1、总结
链表类问题都是in-place,空间复杂度都是O(1)的,在所有的排序算法中,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)的有三个:
1)快速排序(不开辟空间);
2)归并排序(需要开辟O(n)的空间,但是在list问题上不开辟空间);
3)堆排序(首先需要有一个堆)。
while里面写判断条件的时候规律:
如果接下来有head -> next,那么必须判断head是否为空,同理类推。
写链表的题目,一定要注意是否需要返回node,有些题目是void就是没有返回值的,自己经常没注意这个void就直接返回值了。
1.1、Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/#/description
移除重复元素,不全部删除!
思路:使用一个node,相等的时候就node -> next = node -> next -> next,不相等的时候node往后移位,这是个技巧,原来我的做法是使用两个指针,找到第一个不相等的节点就是node ->next.

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL){ return head; } ListNode* node = head; while(node -> next != NULL){ if(node -> val == node -> next -> val){ node -> next = node -> next -> next; } else{ node = node -> next; } } return head; } };
1.2、Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/#/description
删除所有的的重复元素,包括自身。
思路:1)一直纠结while里面写head?? != NULL,记住:只要循环里面有哪个是->next->或者->val->的。那么就写这个不为空,比如这题需要在循环中判断head->next->val和head->next->next-->val,所以在while循环的判断中就需要写head->next !=NULL 而且head->next->next != NULL。
如果是head->next,和head->next->next就写while(head!=NULL&&head->next!=NULL)
2)dummy node标准写法:
哨兵节点使用于头结点不确定的情况,题目中可能需要单独对头结点进行操作,这时候就可以引入哨兵节点。

ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy = head; head = dummy; return dummy -> next;
上面的写法会造成内存泄露,推荐下面的写法:
ListNode dummy(0);//定义一个对象,使用默认构造函数 dummy.next = head; head = &dummy; return dummy.next;
3)因为本题需要知道前驱节点,这样才能将所有重复的节点去掉,所以需要使用head->next和head->next->next。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){ return head; } ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy -> next = head; head = dummy; // ListNode* node; while(head -> next != NULL && head -> next -> next != NULL){ if(head -> next -> val == head -> next ->next -> val){ int flag = head -> next -> val;//这一步是技巧,有重复,就保留这个值,和值相等的都删除 while(head -> next != NULL && head -> next -> val == flag ){ head -> next = head -> next -> next; } } else{ head = head -> next; } } return dummy -> next; } };
1.3 Reverse Linked List
思路:记得保存断开后的下一个节点。
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/#/description

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){ return head; } ListNode* pre = NULL; ListNode* cur = head ; ListNode* post = head -> next; while(cur != NULL){ post =cur -> next; cur -> next = pre; pre = cur; cur = post; } return pre; } };
1.4 Reverse Linked List II
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/#/description
思路:这题需要考虑m和n的关系,m为1的时候,是头结点,这时候很难处理,就需要引入dummy node,技巧点:因为多了一个节点,所以i=1,循环m-1次,找到m的前一个位置,循环里面判断是否为空的判断是为了判断m是否大于链表的长度。
接下来令nNode = mNode,循环n-m次,j =m.j < n。交换相邻节点,记得判断postnNode是否为空,为空则返回,而且也记得上面的总结,后面有postnNode -> next,所以要判断postnNode是否为空,为空则n大于链表长度,返回NULL。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if(head == NULL || m >= n){ return head; } ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy -> next = head; head = dummy; for(int i = 1; i < m;++i){ // if(head == NULL){ // return NULL; // } head = head -> next; } ListNode* premNode = head; ListNode* mNode = head -> next; ListNode* nNode = mNode; ListNode* postnNode = nNode -> next; ListNode* tmp; for(int j = m;j < n;++j){ if(postnNode == NULL){ return NULL; } tmp = postnNode -> next; postnNode -> next = nNode; nNode = postnNode; postnNode = tmp; } premNode -> next = nNode; mNode -> next = postnNode; return dummy -> next; } };
反转链表递归和迭代版本
原题:leetcode 206. Reverse Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list.
迭代版本:
思路:通过举例分析可以知道,在反转其中一个链表后,会发生断裂情况,没法知道下一个链节点,需要建立三个节点,所以需要首先保存后一个节点,然后将后一个结点的next指向前一个节点,接下来依次后退,pPre=pCur;pCur=pNext。

 reverse List
reverse List递归版本:思路和迭代差不多,只不过在最后两个节点交换的时候,使用递归版本实现。递归要考虑到原函数初始定义会在后面递归的时候不断的重新定义,这里思考出现卡顿,所以引入一个辅助函数。

