
- 队友值得学习的地方:
- 课本内容记录详细,课本中的有些错误也能发现并及时纠正。
- 不懂得地方选择自己尝试,选择去敲代码验证。
点评过的同学博客和代码
- 本周结对学习情况
- 20172310
- 结对学习内容
- 第五章内容
- 如何用数组、链表实现对列
- 双向对列的编程
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
虽然这一章使用的是以前的知识,比如相关的数组、栈、多态、继承什么的,但是发现自己还是不能很熟练的运用。很多基础概念还是很模糊,说明自己还是得加油。
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 075/200 | 1/1 | 05/20 | |
| 第二周 | 560/500 | 1/2 | 13/38 | |
| 第三周 | 983/1000 | 1/3 | 21/60 |
补充作业
- (写之前说一下,之前没有看到这个补充作业,现在补充)