1java中的异常处理捕获语句
package 动手动脑五; import javax.swing.*; public class AboutException { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 int i=1, j=0, k; k=i/j; try { k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception //throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!"); } catch ( ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) System.out.println("被0除"); else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } finally { JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"); } } }
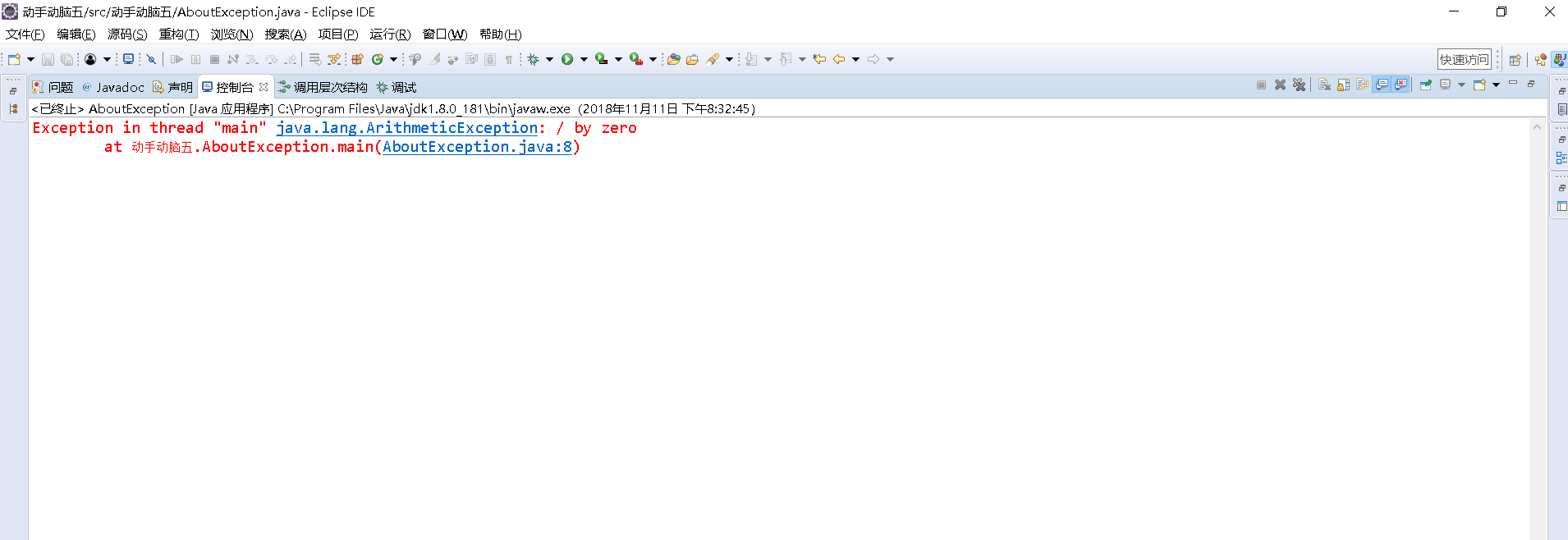
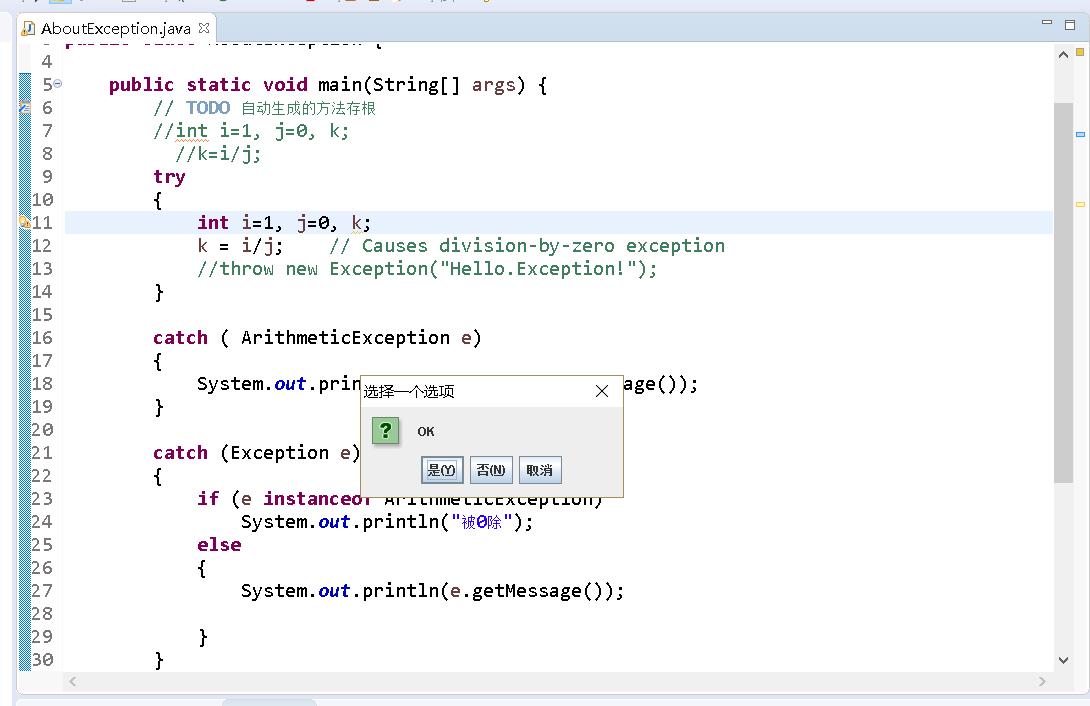
总结:try{}中是写可能发生运行错误的代码,catch{}中用于处理异常的代码,finally{}用于善后的代码,不管是否有异常发生,finally语句块中的语句始终保证被执行。
2多层的异常捕获
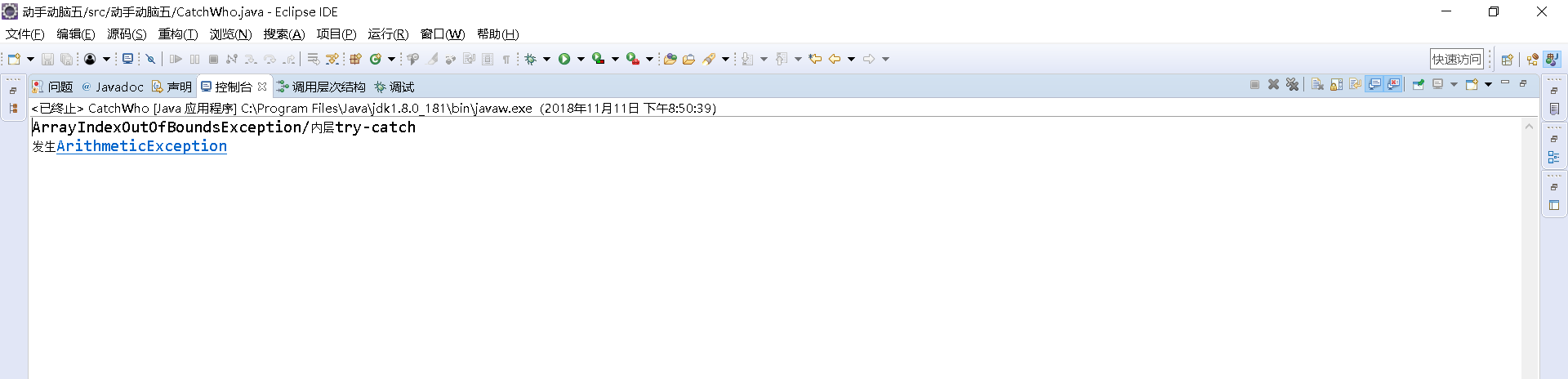
