851. 喧闹和富有
描述:

思路:深度优先(带记忆)。 这个题有点秒。。
853. 车队
描述:

思路:
我们首先对这些车辆按照它们的起始位置降序排序,并且用 (target - position) / speed 计算出每辆车在不受其余车的影响时,行驶到终点需要的时间。对于相邻的两辆车 S 和 F,F 的起始位置大于 S,如果 S 行驶到终点需要的时间小于等于 F,那么 S 一定会在终点前追上 F 并形成车队。这是因为在追上 F 之前,S 的行驶速度并不会减小,而 F 却有可能因为追上前面的车辆而速度减小,因此 S 总能在终点前追上 F。
854. 相似度为 K 的字符串
描述:

思路:

class Solution { public: int res , n ; void dfs(int pos , int step , string& A , string &B) { if (step >= res) return ; if (pos == n) { res = min(res , step) ; return ; } if (A[pos] == B[pos]) { dfs(pos + 1 , step , A , B) ; } else { for (int i = pos + 1 ; i < n ; ++i) { if (A[i] == B[pos] && A[i] != B[i]) { swap(A[i] , A[pos]) ; dfs(pos + 1 , step + 1 , A , B) ; swap(A[i] , A[pos]) ; } } } } int kSimilarity(string A, string B) { n = A.length() ; res = n + 1 ; dfs(0 , 0 , A , B) ; return res ; } };
856. 括号的分数
描述:
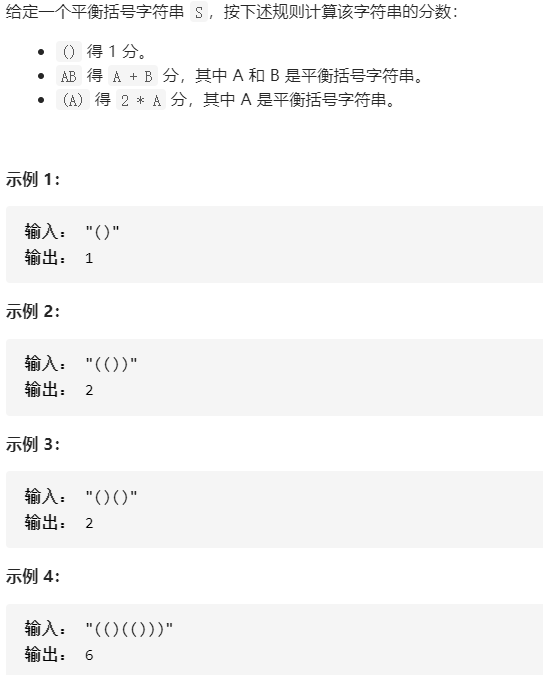
思路:栈
861. 翻转矩阵后的得分
描述:

思路:
先横竖变换保证第一列全部是1
竖变换保证其他列1比0多
862. 和至少为 K 的最短子数组
描述:

思路:前缀和。然后进行双指针判断。
863. 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点
描述:
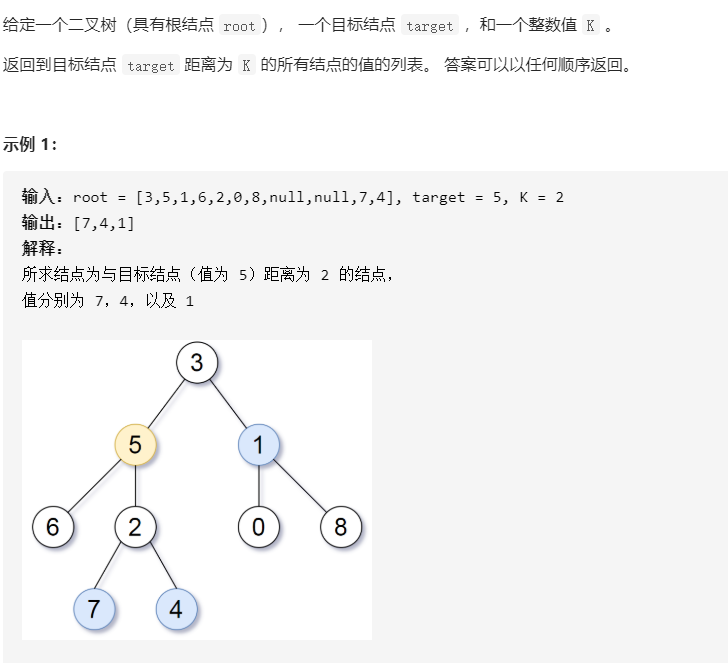
思路:对于tartget进行深度优先,。
866. 回文素数
描述:

