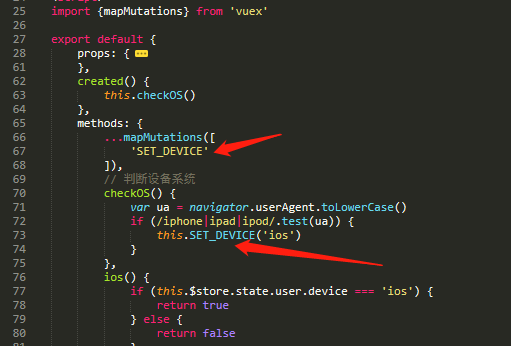
先创建store数据仓库
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' // import user from './modules/user' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ modules: { // user, }, state: {}, mutations: {}, actions: {}, getters })
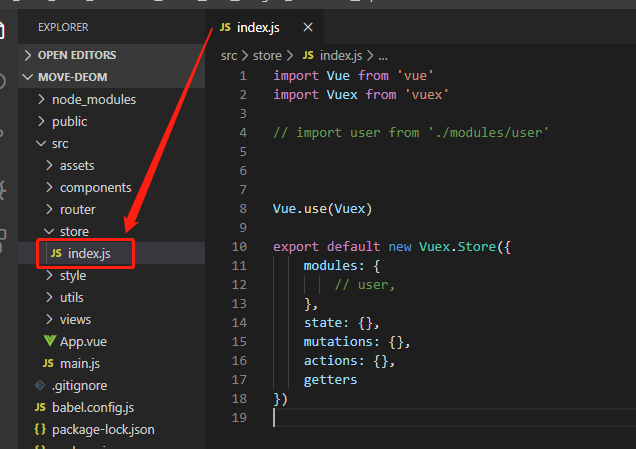
然后在main.js中引入并注册
import store from './store'
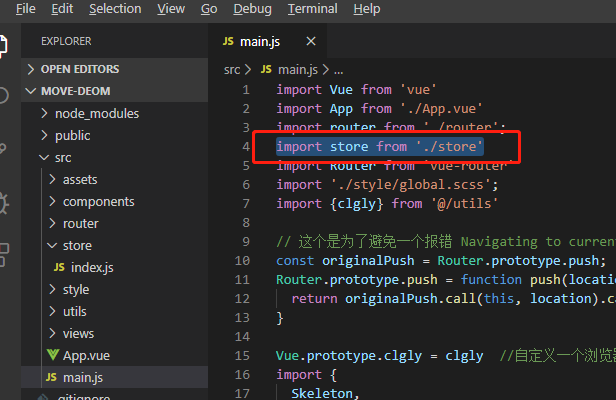
注册
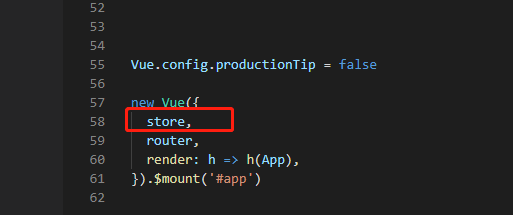
使用vuex
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
在.vue组件中定义一个对象
computed:{ ...mapState([ //mapState本是一个函数,在里面写一个数组,记得加... ‘num’ , //存的数据 ‘id’ ]) }
tore.state.num映射this.num这个this 很重要,这个映射直接映射到当前Vue的this对象上。
然后就可以不用$store.state.num引用了,直接插值
{{num}}{{id}} //引用多个

https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/state.html
let mapState = {num:0,id:111}
let computed = {...mapState}
console.log(computed )
// 在单独构建的版本中辅助函数为 Vuex.mapState import { mapState } from 'vuex' export default { // ... computed: mapState({ // 箭头函数可使代码更简练 count: state => state.count, // 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count` countAlias: 'count', // 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数 countPlusLocalState (state) { return state.count + this.localCount } }) }
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
computed: mapState([ // 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count 'count' ])
mapState 函数返回的是一个对象。我们如何将它与局部计算属性混合使用呢?通常,我们需要使用一个工具函数将多个对象合并为一个,以使我们可以将最终对象传给 computed 属性。但是自从有了对象展开运算符,我们可以极大地简化写法:
computed: { localComputed () { /* ... */ }, // 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中 ...mapState({ // ... }) }
<template>
<div class="home">
<!-- <button class="btn" @click="$store.commit('add',1)">点击加</button>
<button class="btn" @click="$store.commit('reduce',2)">点击减</button> -->
<button class="btn" @click="add(2)">点击加</button>
<button class="btn" @click="reduce(1)">点击减</button>
<div>stor里面的count:{{count}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'home',
data() {
return {}
},
created() {},
computed: {
// 方法一:--------------------------------------
// count(){
// return this.$store.state.count
// },
//方法二:mapState-------------------------------
//写法1:(mapState中用对象的形式获取)
// ...mapState({
// count:state=>state.count
// })
// 写法2:mapState中用数组的形式获取):
...mapState(["count"])
},
methods: {
//方法三:mapMutations -------------------------- 此方法只能写在 methods里面,在其他地方调用即可
...mapMutations(['add', 'reduce'])
}
}
</script>
<style scoped="scoped">
.btn {
display: block;
90%;
height: 45px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
</style>
其它例子
mapState使用:
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
