一、数据回写
数据回写:在做数据更新的时候服务端查询的数据自动填充到表单中。
1.1默认方式
通过前面讲解的 Map Mode ModelMap绑定数据
@RequestMapping("/doLogin")
public String doLogin(String username, String password, Model model) {
if ("zhangsan".equals(username) && "123".equals(password)) {
return "index";
}
model.addAttribute("username", username);
model.addAttribute("password", password);
return "forward:/login";
}
页面中回写
<form action="/doLogin" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" value="${username}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password" value="${password}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="登录"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
2.通过Model方式
如果使用对象去接收客户端传来的数据,那么对象默认会被自动放到model中,在前端页面可以直接使用对象中的数据。
表单代码如下:
/**
*
* 请求地址:
* http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC-06-backvalue/
* add1?username=a13&password=11111
*/
@RequestMapping("/add1")
public String add1(Book book) {
System.out.println(book);
return "/user.jsp";
}
页面中
<form action="add1" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"
value="${book.username }"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>用户密码</td>
<td><input type="text" name="password"
value="${book.password }"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="注册"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
效果

3.@ModelAttribute注解实现
3.1 修改参数回显变量名
在需要回传的对象前添加@ModelAttribute("bb")注解,在界面中就可以通过bb前缀来获取回写信息。



3.2 配置全局变量名
给接口中的每个方法统一返回一份数据
@Controller
public class UserController {
/**
*
* 请求地址: http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC-06-backvalue/
* add1?username=a13&password=11111
*/
@RequestMapping("/add1")
public String add1(@ModelAttribute("bb") Book book) {
System.out.println(book);
return "/user.jsp";
}
/**
* 该类中的其他方法处理请求后都会绑定返回List集合,
* 在页面中可以通过"as"作为key获取
* @return
*/
@ModelAttribute("as")
public List<String> getAllAddress() {
List<String> as = new ArrayList<>();
as.add("深圳");
as.add("广州");
as.add("海口");
return as;
}
}
页面中获取
<body>
获取全局配置返回的信息:<span style="color:red">${as}</span>
<form action="add1" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"
value="${bb.username }"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>用户密码</td>
<td><input type="text" name="password"
value="${bb.password }"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="注册"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
测试效果:

二、异常处理
项目中的异常需要统一处理,正常情况下,需要提前准备好一个错误页面,当项目出错了,将该页面展示给用户。
步骤:
2.1创建自定义异常类(可选)
/**
* 自定义异常
*
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
public class CustomException extends Exception {
private String message;
public CustomException(String message) {
super(message);
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
2.2定义异常处理器
/**
* 自定义异常处理器
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
@Component //注意该类需要交给Spring容器管理
public class MyExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest req
, HttpServletResponse resp, Object obj,
Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.setViewName("/error.jsp");
return mv;
}
}
2.3需要异常处理的地方抛出异常

2.4测试


 搞定
搞定
三、JSON数据交互
3.1响应JSON数据
1. 添加依赖:
对于Gson和jackson这两个json处理依赖,直接添加即可。 除此之外,其他的json解析器如fastjson都需要手动配置HttpMessageConverter.
实际上,在SpringMVC中,是由一个名叫HttpMessageConverter的类来提供对象到JSON字符串的转换的。而SpringMVC默认就提供了Gson和Jackson的HttpMessageConverter,分别是org.springframework.http.converter.json.GsonHttpMessageConverter和MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter。对于其他的JSON解析器,只需要开发者手动配置一下HttpMessageConverter即可。
本案例使用 jackson处理
Jackson的maven坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</dependency>

2.在返回对象上添加@ResponseBody注解即可
/**
* JSON
*
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
@Controller
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public User getUser() {
User user = new User();
List<String> favorites = new ArrayList<>();
favorites.add("足球");
favorites.add("篮球");
user.setFavorites(favorites);
user.setUsername("zhagnsan");
user.setPassword("123");
return user;
}
@GetMapping("/users")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> getALlUser() {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User e = new User();
e.setUsername("zhangsan:" + i);
e.setPassword("pwd:" + i);
users.add(e);
}
return users;
}
@GetMapping("/map")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> user() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("total", 100);
map.put("rows", "aaa");
return map;
}
}
3.测试
JSON对象
 JSON数组嵌套
JSON数组嵌套