思路:

class Solution { public int primePalindrome(int N) { while (true) { if (N == reverse(N) && isPrime(N)) return N; N++; if (10_000_000 < N && N < 100_000_000) N = 100_000_000; } } public boolean isPrime(int N) { if (N < 2) return false; int R = (int) Math.sqrt(N); for (int d = 2; d <= R; ++d) if (N % d == 0) return false; return true; } public int reverse(int N) { int ans = 0; while (N > 0) { ans = 10 * ans + (N % 10); N /= 10; } return ans; } }
869. 重新排序得到 2 的幂
描述:

思路:排列组合问题。 。。。回溯算法。

class Solution { public boolean reorderedPowerOf2(int N) { // Build eg. N = 128 -> A = [1, 2, 8] String S = Integer.toString(N); int[] A = new int[S.length()]; for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); ++i) A[i] = S.charAt(i) - '0'; return permutations(A, 0); } // Return true if A represents a valid power of 2 public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int[] A) { if (A[0] == 0) return false; // no leading zero // Build eg. A = [1, 2, 8] -> N = 128 int N = 0; for (int x: A) N = 10 * N + x; // Remove the largest power of 2 while (N > 0 && ((N & 1) == 0)) N >>= 1; // Check that there are no other factors besides 2 return N == 1; } /** * Returns true if some permutation of (A[start], A[start+1], ...) * can result in A representing a power of 2. */ public boolean permutations(int[] A, int start) { if (start == A.length) return isPowerOfTwo(A); // Choose some index i from [start, A.length - 1] // to be placed into position A[start]. for (int i = start; i < A.length; ++i) { // Place A[start] with value A[i]. swap(A, start, i); // For each such placement of A[start], if a permutation // of (A[start+1], A[start+2], ...) can result in A // representing a power of 2, return true. if (permutations(A, start + 1)) return true; // Restore the array to the state it was in before // A[start] was placed with value A[i]. swap(A, start, i); } return false; } public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) { int t = A[i]; A[i] = A[j]; A[j] = t; } }
870. 优势洗牌
描述:

思路:贪心。田忌赛马

class Solution { public int[] advantageCount(int[] a, int[] b) { int n = b.length; Arrays.sort(a); int[][] pair = new int[n][2]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) pair[i] = new int[]{b[i], i};//把下标保存下来 Arrays.sort(pair, (x, y)->x[0] - y[0]); int[] res = new int[n]; for (int i = 0, r = n - 1, l = 0; i < n; i ++)//r最大值,l标明最小值; { if (a[i] <= pair[l][0]) res[pair[r --][1]] = a[i];//要放到原数组对应的位置上 else res[pair[l ++][1]] = a[i];////要放到原数组对应的位置上 } return res; } }
871. 最低加油次数
描述:


思路:
class Solution { public int minRefuelStops(int target, int startFuel, int[][] stations) { if(stations.length == 0) return startFuel>=target?0:-1; PriorityQueue<Integer>queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((o1,o2)->{ return o2-o1; }); int sum = startFuel; int ans = 0; for(int i = 0;i < stations.length;i++) { while(sum < stations[i][0]) { Integer ii = queue.poll(); if(ii == null)return -1; sum += ii; ans++; } queue.offer(stations[i][1]); } while(sum < target) { Integer ii = queue.poll(); if(ii == null)return -1; sum += ii; ans++; } return ans; } }
873. 最长的斐波那契子序列的长度
描述;

思路:dp[i][j]:表示以A[i],A[j]结尾的斐波那契数列的最大长度


for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { int diff = A[j] - A[i]; if (intMap.count(diff)) { int index = intMap[diff]; if (index < i) { dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[index][i] + 1); } } MAX = max(MAX, dp[i][j]); } }
875. 爱吃香蕉的珂珂
描述:

思路:二分。
877. 石子游戏
描述:

思路:动态规划。
880. 索引处的解码字符串
描述:

思路:栈。
881. 救生艇
描述:

思路:贪心。

class Solution { public int numRescueBoats(int[] people, int limit) { Arrays.sort(people); int i = 0, j = people.length - 1; int ans = 0; while (i <= j) { ans++; if (people[i] + people[j] <= limit) i++; j--; } return ans; } }
886. 可能的二分法
描述;

