什么是 URI URL URN?
URI 全称统一资源标识符, 现在有两个方案, 就是 URL 和 URN.
URL 统一资源定位符, 通常由 scheme, domain, port, location, parameter, 甚至 query, frag构成

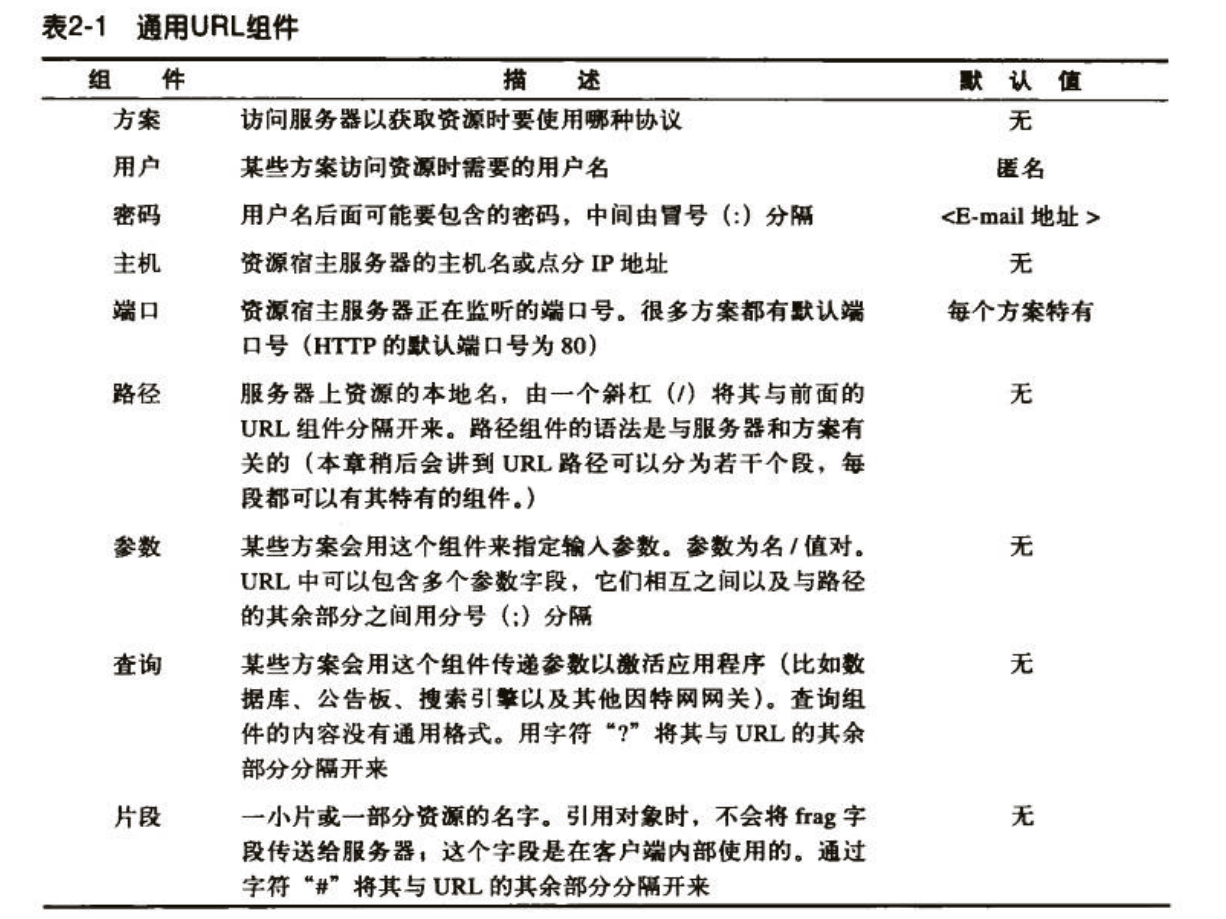
在 JSP 中, request 是一个 HttpServletRequest 实例, 提供了以下几个相关方法
getRequestURI() : String
getRequestURL() : String
getParameter(String key) : String value // 对于 GET 请求, 解析查询字符串(query_string); 对于 POST 请求, 则是 post 的数据
JSP 和 Nginx 一样, 把 URI 定义为以根路径 "/" 开始的资源路径, 即 Location, 因为对于服务器而言, 协议和域名并没有什么卵用, 并且有其它的获取途径.
