-
Java将配置文件当作一种资源(resource)来处理,并且提供了两个类来读取这些资源,一个是Class类,另一个是ClassLoader类。
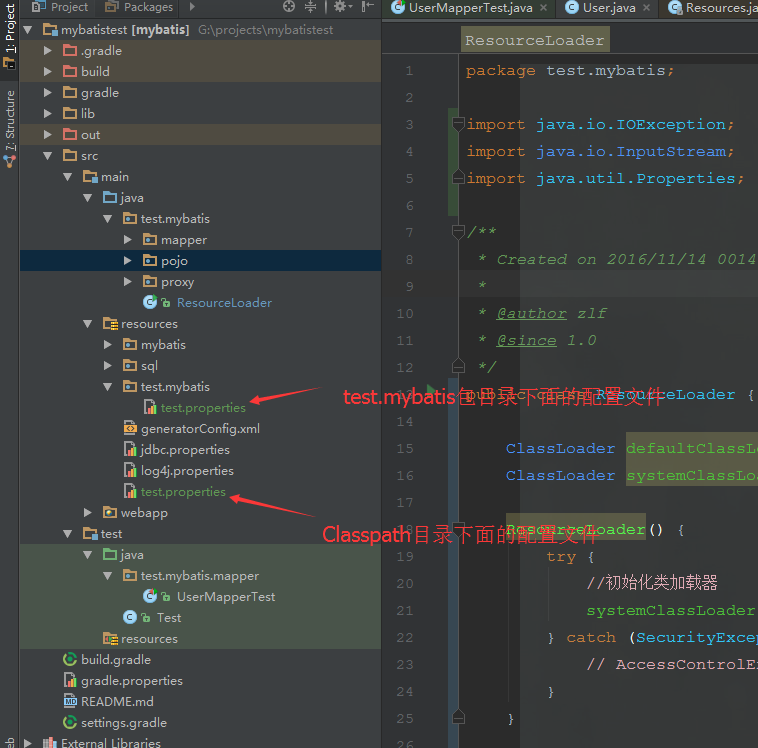
gradle 项目 项目目录结构
用Class类加载资源文件
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name)查找具有给定名称的资源。查找与给定类相关的资源的规则是通过定义类的 class loader 实现的。此方法委托此对象的类加载器。如果此对象通过引导类加载器加载,则此方法将委托给 ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(java.lang.String)。 >
在委托前,使用下面的算法从给定的资源名构造一个绝对资源名:
如果 name 以 ‘/’ 开始 (‘u002f’),则绝对资源名是 ‘/’ 后面的 name 的一部分。 否则,绝对名具有以下形式: modified_package_name/name 其中 modified_package_name 是此对象的包名,该名用 ‘/’ 取代了 ‘.’ (‘u002e’)。
用ClassLoader类加载资源文件
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name)返回读取指定资源的输入流。
完整demo
package test.mybatis; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; /** * Created on 2016/11/14 0014. * * @author zlf * @since 1.0 */ public class ResourceLoader { ClassLoader defaultClassLoader; ClassLoader systemClassLoader; ResourceLoader() { try { //初始化类加载器 systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(); } catch (SecurityException ignored) { // AccessControlException on Google App Engine } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ResourceLoader(); resourceLoader.loadProperties1();//ClassLoader resourceLoader.loadProperties2();//classLoader resourceLoader.loadProperties3();//class resourceLoader.loadProperties4();//class resourceLoader.loadProperties5();//class resourceLoader.loadProperties6();//mybatis中调用系统classLoader resourceLoader.loadProperties7();//mybatis中调用系统classLoader } public void loadProperties1() throws IOException { try ( InputStream input = ResourceLoader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test/mybatis/test.properties"); ) { printProperties(input); } } public void loadProperties2() throws IOException { try ( InputStream input = ResourceLoader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.properties"); ) { printProperties(input); } } public void loadProperties3() throws IOException { try ( InputStream input = ResourceLoader.class.getResourceAsStream("test.properties"); ) { printProperties(input); } } public void loadProperties4() throws IOException { try ( InputStream input = ResourceLoader.class.getResourceAsStream("/test.properties"); ) { printProperties(input); } } public void loadProperties5() throws IOException { try ( InputStream input = ResourceLoader.class.getResourceAsStream("/test/mybatis/test.properties"); ) { printProperties