Map返回JSON数据
 额外说明:
额外说明:
默认情况下,JSON处理的HttpMessageConverter在org.springframework.http.converter.support.AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter类中,如果当前项目的classpath下有jackson或者gson的依赖,则会被该类自动加载,然后,创建相应的HttpMessageConverter。
对于fastjson,由于系统未提供自动支持,因此需要开发者手动配置fastjson的HttpMessageConverter,配置方式如下:
1.引入fastjson依赖
2.加入配置:
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="validatorFactoryBean">
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean
class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
HttpMessageConverter承担两个事:
1.将请求结果转为json
2.将浏览器发送来的json转为对象
3.2 接收JSON数据
注意:json只能是在请求体中,因此,json只能放在post或者put请求中,注意,请勿使用get/delete请求去测试json参数传递。
示例代码如下:
/**
* JSON
*
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
@Controller
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/test2")
@ResponseBody
public void test2(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
通过jquery的ajax发送json数据测试
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="提交JSON数据" onclick="fun1();">
<script type="text/javascript">
function fun1(){
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
url: "test2",
contentType: "application/json",//如果想以json格式把数据提交到后台的话,这个必须有,否则只会当做表单提交
data: JSON.stringify({"username":"sam","password":"12"}),//JSON.stringify()必须有,否则只会当做表单的格式提交
dataType: "json",//期待返回的数据类型
success: function(data){
alert("success:"+data);
},
error:function(data){
alert("error"+data);
}
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
 服务端获取到了ajax提交的json数据
服务端获取到了ajax提交的json数据
 在springmvc中,直接接收json参数,如果参数中有日期的话,不需要定义日期类型转换器,日期的转换由gson/jackson/fastjson来提供。
在springmvc中,直接接收json参数,如果参数中有日期的话,不需要定义日期类型转换器,日期的转换由gson/jackson/fastjson来提供。
四、Restful风格
