教材学习内容总结
教材学习内容总结
第三章
3.1集合
- 集合是一种聚集、组织其他对象的对象。
- 集合分为线性集合与非线性集合。
- 集合中的元素通常是按照它们添加到集合的顺序,或者是按照元素之间的某种内在关系来组织的。
- 集合是一种隐藏了实现细节的抽像。
- 数据结构是一种用于实现集合的基本编成结构。
3.2栈集合
- 栈的元素是按照后进先出(LIFO)的方法进行处理的,最后进入栈的元素最先被移除。
3.3 如何构建一个栈:
- 定义一个java接口StackADT
,表示作用于泛型T
public interface StackADT<T> {//public 保留字 泛型参数
/**
* 弹出栈顶
* @return
*/
public T pop();
public void push(T element);
/**
* 得到栈顶,但不弹出
* @return
*/
public T peek();
public boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 得到栈的大小
* @return
*/
public int Size();
/**
* 打印出栈
* @return
*/
@Override
public String toString();
}
- ArrayStack类:
public class Stack<T> implements StackADT<T>{
/**
* 1. 数组的大小
* 2. 定义一个数组
* 3. 确定栈顶位置
*/
private int size=100;
private T[] stack;
private int top;
public Stack(){//构造函数
top = 0 ;
stack = (T[]) (new Object[size]);
}
public Stack(int a){//方法重载
top = 0 ;
stack = (T[]) (new Object[a]);
}
}
- Push操作:
@Override
public void push(T element) {
if (Size() == stack.length){
expandCapacity();
}
stack[top] = element;
top++;
}
- Pop操作
@Override
public T pop() throws EmptyCollectionException{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Stack");
}
top--;
T result = stack[top];
stack[top]=null;
return result;
}
- peek操作
@Override
public T peek() throws EmptyCollectionException{
if (isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Stack");
}
return stack[top-1];
}
- 打印:
@Override
public String toString(){
String result = "";
for(int i =0;i<Size();i++)
{
result += " " + stack[i];
}
return result;
}
- EmptyCollectionException类
public class EmptyCollectionException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyCollectionException(String collection){
super("The " + collection + " is empty. ");
}
}
- 运行结果:

3.4本章课后作业:
第四章:
4.1链接作为引用
- 对象引用变量可以用来创建链式结构。
- 链表有一些对象构成,其中每个对象指向了链表中的下一个对象。
- 链表会按需求动态增长,因此在本质上没有容量限制。
- 如何创建一个链表:
public class Person
{
private String name;
private String address;
private Person next; //到另一个Person的链接
//其他内容
}
4.2 管理链表
- 访问元素
Person current = first;
for ( int i = 0; i<3; i++){
current = current.next;
}//访问到第四个元素
String s = current.name//得到属性name
- 插入节点
public static void InsertNode(Student Head, Student node){//当.next为null时,插入node
Student node1 = Head;
if (node1==null){
Head=node;}
else {
while(node1.next!= null){
node1=node1.next;
}
node1.next = node;
}
}
public static void InsertNode(Student Head,Student node1,Student node2,Student node3){//将node2插入在node1与node3之间(方法重载)
Student node0 =Head;
while(node0.number != node1.number && node0!= null){
node0 = node0.next;
}
if (node0.number == node1.number){
node0.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;}
else{
System.out.println("没有找到:"+node1.number+"!");
}
}
- 删除节点:
public static void DeleteNode(Student Head, int number){//删除学号为number 的人
Student node = Head;
if (node!=null&&node.number!=number){
while(node.next.number!=number){
node = node.next;
}
node.next =node.next.next;
}
else {
if (node ==null){
System.out.println("链表中没有学号为:"+number+"的这个人。");
}
else {
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
}
4.3用链表建立栈
public class LindedStack<T> implements StackADT<T> {
private int count;//用于计算栈中元素的个数
private LinearNode<T> top;//指向顶栈的指针
public LindedStack(){
count = 0 ;
top = null;
}
@Override
public T pop() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Stack");
T result = top.getElement();
top = top.getNext();
count--;
return result;
}
@Override
public void push(T element) {
LinearNode<T> temp = new LinearNode<T>(element);
temp.setNext(top);
top = temp;
count++;
}
@Override
public T peek() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Stack");}
T result = top.getElement();
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (count == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
@Override
public int Size() {
return count;
}
public String toString(){
String result="";
for (int i =0;i<count;i++){
System.out.println(top.getElement());
top = top.getNext();
}
return result;
}
}
- 测试结果

4.4 本章作业
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 暂时没发现什么问题。
代码托管

上周考试错题总结
- 错题1:
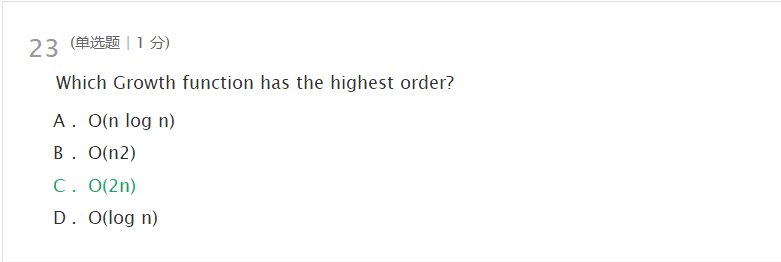
- 原因,理解情况:
- 错题2:2的n次方,不是2n.

- 原因,理解情况:算法的阶次就是算法的复杂度
点评模板:
结对伙伴:20172310
点评队友:
- 队友问题记录的非常仔细,值得自己学习,以后遇到问题得记录下来,不然会忘记。
- 关于课本上遇到的问题,队友没有说明自己的理解情况(比如什么是泛型),至少我觉的官方的讲解太复杂····
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 075/200 | 1/1 | 05/20 | |
| 第二周 | 560/500 | 1/2 | 13/38 |