AOP介绍
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),即面向切面编程,可以说是OOP(Object Oriented Programming,面向对象编程)的补充和完善。
面向切面是面向对象中的一种方式而已。在代码执行过程中,动态嵌入其他代码,叫做面向切面编程。常见的使用场景:
i :日志
ii: 事务
iii:数据库操作
....
面向切面编程的几个核心概念
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| IOC/DI | 本质是就是Java反射+XML解析 |
| AOP | 本质上Java动态代理 |
| 切点 | 要添加代码的地方称作切点 |
| 切面 | 切点+通知 |
| 通知(增强) | 向切点插入的代码称为通知Advice |
| 连接点 | 切点的定义 |
概念先看看,不理解的话根据步骤实现效果后再回来再看下
AOP的实现方式
AOP介绍
面向切面编程,就是将交叉业务逻辑封装成切面,利用AOP的功能将切面织入到主业务逻辑中。所谓交叉业务逻辑是指,通用的、与主业务逻辑无关的代码,如安全检查、事务、日志等。若不使用AOP,则会出现代码纠缠,即交叉业务逻辑与主业务逻辑混合在一起。这样,会使主业务逻辑变的混杂不清
AOP术语介绍
| 术语 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 切面 | 切面泛指交叉业务逻辑。比如事务处理、日志处理就可以理解为切面。常用的切面有通知与顾问。实际就是对主业务逻辑的一种增强 |
| 织入 | 织入是指将切面代码插入到目标对象的过程。 |
| 连接点 | 连接点指切面可以织入的位置。 |
| 切入点 | 切入点指切面具体织入的位置。 |
| 通知(Advice) | 通知是切面的一种实现,可以完成简单织入功能(织入功能就是在这里完成的)。通知定义了增强代码切入到目标代码的时间点,是目标方法执行之前执行,还是之后执行等。通知类型不同,切入时间不同。 |