ListNode* helper(ListNode* pPre, ListNode* pCur) { ListNode* pNext(0), * pRevHead(0); if (pCur == nullptr) return pPre; pNext = pCur->next;//首先保存下一结点值 if (pNext == nullptr) pRevHead = pCur; pCur->next = pPre;//调整指针 return helper(pCur, pNext); } ListNode* reverseListRecur(ListNode* head) { ListNode *pCur = head, *pPre(0), *pRevHead(0); if (head == nullptr) { return head; } pRevHead= helper(pPre, pCur); return pRevHead; }
1.5 Partition List
https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-list/#/description
将比x小的元素放在前面,小的元素放在后面。
思路:使用两个dummy node,分别记录比x大的数和比x小的数,最后将两者合并起来。链表的结尾必须要加上nullptr,这题dummyRight最后要dummyNode -> next = nullptr.

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) { if(head == NULL){ return head; } ListNode* left = new ListNode(0); ListNode* right = new ListNode(0); ListNode* leftDummy = left; ListNode* rightDummy = right; while(head != NULL){ if(head -> val < x){ left -> next = head; left = left -> next; } else{ right -> next = head; right = right -> next; } head = head -> next; } left -> next = rightDummy -> next; right -> next = NULL; return leftDummy -> next; } };
1.6 Sort List
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/#/description
思路:记住归并算法在list结构中 ,所需要的空间复杂度是O(1)的,注意该题边界条件有两个变量需要考虑,不能漏写。
if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){//边界情况 return head; }
这题就使用归并算法。三步走:
1)找中间函数使用快慢指针找到链表的中间,slow = head ,fast = head -> next。快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,当fast为空的时候,就找到了slow = mid;
2)使用递归函数将问题分解,
ListNode* mergeRight = sortList(mid -> next); mid -> next = NULL; ListNode* mergeLeft = sortList(head);
这里有个细节,就是要将mid-> next设为空,不然就会陷入死循环。先传给右边,也可以省掉一个节点。
3)新建dummy node和tail node,哪个大就将该节点赋到tail后面,最后返回dummy -> next。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* findMid(ListNode* head){ ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head -> next; while(fast != NULL && fast -> next != NULL){ fast = fast -> next -> next; slow = slow -> next; } return slow; } ListNode* merge(ListNode* mergeLeft,ListNode* mergeRight){ ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode* tail = dummy; while(mergeLeft != NULL && mergeRight != NULL){ if(mergeLeft -> val < mergeRight -> val){ tail -> next = mergeLeft; mergeLeft = mergeLeft -> next; } else{ tail -> next = mergeRight; mergeRight = mergeRight -> next; } tail = tail -> next; } if(mergeLeft != NULL){ tail -> next = mergeLeft; } if(mergeRight != NULL){ tail -> next = mergeRight; } return dummy -> next; } ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){//边界情况 return head; } ListNode* mid = findMid(head); ListNode* mergeRight = sortList(mid -> next); mid -> next = NULL; ListNode* mergeLeft = sortList(head); ListNode* result = merge(mergeLeft,mergeRight); return result; } };
1.7 Reorder List
https://leetcode.com/problems/reorder-list/#/description
思路:首先找中点,使用快慢指针;然后将右边的元素全部反转,参考reverse函数;最后将两个链表合并。注意点mid这个node属于left链表。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* findMid(ListNode* head){ ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head -> next; while(fast != NULL && fast -> next != NULL){ slow = slow -> next; fast =fast -> next -> next; } return slow; } ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head){ ListNode* pre = NULL; ListNode* cur = head; ListNode* post = head -> next; while(cur != NULL){ post = cur -> next; cur -> next = pre; pre = cur; cur = post; } return pre; } void reorderList(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){ return; } ListNode* mid = findMid(head); ListNode* right = reverse(mid -> next); mid -> next = NULL; ListNode* left = head; ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode* tail = dummy; while(left != NULL || right != NULL){ if(left != NULL){ tail -> next = left; left = left -> next; tail = tail -> next; } if(right != NULL){ tail -> next = right; right = right -> next; tail = tail -> next; } } head = dummy -> next; } };
2 Fast Slow Pointers
2.1 有环链表问题总结
1)Linked List Cycle I
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/#/description
思路:快慢指针,相交的话则有环