RESTful是一种软件设计规范,是客户端和服务端进行数据交互的一个规范。
早期使用JSP页面开发网页时,数据交互基本都是通过表单提交,然后通过内置对象传递。当HTML5兴起,移动互联网兴起,网站后端服务,不仅要考虑PC端的网页,也要考虑移动端数据的展示、小程序、HTML5页面等。如果需要多个终端(Android、iOS、小程序、Pad、HTML5页面)共用一个后端,一般来说主流方案就是使用JSON进行传递。RESTful则规范了请求的URL,注意RESTful只是一个规范,不是一个技术。
在RESTful中:
1.一个URL操作一个资源
2.请求的URL中不能有动词
3.使用HTTP的请求方式来描述请求行为,例如:
GET(查) http://localhost:8080/book/1 查询id为1的书
POST(增) http://localhost:8080/book/1 添加一本书,书的id为1
DELETE(删) http://localhost:8080/book/1 删除id为1的书
PUT(改) http://localhost:8080/book/1 修改id为1的书
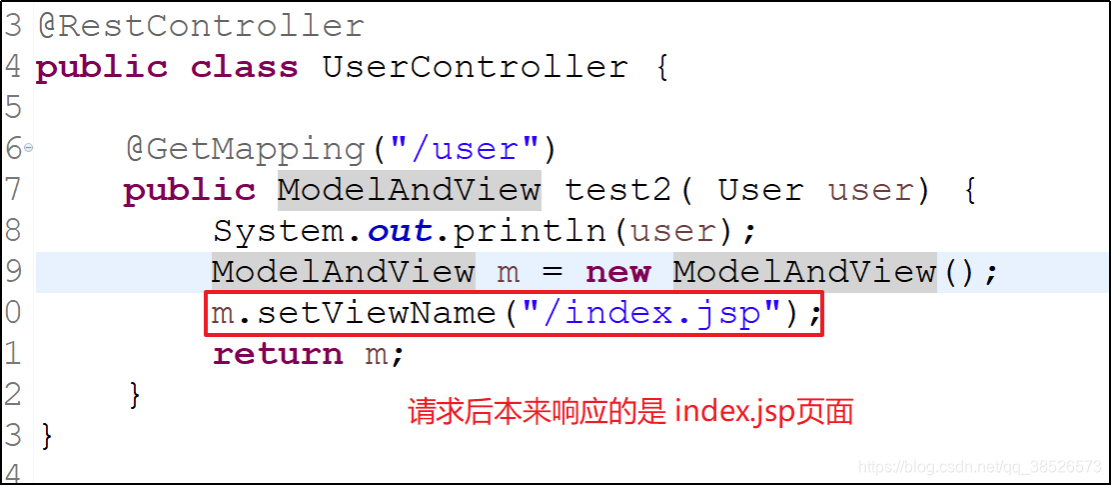
在RESTful接口中,所有的方法都是返回JSON,没有返回页面的(ModelAndView),因此,所有的方法上都需要添加@ResponseBody注解。一个替代的简化方案,是使用 @RestController 代替@Controller。@RestController实际上是一个组合注解,是@Controller和@ResponseBody的组合:
 案例代码
案例代码
/**
* RestFul
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
@RestControllerpublic
class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
/** * 查询所有、分页查询、条件查询 * 一般都是直接使用资源的复数形式来做路径 * * @return */
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getAllUser(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "4") Integer count) {
return userService.getAllUser(page, count);
}
/**
* * 按照id查询 例如 http://localhost:8080/user/1 表示查询id为1的用户 * * @param id
* * @return
*/
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
/** * 使用POST请求来完成添加功能 * * @param user * @return */
@PostMapping("/user")
public RespBean addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
int result = userService.addUser(user);
if (result == 1) {
return RespBean.ok("添加成功!");
}
return RespBean.error("添加失败!");
}
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public RespBean deleteUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
int result = userService.deleteUserById(id);
if (result == 1) {