| 顾问(Advisor) | 顾问是切面的另一种实现,能够将通知以更为复杂的方式织入到目标对象中,是将通知包装为更复杂切面的装配器。 不仅指定了切入时间点,还可以指定具体的切入点 |
AOP的实现方式
| 通知类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 前置通知(MethodBeforeAdvice) | 目标方法执行之前调用 |
| 后置通知(AfterReturningAdvice) | 目标方法执行完成之后调用 |
| 环绕通知(MethodInterceptor) | 目标方法执行前后都会调用方法,且能增强结果 |
| 异常处理通知(ThrowsAdvice) | 目标方法出现异常调用 |
基于Schema-based方式实现
需要添加的jar包
前置通知
- 创建目标接口和实现类
/**
* 定义公共接口
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public interface SomeService {
String doSome();
String say();
}
/**
* 实现类
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService{
@Override
public String doSome() {
System.out.println("doSome ...");
return "hello";
}
@Override
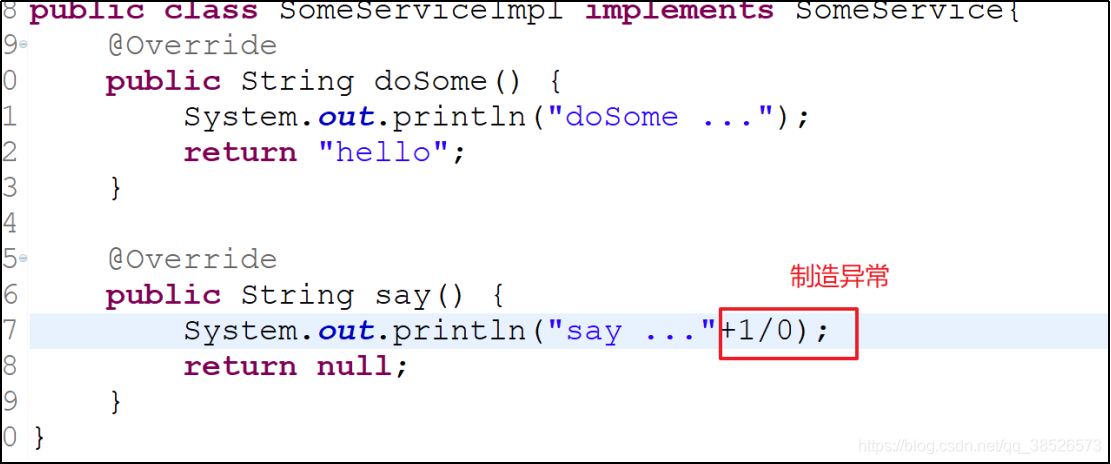
public String say() {
System.out.println("say ...");
return null;
}
}
- 创建切面类
/**
* 切面 前置通知
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* method 目标方法
* args 目标方法参数列表
* target 目标对象
*/
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("前置通知的before方法执行...");
