使用python接口来运行caffe程序,主要的原因是python非常容易可视化。所以不推荐大家在命令行下面运行python程序。如果非要在命令行下面运行,还不如直接用 c++算了。
推荐使用jupyter notebook,spyder等工具来运行python代码,这样才和它的可视化完美结合起来。
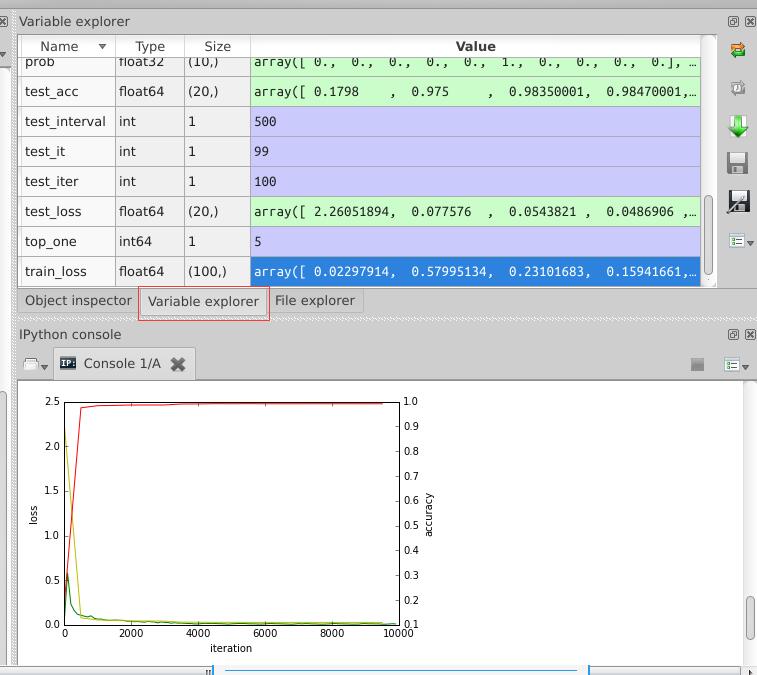
因为我是用anaconda来安装一系列python第三方库的,所以我使用的是spyder,与matlab界面类似的一款编辑器,在运行过程中,可以查看各变量的值,便于理解,如下图:
只要安装了anaconda,运行方式也非常方便,直接在终端输入spyder命令就可以了。
在caffe的训练过程中,我们如果想知道某个阶段的loss值和accuracy值,并用图表画出来,用python接口就对了。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Jul 19 16:22:22 2016 @author: root """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import caffe caffe.set_device(0) caffe.set_mode_gpu() # 使用SGDSolver,即随机梯度下降算法 solver = caffe.SGDSolver('/home/xxx/mnist/solver.prototxt') # 等价于solver文件中的max_iter,即最大解算次数 niter = 9380 # 每隔100次收集一次数据 display= 100 # 每次测试进行100次解算,10000/100 test_iter = 100 # 每500次训练进行一次测试(100次解算),60000/64 test_interval =938 #初始化 train_loss = zeros(ceil(niter * 1.0 / display)) test_loss = zeros(ceil(niter * 1.0 / test_interval)) test_acc = zeros(ceil(niter * 1.0 / test_interval)) # iteration 0,不计入 solver.step(1) # 辅助变量 _train_loss = 0; _test_loss = 0; _accuracy = 0 # 进行解算 for it in range(niter): # 进行一次解算 solver.step(1) # 每迭代一次,训练batch_size张图片 _train_loss += solver.net.blobs['SoftmaxWithLoss1'].data if it % display == 0: # 计算平均train loss train_loss[it // display] = _train_loss / display _train_loss = 0 if it % test_interval == 0: for test_it in range(test_iter): # 进行一次测试 solver.test_nets[0].forward() # 计算test loss _test_loss += solver.test_nets[0].blobs['SoftmaxWithLoss1'].data # 计算test accuracy _accuracy += solver.test_nets[0].blobs['Accuracy1'].data # 计算平均test loss test_loss[it / test_interval] = _test_loss / test_iter # 计算平均test accuracy test_acc[it / test_interval] = _accuracy / test_iter _test_loss = 0 _accuracy = 0 # 绘制train loss、test loss和accuracy曲线 print ' plot the train loss and test accuracy ' _, ax1 = plt.subplots() ax2 = ax1.twinx() # train loss -> 绿色 ax1.plot(display * arange(len(train_loss)), train_loss, 'g') # test loss -> 黄色 ax1.plot(test_interval * arange(len(test_loss)), test_loss, 'y') # test accuracy -> 红色 ax2.plot(test_interval * arange(len(test_acc)), test_acc, 'r') ax1.set_xlabel('iteration') ax1.set_ylabel('loss') ax2.set_ylabel('accuracy') plt.show()
最后生成的图表在上图中已经显示出来了。