思路:深度优先,标记颜色。。类似于二部图的方法,。
887. 鸡蛋掉落
描述:

思路:

def superEggDrop(K: int, N: int): memo = dict() def dp(K, N) -> int: # base case if K == 1: return N if N == 0: return 0 # 避免重复计算 if (K, N) in memo: return memo[(K, N)] res = float('INF') # 穷举所有可能的选择 for i in range(1, N + 1): res = min(res, max( dp(K, N - i), dp(K - 1, i - 1) ) + 1 ) # 记入备忘录 memo[(K, N)] = res return res return dp(K, N)
890. 查找和替换模式
描述:

思路:

class Solution { public List<String> findAndReplacePattern(String[] words, String pattern) { List<String> ans = new ArrayList(); for (String word: words) if (match(word, pattern)) ans.add(word); return ans; } public boolean match(String word, String pattern) { Map<Character, Character> m1 = new HashMap(); Map<Character, Character> m2 = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); ++i) { char w = word.charAt(i); char p = pattern.charAt(i); if (!m1.containsKey(w)) m1.put(w, p); if (!m2.containsKey(p)) m2.put(p, w); if (m1.get(w) != p || m2.get(p) != w) return false; } return true; } }
894. 所有可能的满二叉树
描述:
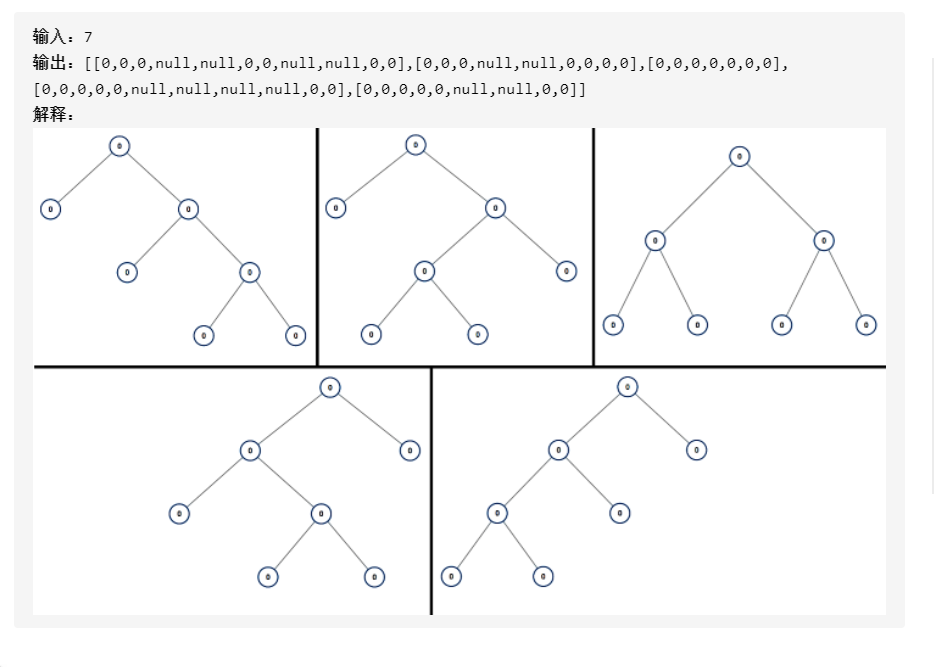
思路:
Java 首先偶数是不能构成满二叉树的。 思路是把总node数分别左边,根,右边进行递归,如7个node可以分成1,1,5;3,1,5;5,1,1(左,根,右)。 5个node又可以分为1,1,3和3,1,1。 3个node又可以分为1,1,1。 1个node直接返回。

class Solution { private HashMap<Integer, List<TreeNode>> hm = null; public List<TreeNode> allPossibleFBT(int N) { List<TreeNode> rtn = new ArrayList<>(); if(N % 2 == 0) return rtn; if(N == 1) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0); rtn.add(root); return rtn; } if(hm == null) hm = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 1; i < N; i += 2) { List<TreeNode> left = hm.getOrDefault(i, null); if(left == null) { left = allPossibleFBT(i); hm.put(i, left); } List<TreeNode> right = hm.getOrDefault(N - 1 - i, null); if(right == null) { right = allPossibleFBT(N - 1 - i); hm.put(N - 1 - i, right); } for(TreeNode l : left) { for(TreeNode r : right) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0); root.left = l; root.right = r; rtn.add(root); } } } return rtn; } }