}
}
- 配置文件中配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 注册目标类 -->
<bean id="someServiceImpl" class="com.dpb.service.SomeServiceImpl" ></bean>
<!-- 注册前置通知 -->
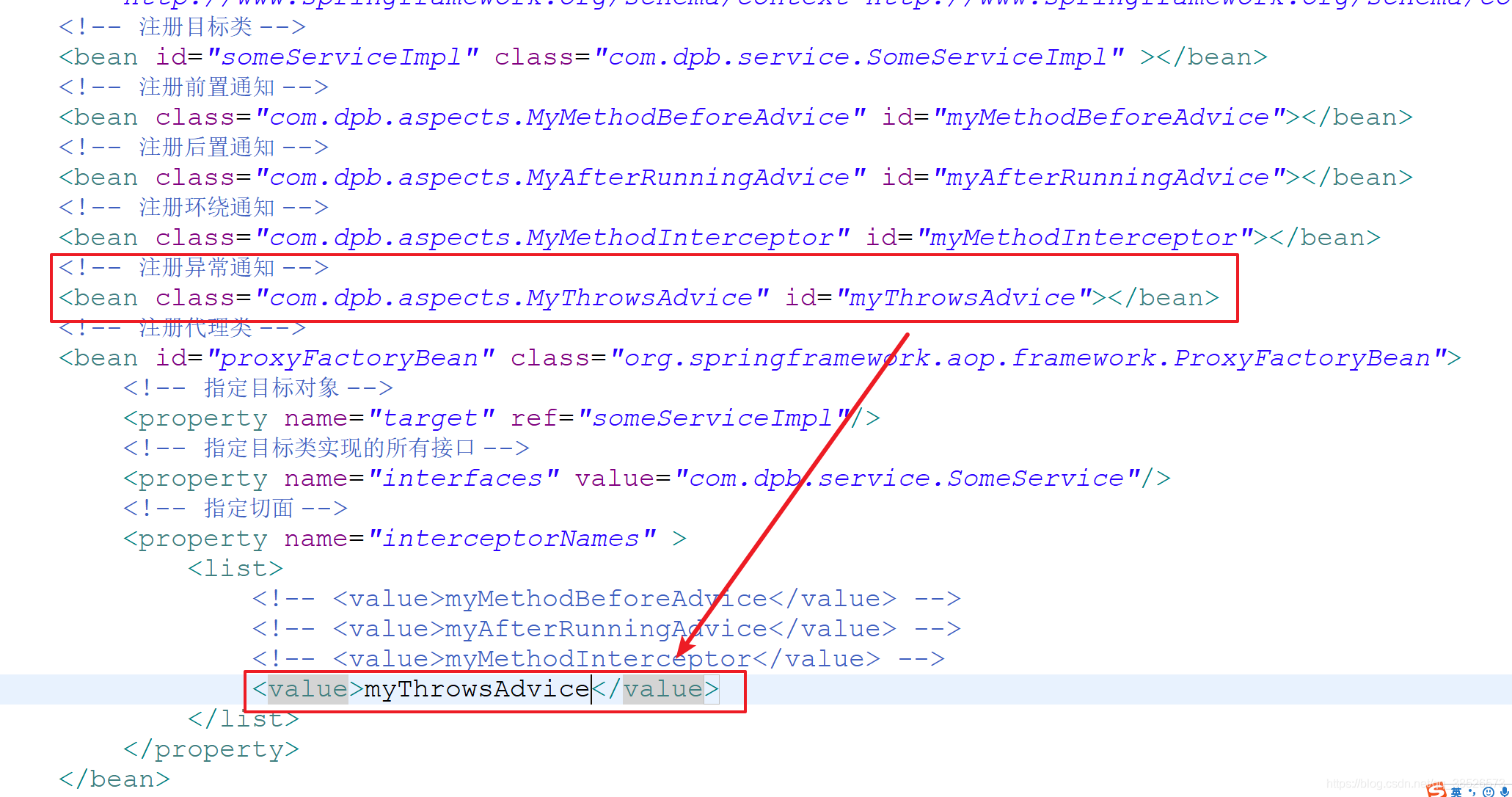
<bean class="com.dpb.aspects.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" id="myMethodBeforeAdvice"></bean>
<!-- 注册代理类 -->
<bean id="proxyFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 指定目标对象 -->
<property name="target" ref="someServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 指定目标类实现的所有接口 -->
<property name="interfaces" value="com.dpb.service.SomeService"/>
<!-- 指定切面 -->
<property name="interceptorNames" >
<list>
<value>myMethodBeforeAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
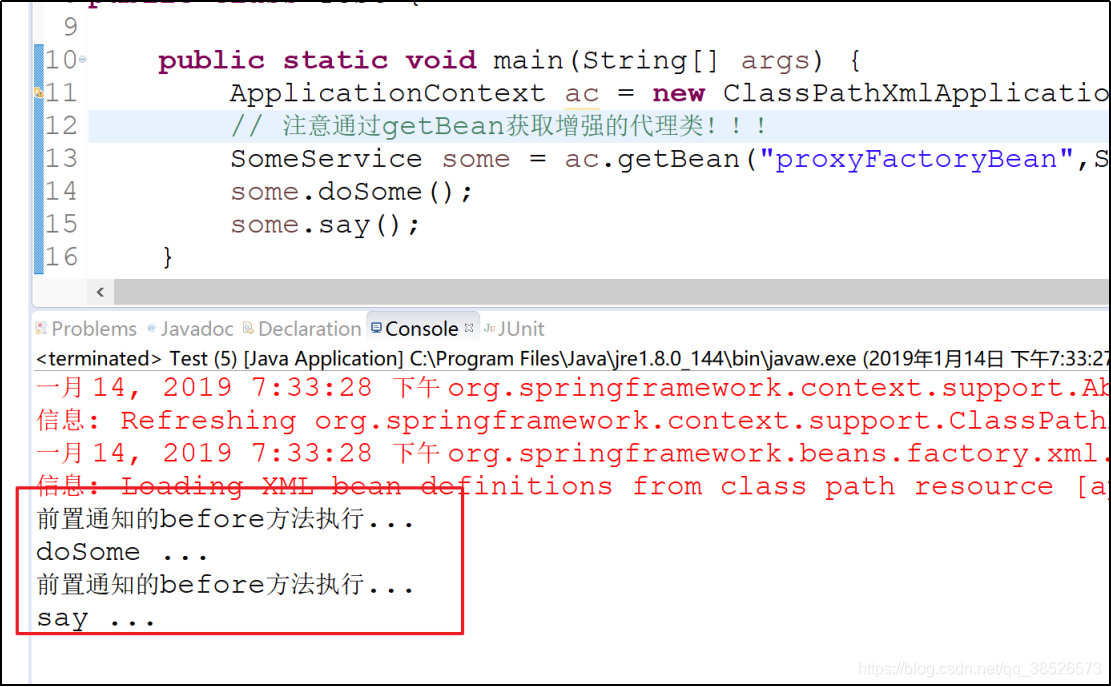
- 测试
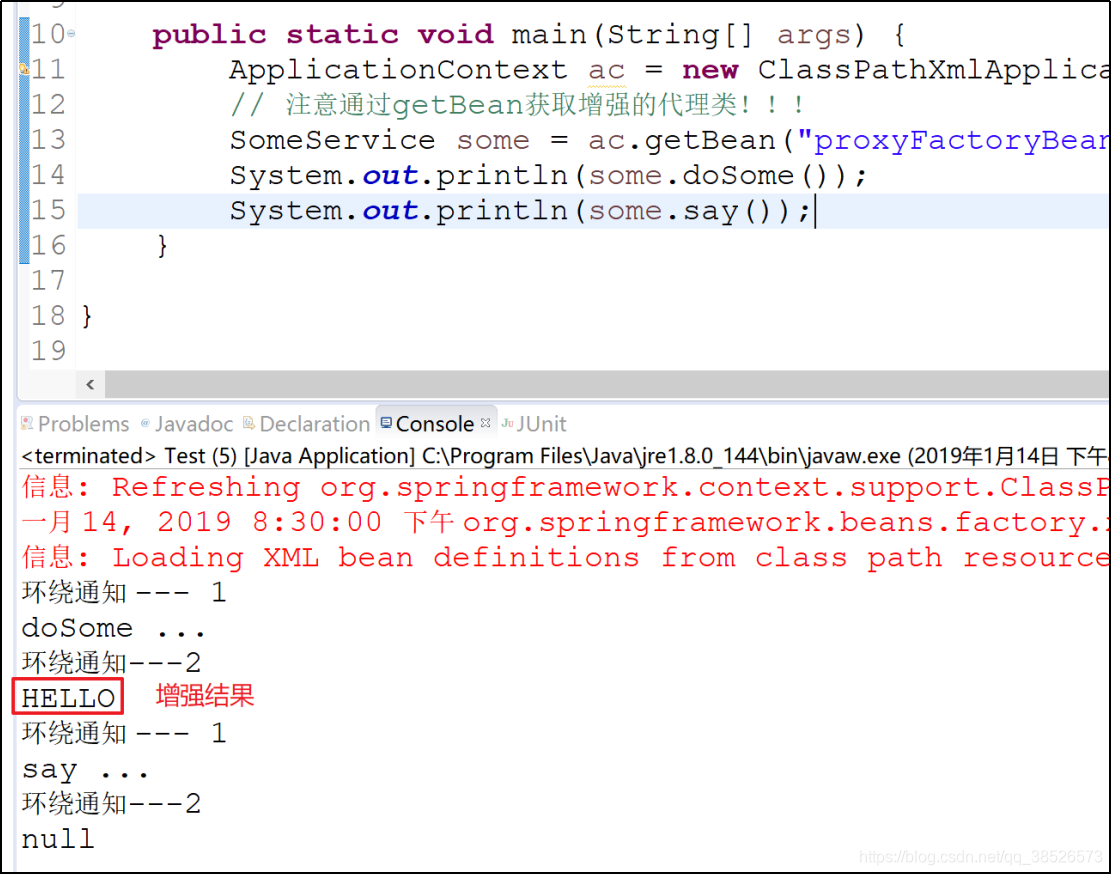
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
// 注意通过getBean获取增强的代理类!!!