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){ return false; } ListNode *slow = head ; ListNode *fast = head -> next; while(fast != NULL && fast -> next != NULL){ slow = slow -> next; fast = fast -> next -> next; if(fast == slow){ return true; } } return false; } };
2)Linked List Cycle II
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/#/description
思路:这题需要知道a = c,然后head和slow每次走一步,相遇的时候就是第一个入口交点,需要注意应该写head != slow -> next,如果写成head == slow,在两个元素组成的环中就会死循环
还有就是最后返回head, return head;//这里不能写成slow,因为两个元素的环就出错。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL){ return NULL; } ListNode * fast = head -> next; ListNode * slow = head; while(fast != NULL && fast -> next != NULL){ slow = slow -> next; fast = fast -> next -> next; if(fast == slow){ break; } } if(fast == NULL ||fast -> next == NULL){ return NULL; } while(head != slow -> next){//如果写成head == slow,在两个元素组成的环中就会死循环 head = head -> next; slow = slow -> next; } return head;//这里不能写成slow,因为两个元素的环就出错 } };
在网上搜集了一下这个问题相关的一些问题,总结如下:
1. 环的长度是多少?
2. 如何找到环中第一个节点(即Linked List Cycle II)?
3. 如何将有环的链表变成单链表(解除环)?
4. 如何判断两个单链表是否有交点?如何找到第一个相交的节点?
首先我们看下面这张图:
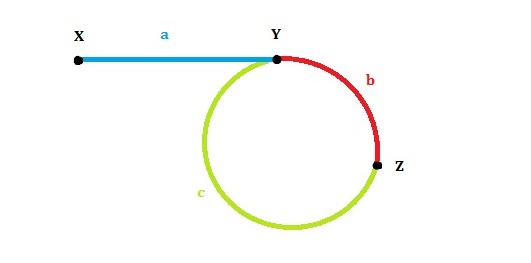
设:链表头是X,环的第一个节点是Y,slow和fast第一次的交点是Z。各段的长度分别是a,b,c,如图所示。环的长度是L。slow和fast的速度分别是qs,qf。
下面我们来挨个问题分析。
1. 方法一(网上都是这个答案):
第一次相遇后,让slow,fast继续走,记录到下次相遇时循环了几次。因为当fast第二次到达Z点时,fast走了一圈,slow走了半圈,而当fast第三次到达Z点时,fast走了两圈,slow走了一圈,正好还在Z点相遇。
方法二:
第一次相遇后,让fast停着不走了,slow继续走,记录到下次相遇时循环了几次。
方法三(最简单):
第一次相遇时slow走过的距离:a+b,fast走过的距离:a+b+c+b。
因为fast的速度是slow的两倍,所以fast走的距离是slow的两倍,有 2(a+b) = a+b+c+b,可以得到a=c(这个结论很重要!)。
我们发现L=b+c=a+b,也就是说,从一开始到二者第一次相遇,循环的次数就等于环的长度。
2. 我们已经得到了结论a=c,那么让两个指针分别从X和Z开始走,每次走一步,那么正好会在Y相遇!也就是环的第一个节点。
3. 在上一个问题的最后,将c段中Y点之前的那个节点与Y的链接切断即可。
4. 如何判断两个单链表是否有交点?先判断两个链表是否有环,如果一个有环一个没环,肯定不相交;如果两个都没有环,判断两个列表的尾部是否相等;如果两个都有环,判断一个链表上的Z点是否在另一个链表上。
如何找到第一个相交的节点?求出两个链表的长度L1,L2(如果有环,则将Y点当做尾节点来算),假设L1<L2,用两个指针分别从两个链表的头部开始走,长度为L2的链表先走(L2-L1)步,然后两个一起走,直到二者相遇。
2.2 Merge k Sorted Lists(important)参考嘻唰唰的链接
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/#/description
思路1:使用优先级队列priority_queue的方法,先压入k个链表的头结点,定义比较函数,小顶堆(a>b,联想队列先进先出),然后选出哪个最小节点,就看看它的下一个节点是否为空,不为空的话就压入队列它的下一个节点。记得要时刻保证队列的大小为k。比较函数写入优先级队列的方法参考另外一个博客优先级队列。
时间复杂度为O(NlogK),

