
如果类提供了一个自定义的构造方法,系统不再提供默认的构造方法。
2
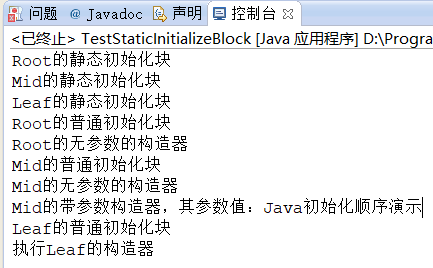
1 .public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 InitializeBlockClass obj=new InitializeBlockClass(); 4 System.out.println(obj.field); 5 6 obj=new InitializeBlockClass(300); 7 System.out.println(obj.field); 8 } 9 } 10 11 Java进行初始化的地方有两个:初始化块和构造函数,其中初始化块又分为静态初始化块和实例初始化块。 12 静态初始化块是类中由static修饰的初始化块,实例初始化块为类中没有任何关键字修饰的初始化语句。 13 如果在主函数中创建对象时没有形参时,如果在类中定义了公共的变量并给与了赋值,那么就会把值赋给主函数中的变量,再调用类中的默认构造函数, 14 如果在主函数中创建对象时有形参,则调用类中对应的构造函数。 15 3.class Root 16 17 { 18 19 static{ 20 21 System.out.println("Root的静态初始化块"); 22 23 } 24 25 { 26 27 System.out.println("Root的普通初始化块"); 28 29 } 30 31 public Root() 32 33 { 34 35 System.out.println("Root的无参数的构造器"); 36 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 class Mid extends Root 42 43 { 44 45 static{ 46 47 System.out.println("Mid的静态初始化块"); 48 49 } 50 51 { 52 53 System.out.println("Mid的普通初始化块"); 54 55 } 56 57 public Mid() 58 59 { 60 61 System.out.println("Mid的无参数的构造器"); 62 63 } 64 65 public Mid(String msg) 66 67 { 68 69 //通过this调用同一类中重载的构造器 70 71 this(); 72 73 System.out.println("Mid的带参数构造器,其参数值:" + msg); 74 75 } 76 77 } 78 class Leaf extends Mid 79 80 { 81 82 static{ 83 84 System.out.println("Leaf的静态初始化块"); 85 86 } 87 88 { 89 90 System.out.println("Leaf的普通初始化块"); 91 92 } 93 94 public Leaf() 95 96 { 97 super("Java初始化顺序演示"); 98 System.out.println("执行Leaf的构造器"); 99 } 100 } 101 102 103 104 public class TestStaticInitializeBlock 105 106 { 107 108 public static void main(String[] args) 109 110 { 111 112 new Leaf(); 113 114 } 115 116 }
静态初始化块的执行顺序:
1.静态初始化块只执行一次。
2.创建子类型的对象时,也会导致父类型的静态初始化块的执行。
4,

数值在[-128,127]之间,便返回指向IntegerCache.cache中已经存在的对象的引用;否则创建一个新的Integer对象。
5.p
ublic class InitializeBlockClass {
{field=200;} public int field=100; public InitializeBlockClass(int value) { this.field=value; } public InitializeBlockClass() { }}public class obj { public static void main(String[] args) { InitializeBlockClass obj=new InitializeBlockClass(); System.out.println(obj.field); obj=new InitializeBlockClass(300); System.out.println(obj.field); }}结果为:100 300