SomeService some = ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean",SomeService.class);
some.doSome();
some.say();
}
}
后置通知
- 接口和之前的一样
- 创建后置通知切面类
/**
* 后置通知切面类
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public class MyAfterRunningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice{
/**
* @param returnValue 目标方法返回值
* @param method 目标方法
* @param args 目标方法参数
* @param target 目标对象
*/
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("后置方法执行了..."+returnValue);
}
}
- 配置文件修改
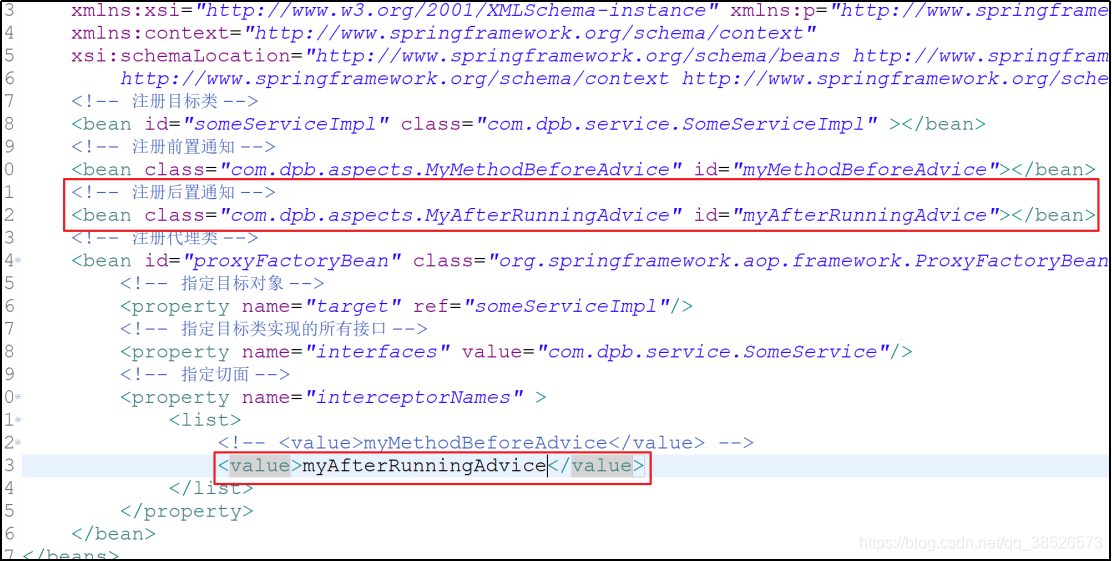
- 测试

环绕通知
- 创建环绕通知切面类
/**
* 环绕通知 切面类
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
/**
* @param invocation 方法调用器
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知 --- 1");
Object res = invocation.proceed();
if(res !=null){
// 增强返回结果
res = ((String)res).toUpperCase();
}
System.out.println("环绕通知---2");
return res;
}
}
- 配置文件注册

- 测试
异常通知
- 创建异常通知切面类
/**
* 异常通知切面类
*
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
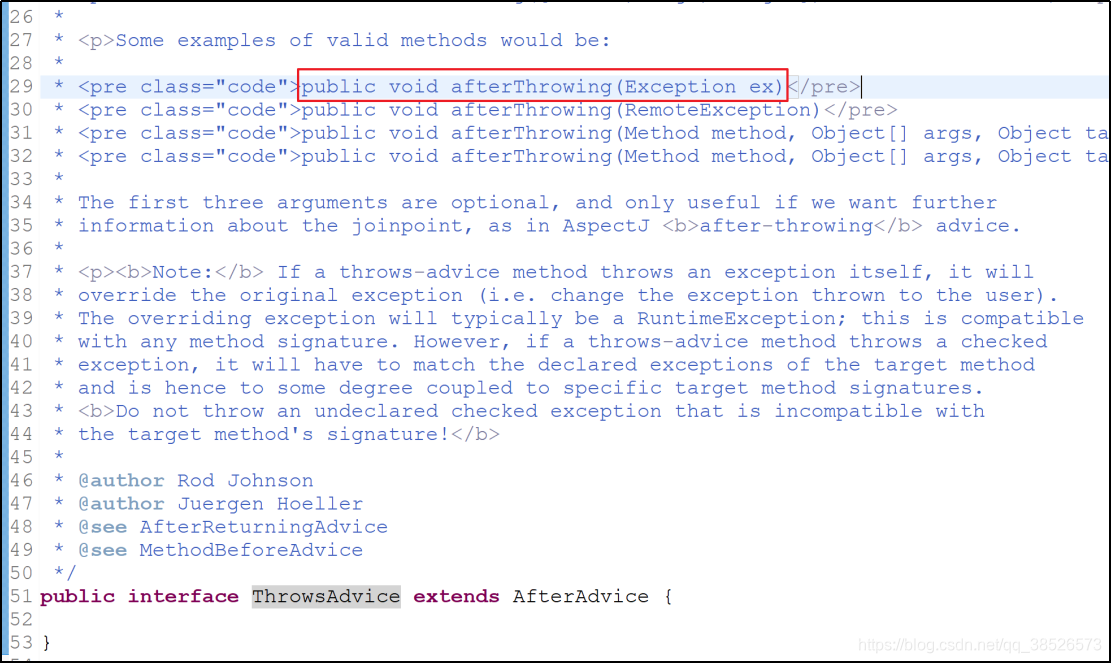
public class MyThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
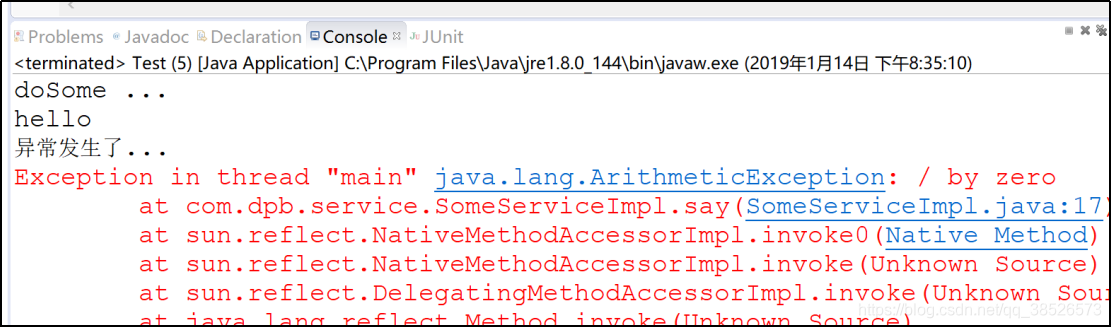
