事务的传播属性(Propagation)
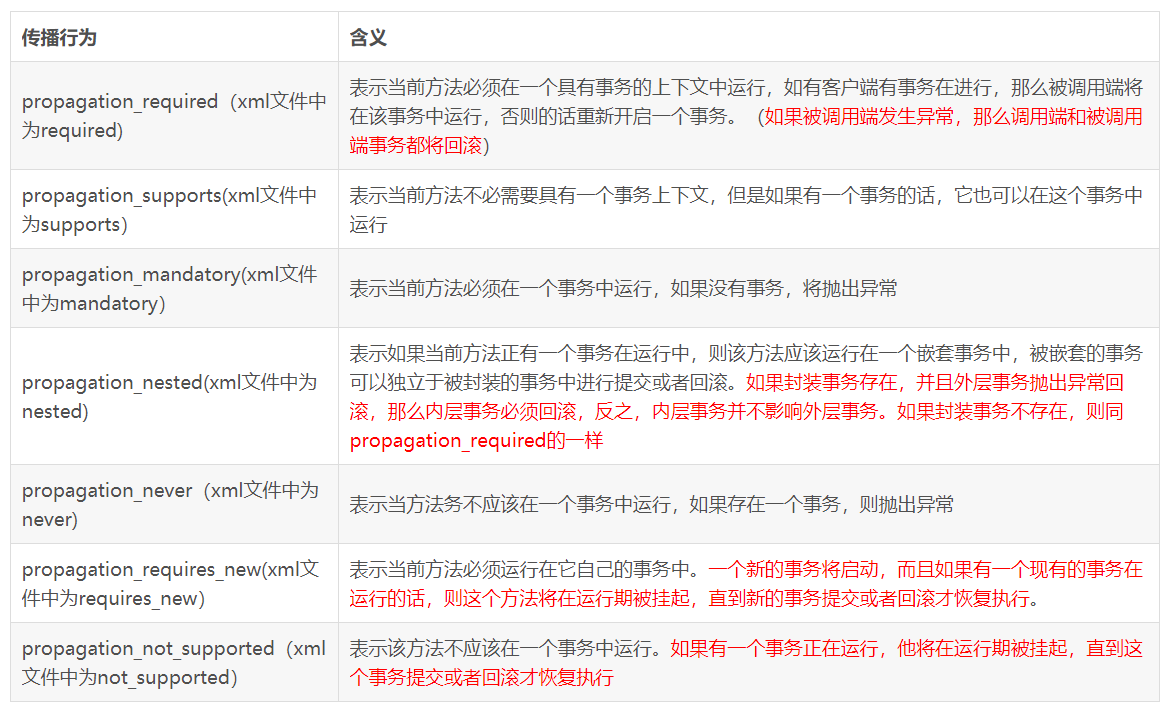
Spring在TransactionDefinition接口中规定了7种类型的事务传播行为,
它们规定了事务方法和事务方法发生嵌套调用时事务如何进行传播:
1.REQUIRED,这个是默认的属性
Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists.
如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务。如果没有事务则开启一个新的事务。
被设置成这个级别时,会为每一个被调用的方法创建一个逻辑事务域。如果前面的方法已经创建了事务,那么后面的方法支持当前的事务,如果当前没有事务会重新建立事务。
2.MANDATORY
Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists.支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
3.NEVER
Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists.
以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
4.NOT_SUPPORTED
Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
5.REQUIRES_NEW
Create a new transaction, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。
6.SUPPORTS
Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists.
支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
7.NESTED
Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists, behave like PROPAGATION_REQUIRED else.
支持当前事务,新增Savepoint点,与当前事务同步提交或回滚。
嵌套事务一个非常重要的概念就是内层事务依赖于外层事务。外层事务失败时,会回滚内层事务所做的动作。而内层事务操作失败并不会引起外层事务的回滚。
8.PROPAGATION_NESTED 与PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW的区别
它们非常类似,都像一个嵌套事务,如果不存在一个活动的事务,都会开启一个新的事务。使用PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW时,内层事务与外层事务就像两个独立的事务一样,一旦内层事务进行了提交后,外层事务不能对其进行回滚。两个事务互不影响。两个事务不是一个真正的嵌套事务。同时它需要JTA 事务管理器的支持。
使用PROPAGATION_NESTED时,外层事务的回滚可以引起内层事务的回滚。而内层事务的异常并不会导致外层事务的回滚,它是一个真正的嵌套事
事务的隔离级别
1.DEFAULT (默认)
这是一个PlatfromTransactionManager默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别.另外四个与JDBC的隔离级别相对应。
2.READ_UNCOMMITTED (读未提交)
这是事务最低的隔离级别,它允许另外一个事务可以看到这个事务未提交的数据。这种隔离级别会产生脏读,不可重复读和幻像读。
3.READ_COMMITTED (读已提交)
保证一个事务修改的数据提交后才能被另外一个事务读取。另外一个事务不能读取该事务未提交的数据。这种事务隔离级别可以避免脏读出现,但是可能会出现不可重复读和幻像读。
4.REPEATABLE_READ (可重复读)
这种事务隔离级别可以防止脏读,不可重复读。但是可能出现幻像读。它除了保证一个事务不能读取另一个事务未提交的数据外,还保证了不可重复读。
5.SERIALIZABLE(串行化)
这是花费最高代价但是最可靠的事务隔离级别。事务被处理为顺序执行。除了防止脏读,不可重复读外,还避免了幻像读。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd" default-autowire="byName"> <import resource="classpath*:spring/spring-config-dao.xml" /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.letv.*.manager" /> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" /> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="query*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="batchSave*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="cancelOrder" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="managers" expression="execution(* com.thb.*.manager..*.*(..)) "/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="managers"/> </aop:config> </beans>
上面配置文件意思是调用 com.thb.下面的任何的任何manager类里的以query,save, update等开头的方法和 cancelorder方法时,在方法层面上事务级别是required,而调用这些manager的别的方法则是support级别。
比如 在下面的 com.letv.ofc.manager.impl.updateStrategyResult() 方法中,又调用了几个别的manager的方法,则这几个别的manager的方法都是required,它们在updateStrategyResult()中会共用一个transaction。结果是这几个方法的SQL 执行只要有一个失败,都会导致其它的方法回滚 (rollback)
public void updateStrategyResult() {
....
saveOrderInfo(orderInfo, remark);
insertOFCSourcingOrderTask(orderQuery);
updateTaskOrder(task, grabObject);
insertWMSDistributionOrderTask(task);
insertOperateLog(orderInfo.getOrderCode(), remark);
lockSkuStock(grabObject);
}
执行某操作,前50次成功,第51次失败
a全部回滚
父类方法加事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
b前50次提交第51次抛异常,ab场景分别如何设置Spring(传播性)
父类方法加事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ,子类方法加事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW