1、POI是什么
Apache POI - the Java API for Microsoft Documents,顾名思义,Apache的三方包,用来操作微软office文档的,多数时候用来操作excel,所以这里就以excel方面来说明。
需要引入两个包,maven地址如下(version 3.9):
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>13
1
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi --> 2
<dependency>3
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>4
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>5
<version>3.9</version>6
</dependency>7
8
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->9
<dependency>10
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>11
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>12
<version>3.9</version>13
</dependency>POI的组件列表中,针对excel的主要是HSSF和XSSF组件,前者针对97-2007的通用版excel,即后缀xls;后者针对2007或更高版的excel,即后缀xlsx。官方概要如下:
HSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel '97(-2007) file format.
XSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format.2
1
HSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel '97(-2007) file format. 2
XSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format.2、POI核心类
面向对象面向对象,既然如此,自然去找找一些能表示excel中内容的类。
2.1 工作簿 Workbook
创建或维护Excel工作簿的所有类的超接口,Workbook,属于org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel包。其下有两个实现类:
- HSSFWorkbook : 有读取.xls 格式和写入Microsoft Excel文件的方法。它与微软Office97-2003版本兼容
- XSSFWorkbook : 有读写Microsoft Excel和OpenOffice的XML文件的格式.xls或.xlsx的方法。它与MS-Office版本2007或更高版本兼容
所以在针对不同版本的excel时,需要对应以上使用不同的Workbook。构造函数中,常用的:
HSSFWorkbook
//直接创建新的
HSSFWorkbook()
//通过输入流创建
HSSFWorkbook(java.io.InputStream s)5
1
//直接创建新的2
HSSFWorkbook()3
4
//通过输入流创建5
HSSFWorkbook(java.io.InputStream s)XSSFWorkbook
//直接创建新的
XSSFWorkbook()
//通过File类创建
XSSFWorkbook(java.io.File file)
//通过输入流创建
XSSFWorkbook(java.io.InputStream is)8
1
//直接创建新的2
XSSFWorkbook()3
4
//通过File类创建5
XSSFWorkbook(java.io.File file)6
7
//通过输入流创建8
XSSFWorkbook(java.io.InputStream is)2.2 标签页 Sheet
HSSFSheet 和 XSSFSheet 都是Sheet接口的实现类,Sheet可以使用Workbook的两个方法获得:
workbook.createSheet();
workbook.createSheet(String sheetName);2
1
workbook.createSheet();2
workbook.createSheet(String sheetName);2.3 行 Row
同理,Row是 HSSFRow 和 XSSFRow 的接口,通过Sheet获取:
sheet.createRow(int rownum);1
1
sheet.createRow(int rownum);2.4 单元格 Cell
同理,Cell是 HSSFCell 和 XSSFCell 的接口,通过Row获取:
row.createCell(int column);
row.createCell(int column, int type);2
1
row.createCell(int column);2
row.createCell(int column, int type);3、创建和读取
其实如果能理解面向对象,就很简单了,另外包括字体,公式,超链接等,都有对应的封装类,此处只提出了核心的几个,需要了解更多的需要自行展开。
例子的话,直接从别人教程里摘出来吧,另,读取的workbook,可以debug瞅瞅内容。
3.1 创建空白工作簿
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
public class CreateWorkBook
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
//Create Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create file system using specific name
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("createworkbook.xlsx"));
//write operation workbook using file out object
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("
createworkbook.xlsx written successfully");
}
}18
1
import java.io.*;2
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;3
public class CreateWorkBook 4
{5
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception 6
{7
//Create Blank workbook8
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); 9
//Create file system using specific name10
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(11
new File("createworkbook.xlsx"));12
//write operation workbook using file out object 13
workbook.write(out);14
out.close();15
System.out.println("16
createworkbook.xlsx written successfully");17
}18
}3.2 打开现有的工作簿
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
public class OpenWorkBook
{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception
{
File file = new File("openworkbook.xlsx");
FileInputStream fIP = new FileInputStream(file);
//Get the workbook instance for XLSX file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fIP);
if(file.isFile() && file.exists())
{
System.out.println(
"openworkbook.xlsx file open successfully.");
}
else
{
System.out.println(
"Error to open openworkbook.xlsx file.");
}
}
}22
1
import java.io.*;2
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;3
public class OpenWorkBook4
{5
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception6
{ 7
File file = new File("openworkbook.xlsx");8
FileInputStream fIP = new FileInputStream(file);9
//Get the workbook instance for XLSX file 10
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fIP);11
if(file.isFile() && file.exists())12
{13
System.out.println(14
"openworkbook.xlsx file open successfully.");15
}16
else17
{18
System.out.println(19
"Error to open openworkbook.xlsx file.");20
}21
}22
}4、方法示例:任意对象List转至为Excel文档(可用注解定义标签名和列名)
写了个方法,可以将某个类的List转换为对应的Excel文档,列名如果在不使用注解的情况下默认为属性名:
类:
@Excel(name = "学生标签页")
public class Student {
@Excel(name = "姓名")
private String name;
private boolean male;
@Excel(name = "身高")
private int height;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean isMale() {
return male;
}
public void setMale(boolean male) {
this.male = male;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
}35
1
(name = "学生标签页")2
public class Student {3
4
(name = "姓名")5
private String name;6
7
private boolean male;8
9
(name = "身高")10
private int height;11
12
public String getName() {13
return name;14
}15
16
public void setName(String name) {17
this.name = name;18