public void afterThrowing(Exception ex){
System.out.println("异常发生了...");
}
}
ThrowsAdvice接口没有定义方法,是个标志接口,在注释中有提示
2. 配置文件配置
3. 测试
基于aspectJ方式实现
对于AOP这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。然而,AspectJ也实现了AOP的功能,且其实现方式更为简捷,使用更为方便,而且还支持注解式开发。所以,Spring又将AspectJ的对于AOP的实现也引入到了自己的框架中。在Spring中使用AOP开发时,一般使用AspectJ的实现方式
aspectJ中的通知类型
| 通知类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 前置通知 | 目标方法执行之前调用 |
| 后置通知 | 目标方法执行完成之后调用 |
| 环绕通知 | 目标方法执行前后都会调用方法,且能增强结果 |
| 异常处理通知 | 目标方法出现异常调用 |
| 最终通知 | 无论程序执行是否正常,该通知都会执行。类似于try..catch中finally代码块 |
AspectJ的切入点表达式
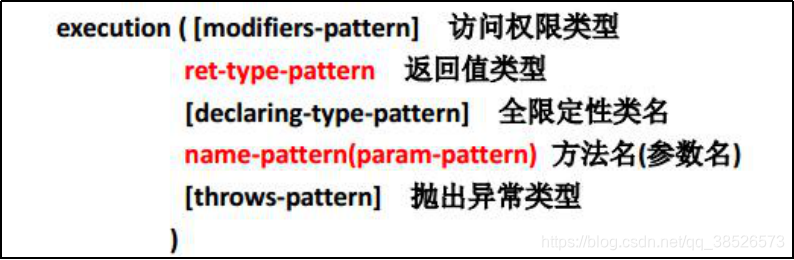
切入点表达式要匹配的对象就是目标方法的方法名。所以,execution表达式中明显就是方法的签名。注意,表达式中加[ ]的部分表示可省略部分,各部分间用空格分开。在其中可以使用以下符号
| 符号 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| * | 0至多个字符 |
| .. | 方法参数中表示任意多个参数,用在包名后表示当前包及其子包路径 |
| + | 用在类名后表示当前类及子类,用在接口后表示接口及实现类 |
举例
举例:
execution(public * (..))
指定切入点为:任意公共方法。
execution( set (..))
指定切入点为:任何一个以“set”开始的方法。
execution( com.xyz.service..(..))
指定切入点为:定义在service包里的任意类的任意方法。
execution(* com.xyz.service...(..))
指定切入点为:定义在service包或者子包里的任意类的任意方法。“..”出现在类名中时,
后面必须跟“”,表示包、子包下的所有类。
execution( .service..(..))