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: struct cmp{ bool operator()(ListNode *a,ListNode *b){ if(a != NULL && b != NULL){ return a -> val > b-> val; } } }; ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { int n = lists.size(); if(n == 0){ return NULL; } priority_queue<ListNode *,vector<ListNode *>,cmp> que; for(int i = 0;i < n;++i){ if(lists[i] != NULL){//保证压入优先级队列的是非空的链表节点,不然后面tmp-> next会出错 que.push(lists[i]); } } ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode *tail = dummy; while(!que.empty()){ ListNode *tmp = que.top(); que.pop(); tail -> next = tmp; tail = tail -> next; if(tmp -> next != NULL){//压入当前链表的下一个节点,保持链表的长度为k que.push(tmp -> next); } } return dummy -> next; } };
思路2:采用递归中的分治算法,也是二分方法,先处理相等的时候,递归基,然后再归并。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergesort(ListNode* left,ListNode* right){ ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode* tail = dummy; while(left != NULL && right != NULL){ if(left -> val < right -> val){ tail -> next = left; left = left -> next; } else{ tail -> next = right; right = right -> next; } tail = tail -> next; } if(left != NULL){ tail -> next = left; } if(right != NULL){ tail -> next = right; } return dummy -> next; } ListNode* merge(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int start,int end){ int mid; if(start == end){//mergesort先处理边界情况 return lists[start]; } mid = start + (end - start) / 2; ListNode* left = merge(lists,start,mid); ListNode* right = merge(lists,mid + 1,end); ListNode* tail = mergesort(left,right); return tail; } ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { //mergeSort binarySearch if(lists.size() == 0){ return NULL; } ListNode* result = merge(lists,0,lists.size() - 1); return result; } };
迭代版本:

class Solution { public: ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) { if(lists.empty()) return NULL; int end = lists.size()-1; while(end>0) { int begin = 0; while(begin<end) { lists[begin] = merge2Lists(lists[begin], lists[end]); begin++; end--; } } return lists[0]; } ListNode* merge2Lists(ListNode *h1, ListNode *h2) { ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0), *tail = dummy; while(h1 && h2) { if(h1->val<=h2->val) { tail->next = h1; h1 = h1->next; } else { tail->next = h2; h2 = h2->next; } tail = tail->next; } tail->next = h1 ? h1 : h2; return dummy->next; } };
2.3 138. Copy List with Random Pointer
https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/#/description
思路:建立两个节点,哨兵节点最后返回结果,一个随着计算进行next,首先只要当前节点不为空,就不断将node压入一个哈希表unordered_map,这个map里面可以是原来表的node,value是新的node,接下来的循环是拷贝随机指针,Map[tmp] -> random = Map[tmp -> random];

/** * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. * struct RandomListNode { * int label; * RandomListNode *next, *random; * RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /** * @param head: The head of linked list with a random pointer. * @return: A new head of a deep copy of the list. */ RandomListNode *copyRandomList(RandomListNode *head) { // write your code here unordered_map<RandomListNode*, RandomListNode*> old2new; RandomListNode* dummy = new RandomListNode(-1); RandomListNode* tmp = head; RandomListNode* curr = dummy; while (tmp) { RandomListNode* newNode = new RandomListNode(tmp->label); old2new[tmp] = newNode; curr->next = newNode; curr = curr -> next;//如果这里写成newNode = newNode -> next,那么最后dummy->next 指向的是最后一个节点。而且下一个next对象还没创建,不知道指向谁,就会出错 tmp = tmp->next; } tmp = head; while (tmp) { if (tmp->random) { old2new[tmp]->random = old2new[tmp->random]; } tmp = tmp-> next; } return dummy->next; } };
调整只需要O(1)空间复杂度的解法:
思路:三部曲:
1. 在原链表的每个节点后面拷贝出一个新的节点
2. 依次给新的节点的随机指针赋值,因为在第一步中,新节点和旧节点都指向相同的随机指针元素,这个赋值非常容易 cur->next->random = cur->random->next,要注意这里cur->random不能为空,初始化都为空,只有不为空的时候才需要调整。
3. 断开链表可得到深度拷贝后的新链表,这里需要注意的地方是
if(tmp->next != NULL){ //只有一个节点的时候1 -> 1' -> NULL;tmp -> next == NULL tmp -> next = tmp -> next -> next; }

/** * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. * struct RandomListNode { * int label; * RandomListNode *next, *random; * RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: RandomListNode *copyNext(RandomListNode *head){ RandomListNode *h = head; while(h != NULL){ RandomListNode *newNode = new RandomListNode(h -> label); newNode -> next = h -> next; newNode -> random = h -> random; h -> next = newNode; h = h -> next -> next; } return head; } RandomListNode *adjustRandomPoint(RandomListNode *head){ RandomListNode *h = head; while(h!= NULL){ if( h -> random != NULL){//开始都初始为空,只有随机指针不为空的时候才需要进行操作 h -> next -> random = h -> random -> next; } h = h -> next -> next; } return head; } RandomListNode *splitLink(RandomListNode *head){ RandomListNode *h = head -> next; while(head != NULL){ RandomListNode *tmp = head -> next; head -> next = tmp -> next; if(tmp->next != NULL){//只有一个节点的时候1 -> 1' -> NULL;tmp -> next == NULL tmp -> next = tmp -> next -> next; } head = head -> next; } return h; } RandomListNode *copyRandomList(RandomListNode *head) { if(head == NULL){ return head; } RandomListNode *copyNextNode = copyNext(head); RandomListNode *adjustRandonPointNode = adjustRandomPoint(copyNextNode); RandomListNode *result = splitLink(adjustRandonPointNode); return result; } };
正常思路的好方法:记住要先保存head,因为后面要copy随机节点。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. * struct RandomListNode { * int label; * RandomListNode *next, *random; * RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: RandomListNode *copyRandomList(RandomListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr){ return head; } unordered_map<RandomListNode *,RandomListNode *> oldToNew; //copy next RandomListNode *dummy = new RandomListNode(0); RandomListNode *p = dummy; RandomListNode *cur = head; while(cur != nullptr){ RandomListNode *tmp = new RandomListNode(cur -> label); oldToNew[cur] = tmp; cur = cur -> next; dummy -> next = tmp; dummy = dummy -> next; } //copy Random cur = head; dummy = p -> next; while(cur != nullptr){ if(cur -> random != nullptr){ oldToNew[cur] -> random = oldToNew[cur -> random]; } cur = cur -> next; dummy = dummy -> next; } return p -> next; } };
分析复杂度的方法:
看均到每个节点上的复杂度是多少,然后乘以N个节点,就可以得到总的时间复杂度。
2.4 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree/#/description
排序链表转化为二叉搜索树
思路:二叉树中序递归遍历的思路,首先求出链表的长度,然后定义递归函数helper(*&head,start,end),参考了嘻唰唰的思路----->这里这个函数所做的是将*head为头的linked list构建成一个BST,然后返回BST的root,而同时,也将head移动到linked list中第end+1个节点。因为*head既是输入参数,也是返回参数,所以这里用到了指针的引用*&head。注意不能错写成了&*head。理解*&的方法是从右向左读:首先是一个引用,然后是一个对指针的引用,最后是一个对ListNode指针的引用。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode *helper(ListNode *&head,int start,int end){ if(start > end){ return NULL; } int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; TreeNode *leftNode = helper(head,start,mid - 1); TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(head -> val); head = head -> next;//记住链表分割的时候一定要修改传递的head节点 TreeNode *rightNode = helper(head,mid + 1,end); root -> left = leftNode; root -> right = rightNode; return root; } TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL){ return NULL; } int len = 0;//len必须初始化为0,后面才能进行自增操作 ListNode *cur = head; while(cur != NULL){ cur = cur -> next; ++len; } TreeNode *result; result = helper(head,0,len - 1); return result; } };
思路2:可以直接使用全局变量,避免复杂的写法。
思路3:先找到中间点,然后找left,在找right,递归执行,每次需要使用快慢指针找到中间点。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* toBST(ListNode *head,ListNode *tail){ if(head == tail){//这里容易写错 return nullptr; } ListNode* fast = head -> next; ListNode* slow = head; while(fast != tail && fast -> next != tail){ fast = fast -> next -> next; slow = slow -> next; } TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(slow -> val); newNode -> left = toBST(head,slow); newNode -> right = toBST(slow -> next,tail); return newNode; } TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) { if(head == nullptr){ return nullptr; } TreeNode* result = toBST(head,nullptr); return result; } };
另一道简单的数组题和这个思路差不多,108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* helper(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){ if(start > end){ return NULL; } int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; TreeNode* leftNode = helper(nums,start,mid - 1); TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]); TreeNode* rightNode = helper(nums,mid + 1,end); root -> left = leftNode; root -> right = rightNode; return root; } TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) { int len = nums.size(); if(len == 0){ return NULL; } return helper(nums,0,len - 1); } };
2.5 二叉搜索树与双向链表
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/947f6eb80d944a84850b0538bf0ec3a5?tpId=13&tqId=11179&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
思路:题目中说要求不能创建任何新的结点,指的是不能new一个节点出来,但是可以创建局部变量。二叉树有左右两个指针,而链表也有前后两个指针,helper函数里面有两个节点,第二个pre是传引用的形式,最后的结果pre指向链表的最后一个节点,所以要得到头结点,需要不断的pre = pre -> left;
1)先将左子树构建成一个链表
2)root -> left = pre;pre -> right = root
pre = root ;
3)接下来转入右子树,将右子树转化为链表,递归执行

