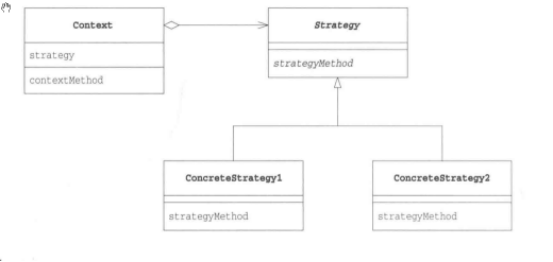
Strategy
无论什么程序,其目的都是解决问题。而为了解决问题,我们又需要编写特定的算法。使用Strategy模式可以整体地替换算法的实现部分。能够整体地替换算法,能让我们轻松地以不同的算法去解决同一个问题,这种模式就是Strategy模式。(整体替换算法)
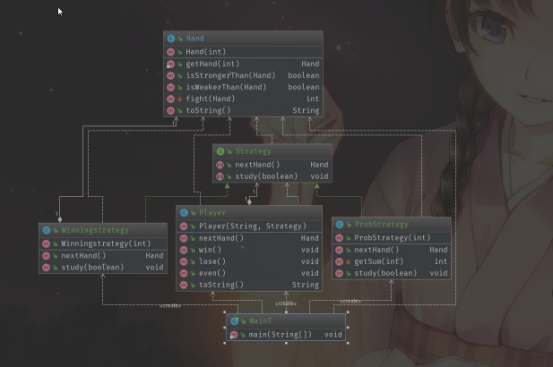
理清职责
-
|名字|说明
|Hand表示猜拳游戏中的“手势”的类
|strategy|表示猜拳游戏中的策略的类
|Winningstrategy |表示“如果这局猜拳获胜,那么下一局也出一样的手势”这一策略的类表示“根据上一局的手势从概率上计算出下一局的手势从之前的猜拳结果计算下一局|
|Probstrategy出各种拳的概率”这一策略的类
|Player表示进行猜拳游戏的选手的类
|Main测试程序行为的类 -
具体说明
- 比如C++ 的STL 的Sort 以及在Java中Arrays.sort()都是可以使用策略模式来根据情况构造解决办法的
- 如果使用Strategy模式,在程序运行中也可以切换ConcreteStrategy角色。例如,在内存容量少的运行环境中可以使用slowButLessMemoryStrategy(速度慢但省内存的策略),而在内存容量多的运行环境中则可以使用FastButMoreMemorystrategy(速度快但耗内存的策略)。
UML
Code
- Hand:
public class Hand {
// 石头
private static final int HANDVALUE_GUU=0;
// 剪刀
private static final int HANDVALUE_GHO=1;
// 布
private static final int HANDVALUE_PAA=2;
private static final Hand[] HANDS=new Hand[]{
new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_GHO),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA),
};
public static final String name[]={
"石头","剪刀","布"
};
private int handvalue;
public Hand(int handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handvalue){
return HANDS[handvalue];
}
// 胜利
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand hand){
return fight(hand)==1;
}
// 战败
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand hand){
return fight(hand)==-1;
}
/**
* 计分: 平 0 胜1 负 -1
* @param hand
* @return
*/
private int fight(Hand hand) {
if(this==hand){
return 0;
}else if((this.handvalue+1)% 3 ==hand.handvalue){
return 1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name[this.handvalue];
}
}
- Player
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losrcount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) {
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand(){
return strategy.nextHand();
}
/**
* 分别是 胜利 负 平局
*/
public void win(){
strategy.study(true);
gamecount++;
wincount++;
}
public void lose(){
strategy.study(false);
losrcount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even(){
gamecount++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Player{" +
"wincount=" + wincount +
", losrcount=" + losrcount +
", gamecount=" + gamecount +
'}';
}
}
- ProbStrategy
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
this.random=new Random(seed);
}
private int pevHandValue=0;
private int currentHandValue=0;
private int [] [] history=new int[][]{
{1,1,1},
{1,1,1},
{1,1,1}
};
/**
* 如果该随机数在0至3(不含3)之间,那么出石头
* 如果该随机数在3至8(不含8)之间,那么出剪刀
* 如果该随机数在8至15(不含15)之间,那么出布
* @return
*/
@Override
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet=random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handValue=0;
if(bet<history[currentHandValue][0]){
handValue=0;
}else if(bet<(history[currentHandValue][0]+history[currentHandValue][1])){
handValue=1;
}else {
handValue=2;
}
pevHandValue=currentHandValue;
currentHandValue=handValue;
return Hand.getHand(handValue);
}
private int getSum(int currentHandValue) {
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum+=history[currentHandValue][i];
}
return sum;
}
@Override
public void study(boolean win) {
if(win){
history[pevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;
}else{
history[pevHandValue][(currentHandValue+1)%3]++;
history[pevHandValue][(currentHandValue+2)%3]++;
}
}
}
- Strategy
public interface Strategy {
/**
* nextHand方法的作用是“获取下一局要出的手势”。调用该方法后,
* 实现了strategy接口的类会绞尽脑汁想出下一局出什么手势。
* @return
*/
Hand nextHand();
/**
*study方法的作用是学习“上一局的手势是否获胜了”。
* 如果在上一局中调用nextHand方法获胜了,就接着调用study(true);
* 如果输了,就接着调用study(false)。这样,Strategy接口的实现类就会改变自己的内部状态,
* 从而为下一次nextHand被调用时究竟是返回“石头”“剪刀”还是“布”提供判断依据。
* @param win
*/
void study(boolean win);
}
- Winningstrategy
public class Winningstrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
// 存储上一局状态
private boolean won=false;
private Hand preHand;
/**
* 有预见性的随机数种子
* @param seed
*/
public Winningstrategy(int seed) {
this.random =new Random(seed);
}
@Override
public Hand nextHand() {
if (!won) {
preHand= Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return preHand;
}
@Override
public void study(boolean win) {
won=win;
}
}
- 测试
public class MainT {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Player tom = new Player("tom", new Winningstrategy(2));
Player cat = new Player("cat", new ProbStrategy(3));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Hand hand = tom.nextHand();
Hand hand1 = cat.nextHand();
if(hand.isStrongerThan(hand1)){
System.out.println("tom is win");
tom.win();
cat.lose();
}else if(hand1.isStrongerThan(hand)){
System.out.println("cat is win");
cat.win();
tom.lose();
}else{
System.out.println("Even----");
cat.even();
tom.even();
}
}
System.out.println(tom);
System.out.println(cat);
}
}