指定只有一级包下的serivce子包下所有类(接口)中的所有方法为切入点
execution( ..service..*(..))
指定所有包下的serivce子包下所有类(接口)中的所有方法为切入点
AspectJ对于AOP的实现有两种方式:
引入jar包
注解方式
前置通知
1.创建接口和实现类
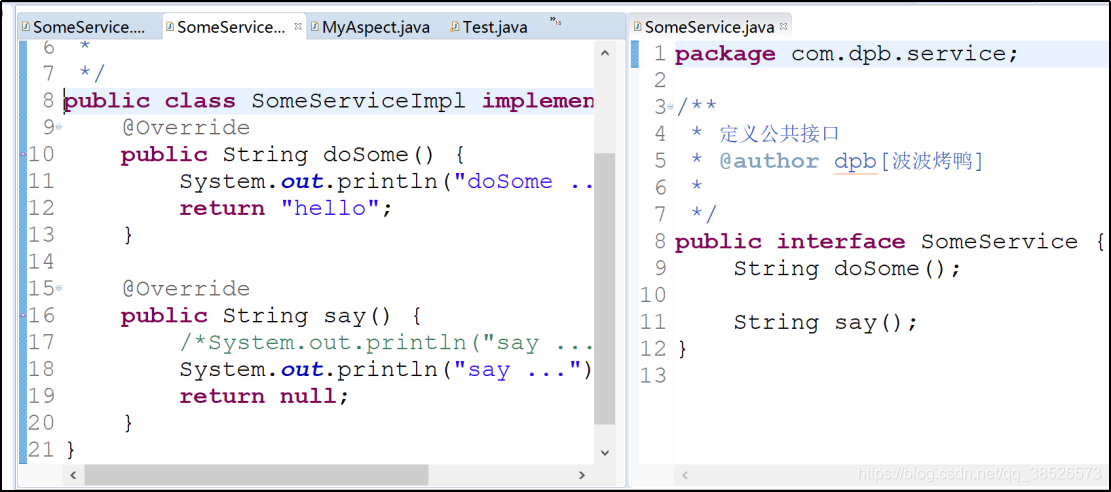
2.创建切面类
@Aspect // 表示是一个切面类
public class MyAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..))")
public void beforeMethod(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
}
3.配置文件中配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 注册目标类 -->
<bean id="someServiceImpl" class="com.dpb.service.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!-- 注册切面类 -->
<bean class="com.dpb.aspect.MyAspect" id="myAspect"/>
<!-- 注册自动代理 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
4.测试
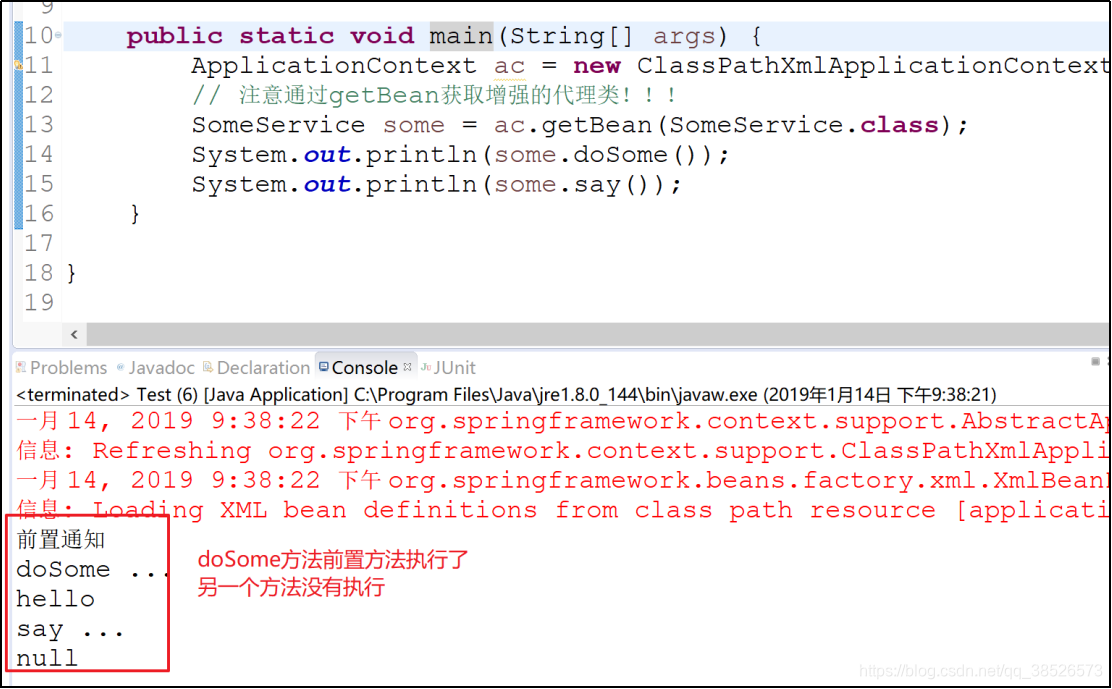
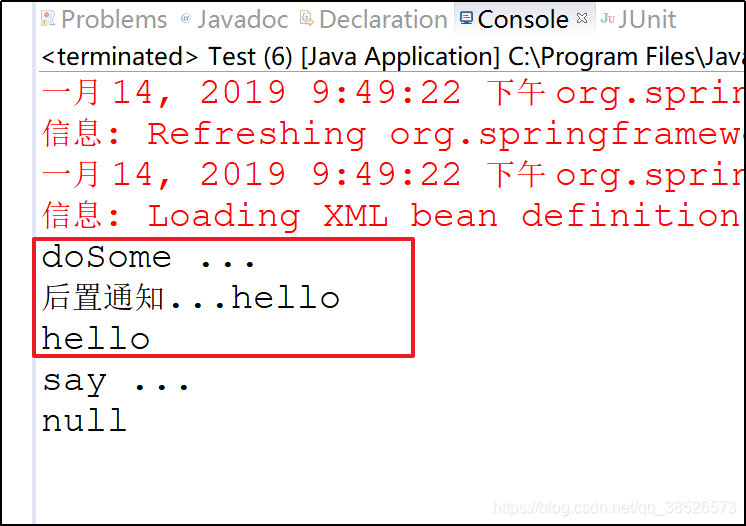
后置通知
1.切面类
@Aspect // 表示是一个切面类
public class MyAspect {
/*@Before("execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..))")
public void beforeMethod(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}*/
/**
