1,C 语言中讨论了原生含义,C++ 中有必要考虑前置、后置操作符能够重载,有何问题;
2,值得思考的问题:
1,下面的代码有没有区别?为什么?
1,i++ // i 的值作为返回值,i 自增 1;
2,++i // i 自增 1,i 的值作为返回值;
3,没有使用返回值,由于编译器(不同的编译器都是一样的)的优化,在工程上面,这两行代码没有区别;
2,真的有区别吗?编程实验:
1,main.cpp 文件:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int i = 0; 9 10 i++; 11 12 ++i; 13 14 return 0; 15 }
2,底层对应代码:
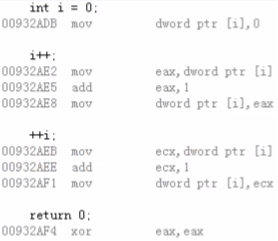
1,工程上除了使用的寄存器有差别之外,本质没有什么差别;
2,这是由于编译器的优化,这里是单独存在的、并没有使用它们的返回值,这个时候编译器的优化就是将返回值抛弃,得到的汇编代码就是上述内容;
3,现代编译器中的自增特性:
1,现代编译器产品会对代码进行优化;
2,优化使得最终的二进制程序更加高效;
3,优化后的二进制程序丢失了 C/C++ 的原生语义;
4,不可能从编译后的二进制程序还原 C/C++ 程序;
4,思考:
1,++ 操作符可以重载吗?如何区分前置 ++ 和后置 ++ ?
1,可以,-- 操作符也可以;
5,++ 操作符重载:
1,++ 操作符可以被重载:
1,全局函数和成员函数局可以进行重载;
2,重载前置 ++ 操作符不需要额外的参数;
3,重载后置 ++ 操作符需要一个 int 类型的占位参数;
2,++ 操作符的重载编程实验:
1,main.cpp 文件:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Test 7 { 8 int mValue; 9 public: 10 Test(int i) 11 { 12 mValue = i; 13 } 14 15 int value() 16 { 17 return mValue; 18 } 19 20 Test& operator ++ () // ++ 后返回自身; 21 { 22 ++mValue; // 先将当前操作数加 1; 23 24 return *this; // 加 1 后返回当前的操作数; 25 } 26 27 /* 若这个操作符不实现,则编译器显示:error: no 'operator++(int) declared for poatfix '++', try prefix operator instead */ 28 /* C 语言中定义,如果是后置 ++,它先将当前操作数值保存在临时对象中;于是这里借助局部对象 ret 保存下来,之后返回 */ 29 Test operator ++ (int) // 占位参数为 int 类型; 30 { 31 Test ret(mValue);// ++ 之前的值先返回,当然这里先存储着返回值,之后再 ++; 32 33 mValue++; // 然后 ++ 34 35 return ret; 36 } 37 }; 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 Test t(0); 42 43 t++; 44 45 ++t; 46 47 return 0; 48 }
2,上述 main() 中的两行加加代码,因为调用函数不一样,所以有差异,并 且前置 ++ 效率更高,因为它的实现没有生成额外的对象,意味着不需要过 多的栈内存,不需要调用构造、析构函数;
6,真正的区别(本博文2 中的思考):
1,对于基础类型的变量:
1,前置 ++ 的效率与后置 ++ 的效率基本相同;
1,编译器会优化;
2,根据项目组编码规范进行选择;
2,对于类类型的对象:
1,前置 ++ 的效率高于后置 ++;
2,尽量使用前置 ++ 操作符提高程序效率;
7,复数类的进一步完善 class Complex 编程实验:
1,Complex.h 文件:
1 #ifndef _COMPLEX_H_ 2 #define _COMPLEX_H_ 3 4 class Complex 5 { 6 double a; 7 double b; 8 public: 9 Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0); 10 double getA(); 11 double getB(); 12 double getModulus(); 13 14 Complex operator + (const Complex& c); 15 Complex operator - (const Complex& c); 16 Complex operator * (const Complex& c); 17 Complex operator / (const Complex& c); 18 19 bool operator == (const Complex& c); 20 bool operator != (const Complex& c); 21 22 Complex& operator = (const Complex& c); 23 24 /* 本博文重载了下面两个操作符 */ 25 Complex& operator ++ (); 26 Complex operator ++ (int); 27 };
2,Complex.cpp 文件:
1 #include "Complex.h" 2 #include "math.h" 3 4 Complex::Complex(double a, double b) 5 { 6 this->a = a; 7 this->b = b; 8 } 9 10 double Complex::getA() 11 { 12 return a; 13 } 14 15 double Complex::getB() 16 { 17 return b; 18 } 19 20 double Complex::getModulus() 21 { 22 return sqrt(a * a + b * b); 23 } 24 25 Complex Complex::operator + (const Complex& c) 26 { 27 double na = a + c.a; 28 double nb = b + c.b; 29 Complex ret(na, nb); 30 31 return ret; 32 } 33 34 Complex Complex::operator - (const Complex& c) 35 { 36 double na = a - c.a; 37 double nb = b - c.b; 38 Complex ret(na, nb); 39 40 return ret; 41 } 42 43 Complex Complex::operator * (const Complex& c) 44 { 45 double na = a * c.a - b * c.b; 46 double nb = a * c.b + b * c.a; 47 Complex ret(na, nb); 48 49 return ret; 50 } 51 52 Complex Complex::operator / (const Complex& c) 53 { 54 double cm = c.a * c.a + c.b * c.b; 55 double na = (a * c.a + b * c.b) / cm; 56 double nb = (b * c.a - a * c.b) / cm; 57 Complex ret(na, nb); 58 59 return ret; 60 } 61 62 bool Complex::operator == (const Complex& c) 63 { 64 return (a == c.a) && (b == c.b); 65 } 66 67 bool Complex::operator != (const Complex& c) 68 { 69 return !(*this == c); 70 } 71 72 Complex& Complex::operator = (const Complex& c) 73 { 74 if( this != &c ) 75 { 76 a = c.a; 77 b = c.b; 78 } 79 80 return *this; 81 } 82 83 Complex& Complex::operator ++ () 84 { 85 a = a + 1; 86 b = b + 1; 87 88 return *this; 89 } 90 91 Complex Complex::operator ++ (int) 92 { 93 Complex ret(a, b); 94 95 a = a + 1; 96 b = b + 1; 97 98 return ret; 99 } 100 101 #endif
8,小结:
1,编译优化使得最终的可执行程序更加高效;
2,前置 ++ 操作符和后置 ++ 操作符都可以被重载;
3,++ 操作符的重载必须符合其原生语义;
4,对于基础类型,前置 ++ 与后置 ++ 的效率几乎相同;
5,对于类类型,前置 ++ 的效率高于后置 ++;
1,对于类类型,工程中尽量使用前置 ++;