return RespBean.ok("删除成功!");
}
return RespBean.error("删除失败!");
}
@PutMapping("/user")
public RespBean updateUserById(@RequestBody User user) {
int result = userService.updateUserById(user);
if (result == 1) {
return RespBean.ok("修改成功!");
}
return RespBean.error("修改失败!");
}
}
五、拦截器
1.简介
SpringMVC中的拦截器对应了Web基础中的过滤器。
拦截器和过滤器的区别:
1.一般来说,如果使用了SpringMVC框架,然后有拦截器的需求,建议使用拦截器而不是过滤器
2.过滤器依赖于Servlet容器,而拦截器是SpringMVC自带的,不依赖容器
3.拦截器的功能更为强大,因为拦截器是一中AOP风格的过滤器(实际上这个功能过滤器也能实现,只是没有拦截器这么简单明了)
2.使用
2.1定义拦截器
/**
* 自定义拦截器
* @author dpb【波波烤鸭】
*
*/
public class FirstIntercepter implements HandlerInterceptor{
/**
* 进入Handler之前调用的方法
* 处理:
* 用于身份确认和授权
* 比如确认当前请求是否登陆,如果登陆就方法,否则拦截跳回登陆界面
* @return
* true 放过
* false 拦截
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("preHandle 执行了...");
return true;
}
/**
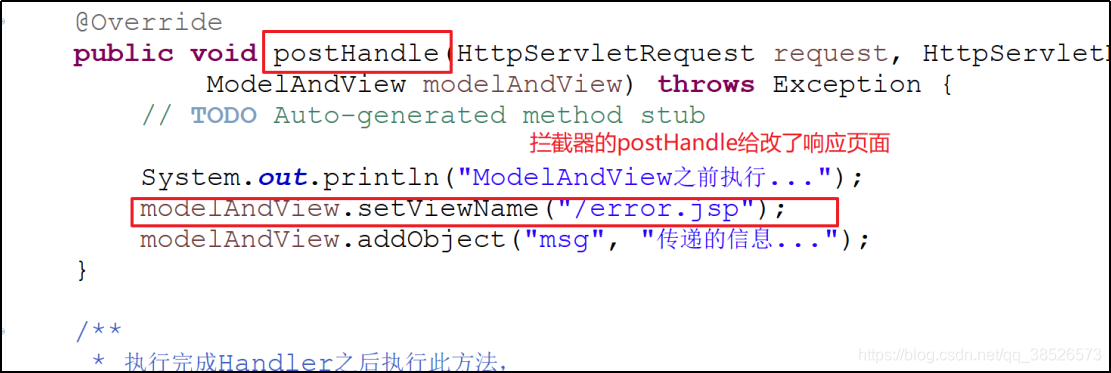
* 进入Handler之后,返回ModelAndView对象之前执行
* 可以修改调整的视图
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("ModelAndView之前执行...");
modelAndView.setViewName("/error.jsp");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", "传递的信息...");
}
/**
* 执行完成Handler之后执行此方法,
* 应用场景:
* 统一异常处理,统一日志处理,资源释放
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行完Handler到返回客户端之前执行...");
}
}
2.2配置拦截条件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dpb.*"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 拦截器的配置 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!-- ** 表示当前目录及其子目录路径 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.dpb.interceptor.FirstIntercepter"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
</beans>
2.3测试
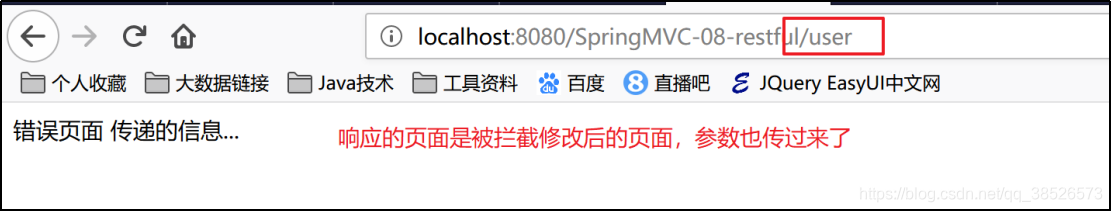
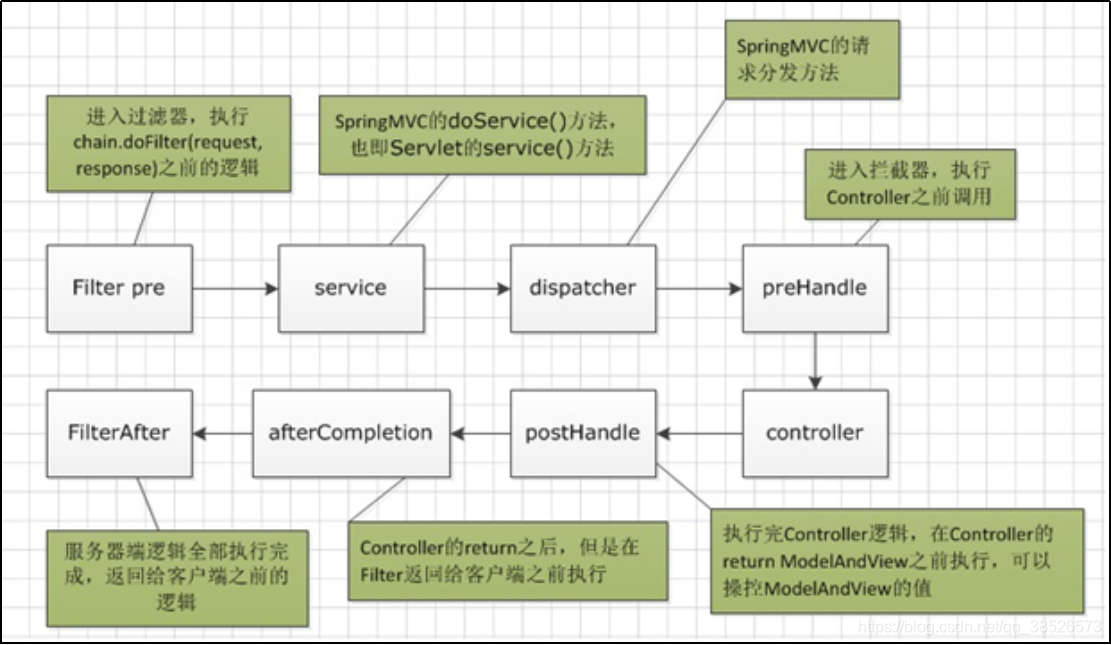
3.拦截器工作原理
上一篇:SpringMVC教程3
下一篇:整合Spring和SpringMVC