computed:{
...mapState({
// car:'car',//最简单的写法
car:state=>state.car//也可以这样写
})
},
//如果要监听car的数据改变,可以结合watch来使用。methods方法中也可以通过this.car访问到。
mapMutations使用:
import {mapMutations} from "vuex";
methods: {
...mapMutations(["addToCar"]),//映射成this.addToCar
cz() {
this.addToCar("change");
}
},
其他使用方式了
<template>
<div id="example">
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
{{count}}
{{dataCount}}
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<div>{{sex}}</div>
<div>{{from}}</div>
<div>{{myCmpted}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
data () {
return {
str: '国籍',
dataCount: this.$store.state.count
}
},
computed: mapState({
count: 'count', // 第一种写法
sex: (state) => state.sex, // 第二种写法
from: function (state) { // 用普通函数this指向vue实例,要注意
return this.str + ':' + state.from
},
// 注意下面的写法看起来和上面相同,事实上箭头函数的this指针并没有指向vue实例,因此不要滥用箭头函数
// from: (state) => this.str + ':' + state.from
myCmpted: function () {
// 这里不需要state,测试一下computed的原有用法
return '测试' + this.str
}
}),
methods: {
increment () {
this.$store.commit('increment')
},
decrement () {
this.$store.commit('decrement')
}
},
created () {
// 写个定时器,发现computed依旧保持了只要内部有相关属性发生改变不管是当前实例data中的改变,还是vuex中的值改变都会触发dom和值更新
setTimeout(() => {
this.str = '国家'
}, 1000)
}
}
</script>
https://blog.csdn.net/dkr380205984/article/details/82185740
实例
index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import user from './modules/user' // import getters from './getters' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ modules: { user, }, state: {}, mutations: {}, actions: {}, // getters //其他数据这里可以自定义 })

user.js
import Vue from 'vue' // import {getUserInfo, getLogin} from "../../api/login"; import session from '../sessionStorage' // import local from '../localStorage' // import {getToken,removeToken} from "../../utils/auth"; const user = { state: { // token: getToken(), device: 'android', wxUserInfo: session.$getSessionStorageByName('wxUserInfo') || '', aliUserInfo: session.$getSessionStorageByName('aliUserInfo') || '', info: session.$getSessionStorageByName('userInfo') || {} }, mutations: { SET_DEVICE: (state, device) => { state.device = device }, // SET_TOKEN: (state, token) => { // state.token = token // }, }, actions: { // 登录 // Login({commit}, userInfo) { // userInfo.username = userInfo.username.trim() // return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // getLogin(userInfo).then(res => { // if (res.status === 1) { // session.$setSessionStorageByName('userId', res.data.id) // } // resolve(res) // }).catch(error => { // reject(error) // }) // }) // }, } } export default user
使用sotre中的函数