同时, JSP 废除了 parameter, 把 query 当做 parameter, 在我看来这确实是过度设计.
flag 主要影响浏览器的显示位置, 服务器不必太过关心.
因此, 以 ";" 和 "#" 为标识的 parameter 和 flag 可以忽略, 我们只关心 URI 和 query.
编写一个 mod.jsp, JSP 代码如下:
<%
System.out.println("URL: " + request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println("URI: " + request.getRequestURI());
System.out.println("参数: " + request.getParameter("param1"));
System.out.println("查询: " + request.getParameter("query1"));
System.out.println("查询字符串: " + request.getQueryString());
%>
访问 http://abc.com/store/mod.jsp;param1=1;param2=2?query1=3&query2=4#id, 结果如下:
URL: http://abc.com/Shop/mod.jsp;param1=1;param2=2
URI: /Shop/mod.jsp;param1=1;param2=2
参数: null
查询: 3
查询字符串: query1=3&query2=4
我们遍历 parameter
Enumeration<String> params = request.getParameterNames();
while (params.hasMoreElements()) {
String param = params.nextElement();
System.out.println(param + " -> " + request.getParameter(param));
}
结果
query1 -> 3
query2 -> 4
所以不要在 JSP 中使用参数, 而使用查询.
! 关于 URL 编码的问题
现代浏览器默认使用 UTF-8 编码, 然而 RUL 规定只能使用 ASCII 编码, 所有非ASCII 字符都需要经过 URLEncoder 编码才行.
如"你好"可以编码为"%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD", 这显然是 UTF-8 编码, UTF-8 编码是无字节序大小端影响的, 便于网络传输.
然而, 如果上游服务器不知道这个编码的话, 就无法正确 Decode, 因此需要在 tomcat 中设置 URIEncoding 为"UTF-8".
JDK 中 java.net.URLEncoder 和 java.net.URLDecoder 类实现了 URL 编码和解码, 并且可选择编码.
JavaScript 中也有对应的函数:
encodeURI()
decodeURI()
encodeURIComponent()
decodeURIComponent()
"; / ? : @ & = + $ , #",这些在encodeURI()中不被编码的符号,在encodeURIComponent()中统统会被编码。这适合于将网址作为参数时使用.
如何编写 JSP 页面
需要清楚 JSP 页面其实是 Java 代码的一种简略形式, 因此可以保持 Java 的编程方式:
<body class="center">
<%
String id = request.getParameter("id");
if (id == null || "".equals(id)) { // 使用 Cookie 判断用户
%>
<H1>欢迎您, 游客</H1>
<a href='register'>注册</a>
<a href='login'>登录</a>
<%
} else {
%>
<H1>欢迎您, ${ param.uid }</H1>
<%
}
%>
可恶的是, 这些<%%>标记都会留下一行空行, 可以在 html 最后一行加入
</html>
<%@ page trimDirectiveWhitespaces="true"%>
HttpURLConnection
package net;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImageFilter;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpURL {
static {
System.setProperty("http.agent", "Chrome");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL u = new URL("http://deve.cf/100MB.test");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) u.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.connect();
System.out.println(conn.getContentType() + ": " + conn.getContentLength());
File f = new File("G:\Code\a.zip");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(conn.getInputStream());
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
byte[] bs = new byte[102400];
int count = 0;
while (true) {
int n = bis.read(bs);
if (n == 0 || n == -1) {
System.out.println("n = " + n);
break;
}
fos.write(bs, 0, n);
count += n;
}
System.out.println("count = " + count);
fos.close();
bis.close();
conn.disconnect();
}
}