1 public class CatchWho { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 11 throw new ArithmeticException(); 12 } 13 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 14 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 15 } 16 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 17 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 18 } 19 } 20 }
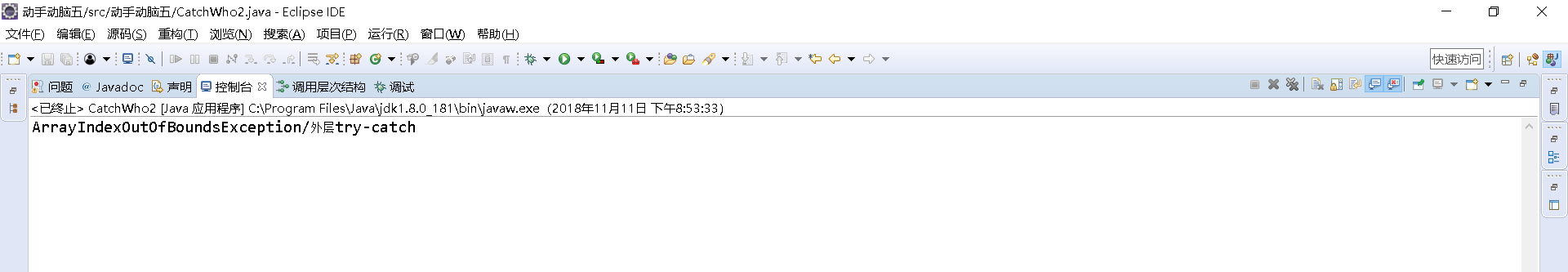
1 public class CatchWho2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 throw new ArithmeticException(); 11 } 12 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 13 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 14 } 15 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 16 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
3
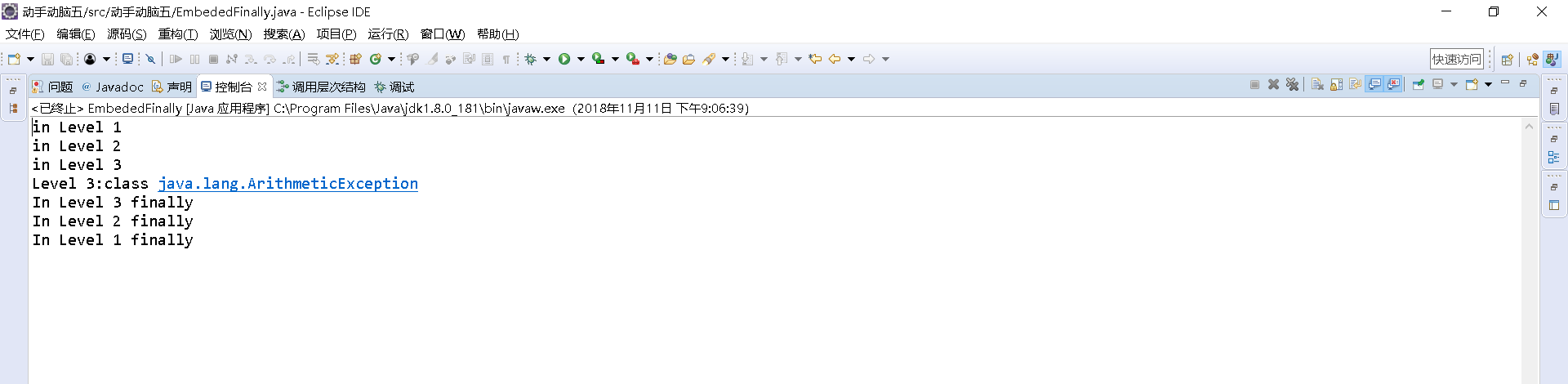
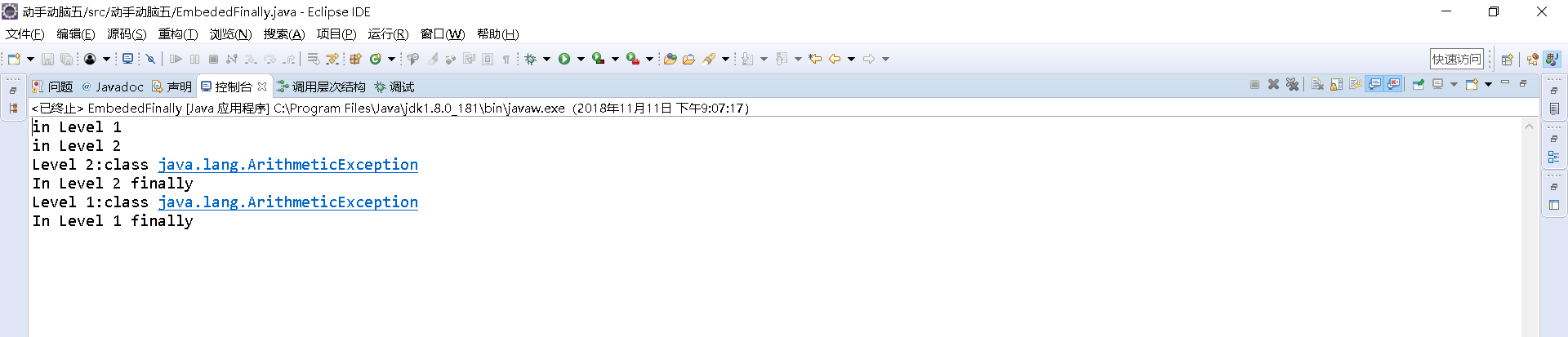