* 后置通知
*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..))",returning="msg")
public void beforeMethod(Object msg){
System.out.println("后置通知..."+msg);
}
}
2.测试
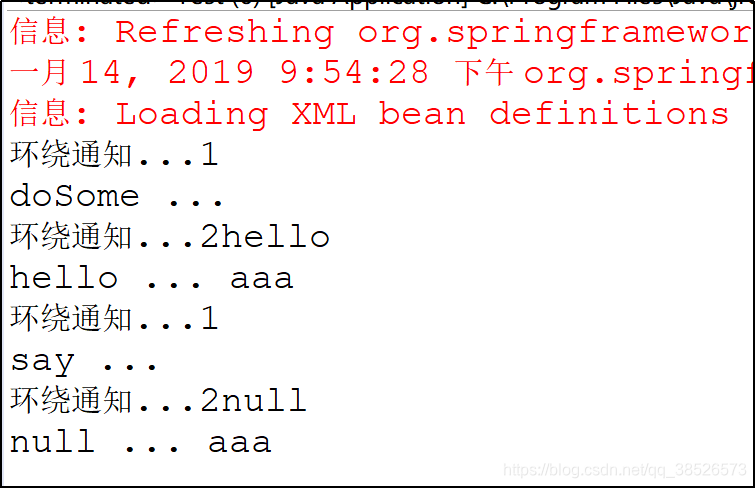
环绕通知
1.切面类
@Aspect // 表示是一个切面类
public class MyAspect {
/*@Before("execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..))")
public void beforeMethod(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}*/
/**
* 后置通知
* @throws Throwable
*/
/*@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.dpb.service.*.doSome(..))",returning="msg")
public void beforeMethod(Object msg){
System.out.println("后置通知..."+msg);
}*/
/**
* 环绕通知
* @param pjp
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around("execution(* *..service.*.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕通知...1");
Object res = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知...2"+res);
res = res+" ... aaa";
return res;
}
}
2.测试
异常通知
1.切面类中的方法
@AfterThrowing("execution(* *..service.*.*(..))")
public void throwsMethod(){
System.out.println("异常触发了...");
}
2.测试


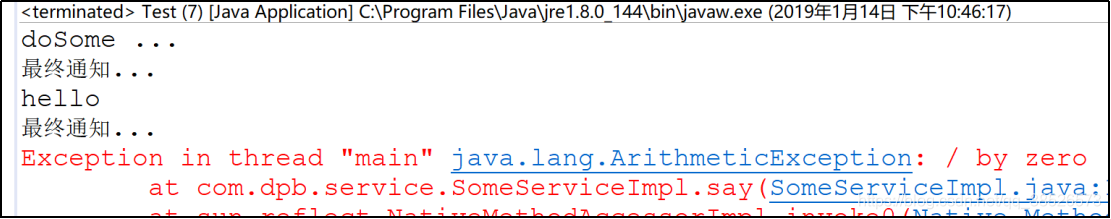
最终通知
1.切面方法
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("execution(* *..service.*.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知...");
}
2.测试

XML方式
接口和实现类还是用上个案例的
切面类
/**
* 切面类
* @author dpb[波波烤鸭]
*
*/
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 前置通知
*/
public void beforeMethod(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
public void afterMethod(Object msg){
System.out.println("后置通知..."+msg);
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕通知...1");
Object res = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知...2"+res);
res = res+" ... aaa";
return res;
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
public void throwsMethod(Exception e){
System.out.println("异常触发了...");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知...");
}
}
配置文件修改
1.前置通知
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 注册目标类 -->
<bean id="someServiceImpl" class="com.dpb.service.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!-- 注册切面类 -->
<bean class="com.dpb.aspect.MyAspect" id="myAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))" id="pointcut"/>
<!-- 配置切面类 -->
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>

2.后置通知

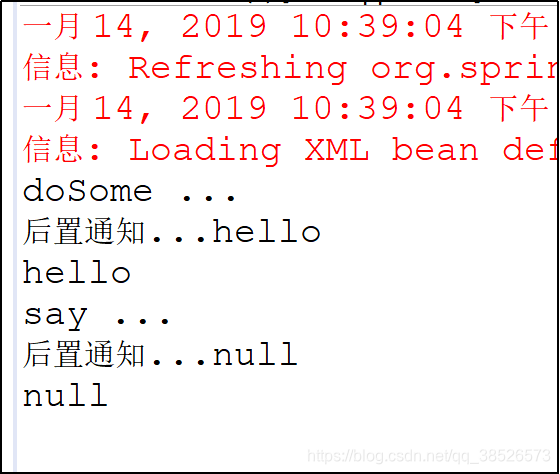
3.环绕通知


4.异常通知


5.最终通知

JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate就是采用AOP思想,将Jdbc操作中的模板代码全部简化,开发者只需要完成最最核心的SQL以及结果的检索。
使用步骤:
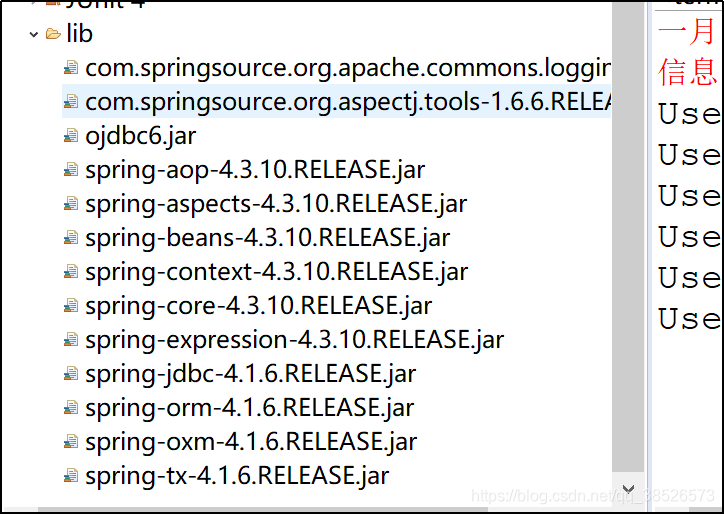
导入jar包
创建CRUD工具类
public class TestJdbc {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Before
public void beforeMethod(){
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setUrl("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl");
ds.setDriverClassName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
ds.setUsername("pms");
ds.setPassword("pms");
jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
}
/**
* 添加数据
*/
@Test
public void add(){
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_sysuser(id,uname,nickname)values(?,?,?)",133,"aaa","测试");
//System.out.println("111");
}
/**
* 修改数据
*/
@Test
public void udpate(){
jdbcTemplate.update("update t_sysuser set uname=? ,nickname=? where id=?","bbb","呵呵",133);
//System.out.println("111");
}
/**
* 删除数据
*/
@Test
public void delete(){
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from t_sysuser where id=?",133);
//System.out.println("111");
}
/**
* 查询数据第一种方式
*/
@Test
public void query(){
List<User> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from t_sysuser", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int index) throws SQLException {
User u = new User();
u.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
u.setUname(rs.getString("uname"));
u.setNickname(rs.getString("nickname"));
return u;
}
});
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//System.out.println("111");
}
/**
* 查询数据第二种方式
*/
@Test
public void query1(){
List<User> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from t_sysuser", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class));
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}

java中的乱码
1.项目编码
2. 文件本身的编码(jsp或者html的head中指定的编码)
3. GET请求乱码(修改Tomcat配置)
4. POST请求乱码(Java代码解决,可以使用过滤器统一解决)
5. 响应乱码(修改响应编码,主要是修改content-type)
6. 数据库乱码:
1. 确认乱码根源(数据库乱码还是java中乱码)
2. 通过在java中打印日志,确认乱码的根源 2. 通过在java中打印日志,确认乱码的根源
3. 第三种情况,数据在从Java到数据库实例的过程中乱码了,此时修改数据库连接地址即可解决: dbc:mysql:///test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
上一篇: Spring-IOC实现【02-其他实现方式】
下一篇:Spring之事务管理