Rock... Paper!
After Karen have found the deterministic winning (losing?) strategy for rock-paper-scissors, her brother, Koyomi, comes up with a new game as a substitute. The game works as follows.
A positive integer n is decided first. Both Koyomi and Karen independently choose n distinct positive integers, denoted by x1, x2, ..., xnand y1, y2, ..., yn respectively. They reveal their sequences, and repeat until all of 2n integers become distinct, which is the only final state to be kept and considered.
Then they count the number of ordered pairs (i, j) (1 ≤ i, j ≤ n) such that the value xi xor yj equals to one of the 2n integers. Here xormeans the bitwise exclusive or operation on two integers, and is denoted by operators ^ and/or xor in most programming languages.
Karen claims a win if the number of such pairs is even, and Koyomi does otherwise. And you're here to help determine the winner of their latest game.
The first line of input contains a positive integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2 000) — the length of both sequences.
The second line contains n space-separated integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 2·106) — the integers finally chosen by Koyomi.
The third line contains n space-separated integers y1, y2, ..., yn (1 ≤ yi ≤ 2·106) — the integers finally chosen by Karen.
Input guarantees that the given 2n integers are pairwise distinct, that is, no pair (i, j) (1 ≤ i, j ≤ n) exists such that one of the following holds: xi = yj; i ≠ j and xi = xj; i ≠ j and yi = yj.
Output one line — the name of the winner, that is, "Koyomi" or "Karen" (without quotes). Please be aware of the capitalization.
3
1 2 3
4 5 6
Karen
5
2 4 6 8 10
9 7 5 3 1
Karen
In the first example, there are 6 pairs satisfying the constraint: (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 2) and (3, 3). Thus, Karen wins since 6 is an even number.
In the second example, there are 16 such pairs, and Karen wins again.
简单的模拟题;
AC代码:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<map> 3 using namespace std; 4 int n,num[2][2005]; 5 map<int,int> vis; 6 int main() 7 { 8 scanf("%d",&n); 9 for(int r=0;r<2;r++) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {scanf("%d",&num[r][i]);vis[num[r][i]]=1;} 10 int pair=0; 11 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 12 { 13 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 14 { 15 if(vis.count(num[0][i]^num[1][j])) pair++; 16 } 17 } 18 if(pair%2) printf("Koyomi "); 19 else printf("Karen "); 20 }
Even if the world is full of counterfeits, I still regard it as wonderful.
Pile up herbs and incense, and arise again from the flames and ashes of its predecessor — as is known to many, the phoenix does it like this.
The phoenix has a rather long lifespan, and reincarnates itself once every a! years. Here a! denotes the factorial of integer a, that is, a! = 1 × 2 × ... × a. Specifically, 0! = 1.
Koyomi doesn't care much about this, but before he gets into another mess with oddities, he is interested in the number of times the phoenix will reincarnate in a timespan of b! years, that is, 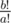 . Note that when b ≥ a this value is always integer.
. Note that when b ≥ a this value is always integer.
As the answer can be quite large, it would be enough for Koyomi just to know the last digit of the answer in decimal representation. And you're here to provide Koyomi with this knowledge.
The first and only line of input contains two space-separated integers a and b (0 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 1018).
Output one line containing a single decimal digit — the last digit of the value that interests Koyomi.
2 4
2
0 10
0
107 109
2
In the first example, the last digit of 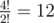 is 2;
is 2;
In the second example, the last digit of 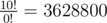 is 0;
is 0;
In the third example, the last digit of 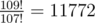 is 2.
is 2.
简单模拟题,稍微做一些特别的处理即可;
AC代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef unsigned long long LLU; 4 LLU n,m; 5 int main() 6 { 7 cin>>n>>m; 8 int ans=1; 9 for(LLU i=m;i>n;i--) 10 { 11 ans*=i%10; 12 ans%=10; 13 if(ans==0) break; 14 } 15 cout<<ans; 16 }
题解:
对于两堆岛,假设岛堆1有m个岛,岛堆2有n个岛,且满足m<=n,则不难得到两个两堆岛间建立桥的方案数:
$f(m,n)=sum_{i=0}^{m}C_{m}^{i}A_{n}^{i}=sum_{i=0}^{m}C_{m}^{i}C_{n}^{i}i!$
关于如何求组合数C(n,m):http://www.cnblogs.com/xienaoban/p/6798058.html
因为我们看到,a,b,c最大不超过5000,所以可以用迭代的方式求组合数和阶乘;
最后根据公式计算出答案即可;
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #define MAX 5003 4 #define MOD 998244353 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef long long ll; 7 ll C[MAX][MAX],fac[MAX]; 8 void calc_Cmn()//求组合数 9 { 10 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++) 11 { 12 C[i][0]=C[i][i]=1; 13 for(int j=1;j<i;j++) C[i][j]=(C[i-1][j-1]+C[i-1][j])%MOD; 14 } 15 } 16 void calc_factorial()//求阶乘 17 { 18 fac[0]=fac[1]=1; 19 for(int i=2;i<MAX;i++) fac[i]=(fac[i-1]*i)%MOD; 20 } 21 ll f(int m,int n) 22 { 23 ll ret=0; 24 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 25 { 26 ret+=(((C[m][i]*C[n][i])%MOD)*fac[i])%MOD; 27 ret=ret%MOD; 28 } 29 return ret; 30 } 31 int main() 32 { 33 calc_Cmn(); 34 calc_factorial(); 35 int x,y,z,m,n; 36 scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); 37 38 m=min(x,y), n=max(x,y); 39 ll ans1=f(m,n); 40 m=min(x,z), n=max(x,z); 41 ll ans2=f(m,n); 42 m=min(y,z), n=max(y,z); 43 ll ans3=f(m,n); 44 45 printf("%I64d ",(((ans1*ans2)%MOD)*ans3)%MOD); 46 }
PS.里面包含了求组合数和阶乘的算法模板