1 int result; 2 3 try { 4 5 System.out.println("in Level 1"); 6 7 8 try { 9 10 System.out.println("in Level 2"); 11 // result=100/0; //Level 2 12 13 try { 14 15 System.out.println("in Level 3"); 16 17 result=100/0; //Level 3 18 19 } 20 21 catch (Exception e) { 22 23 System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); 24 25 } 26 27 28 finally { 29 30 System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); 31 32 } 33 34 35 // result=100/0; //Level 2 36 37 38 } 39 40 catch (Exception e) { 41 42 System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); 43 44 } 45 finally { 46 47 System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); 48 49 } 50 51 // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 52 53 } 54 55 catch (Exception e) { 56 57 System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); 58 59 } 60 61 finally { 62 63 . System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); 64 65 } 66 67 } 68 69 }
1 public class SystemExitAndFinally { 2 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) 5 { 6 7 try{ 8 9 10 System.out.println("in main"); 11 12 throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); 13 14 //System.exit(0); 15 16 17 } 18 19 catch(Exception e) 20 21 { 22 23 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 24 25 System.exit(0); 26 27 } 28 29 finally 30 31 { 32 33 System.out.println("in finally"); 34 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 40 }
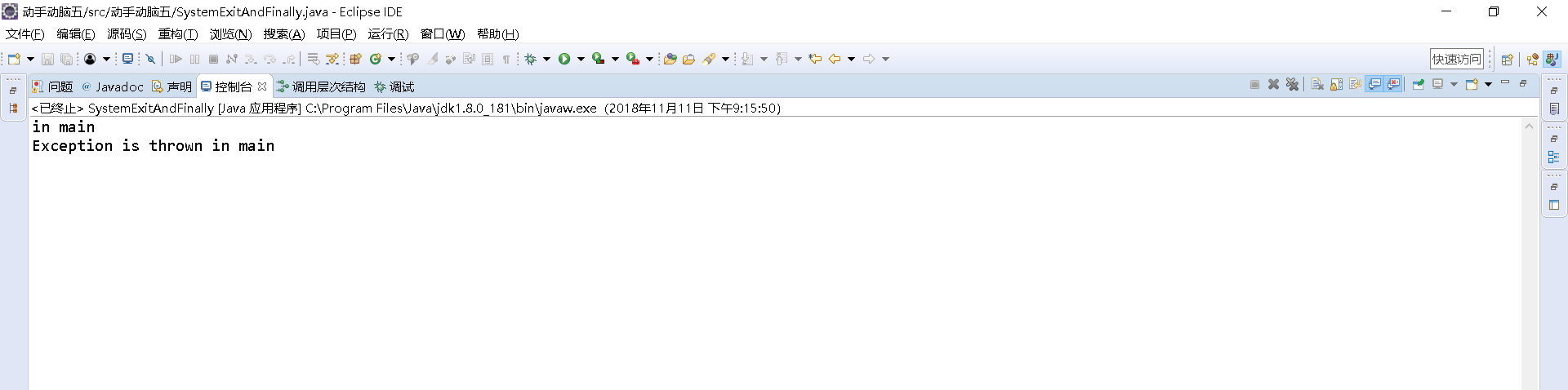
实验总结:
如果finally块中的代码过多会导致字节码条数”膨胀”,因为finally中的字节码会被”复制”到try块和所有的catch块中,出异常了。System.out.println("F")不在finally里。而只有finally里的语句才会不论如何都会执行