/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: void helper(TreeNode* root,TreeNode*& pre){ if(root == nullptr ){ return; } helper(root -> left,pre); root -> left = pre; if(pre != nullptr){ pre -> right = root; } pre = root;//记住pre始终指向当前节点的前一个节点 helper(root -> right,pre); } TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* root){ if(root == nullptr ){ return root; } if(root -> left == nullptr && root -> right == nullptr){ return root; } TreeNode* pre = nullptr; helper(root,pre); TreeNode* head = pre; while(head != nullptr && head -> left != nullptr){ head = head -> left; } return head; } };
2.6 25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/#/description
思路:这题我是联想给定一个链表,反转第m和n之间链表的解法,在画图分析的基础上,增加了一个外层循环,循环次数是k/listLen;因为要修改第一个节点,所以需要一个dummy node,
每次调整k之后,需要将prem和m节点进行调整:
prem = m;
m = postn;
还有记得循环的次数可以通过举两个节点的简单例子进行确定。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int getLen(ListNode *head){ int len = 0; while(head != nullptr){ head = head -> next; ++len; } return len; } ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { int listLen = getLen(head); if(head == nullptr || k > listLen){ return head; } ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy -> next = head; head = dummy; int times = listLen / k; ListNode *prem = head; ListNode *m = head -> next; for(times;times > 0;--times){ ListNode *n = m; ListNode *postn = n -> next; for(int i = 1;i < k && postn != nullptr;++i){ ListNode *tmp = postn -> next; postn -> next = n; n = postn; postn = tmp; } prem -> next = n; m -> next = postn; prem = m; m = postn; } return dummy -> next; } };