}19
20
public boolean isMale() {21
return male;22
}23
24
public void setMale(boolean male) {25
this.male = male;26
}27
28
public int getHeight() {29
return height;30
}31
32
public void setHeight(int height) {33
this.height = height;34
}35
}测试方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("小红");
student1.setMale(false);
student1.setHeight(167);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setName("小明");
student2.setMale(true);
student2.setHeight(185);
list.add(student1);
list.add(student2);
File file = new File("C:/Users/Dulk/Desktop/1314.xls");
createExcel(list, file);
}18
1
public static void main(String[] args) {2
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();3
Student student1 = new Student();4
student1.setName("小红");5
student1.setMale(false);6
student1.setHeight(167);7
8
Student student2 = new Student();9
student2.setName("小明");10
student2.setMale(true);11
student2.setHeight(185);12
13
list.add(student1);14
list.add(student2);15
16
File file = new File("C:/Users/Dulk/Desktop/1314.xls");17
createExcel(list, file);18
}输出结果:
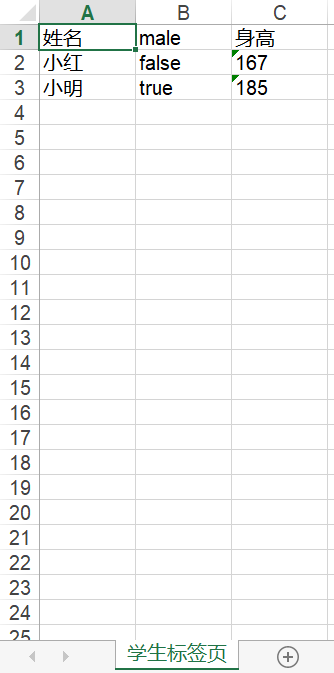
注解:
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Excel {
//设置名称
public String name() default "";
}9
1
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;2
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;3
4
5
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)6
public @interface Excel {7
//设置名称8
public String name() default "";9
}方法:
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Excel的操作工具类
*/
public class ExcelUtil {
private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(ExcelUtil.class);
/**
* 获取某个File文件对应的Workbook工作簿对象
*/
public static Workbook gainWorkbook(File file) throws ExcelException {
if (!isExcel(file)) {
throw new ExcelException("文件不是Excel类型");
}
//如果文件不存在则新建
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
Workbook workbook = isOlderEdition(file) ? new HSSFWorkbook() : new XSSFWorkbook();
workbook.write(os);
log.debug("文件不存在,新建该Excel文件");
os.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
return isOlderEdition(file) ? new HSSFWorkbook(is) : new XSSFWorkbook(is);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 判断某个Excel文件是否是2003-2007通用旧版
*/
private static boolean isOlderEdition(File file) {
return file.getName().matches(".+\.(?i)xls");
}
/**
* 判断文件是否是一个Excel文件
*/
private static boolean isExcel(File file) {
String fileName = file.getName();
String regXls = ".+\.(?i)xls";
String regXlsx = ".+\.(?i)xlsx";
return fileName.matches(regXls) || fileName.matches(regXlsx);
}
/**
* 将某个对象的List转换为Excel工作簿
*/
public static <E> Workbook createExcel(List<E> list, File file) {
String sheetName = "default";
if (list.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
Workbook workbook = null;
try {
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Excel.class)) {
Excel excel = (Excel) clazz.getAnnotation(Excel.class);
sheetName = excel.name();
}
workbook = gainWorkbook(file);
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(sheetName);
//创建首行
Row line = sheet.createRow(0);
for (int k = 0; k < fields.length; k++) {
Cell cell = line.createCell(k);
String columnName = fields[k].getName();
if (fields[k].isAnnotationPresent(Excel.class)) {
Excel excel = fields[k].getAnnotation(Excel.class);
columnName = excel.name();
}
cell.setCellValue(columnName);
}
//创建数据
for (int i = 1; i <= list.size(); i++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(i);
for (int j = 1; j <= fields.length; j++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(j - 1);
String fieldName = fields[j - 1].getName();
String fieldFirstLetterUpper = fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase();
String prefix = "get";
if ("boolean".equals(fields[j - 1].getType().getName())) {
prefix = "is";
}
String methodName = prefix + fieldFirstLetterUpper + fieldName.substring(1);
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName);
cell.setCellValue(String.valueOf(method.invoke(list.get(i - 1))));
}
}
log.debug("List读入完毕");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(os);
os.close();
} catch (ExcelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return workbook;
}
}x
1
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;2
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;3
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;4
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;5
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;6
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;7
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;8
9
import java.io.File;10
import java.io.FileInputStream;11
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;12
import java.io.FileOutputStream;13
import java.io.IOException;14
import java.io.InputStream;15
import java.io.OutputStream;16
import java.lang.reflect.Field;17
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;18
import java.lang.reflect.Method;19
import java.util.ArrayList;20
import java.util.List;21
22
/**23
* Excel的操作工具类24
*/25
public class ExcelUtil {26
private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(ExcelUtil.class);27
28
/**29
* 获取某个File文件对应的Workbook工作簿对象30
*/31
public static Workbook gainWorkbook(File file) throws ExcelException {32
if (!isExcel(file)) {33
throw new ExcelException("文件不是Excel类型");34
}35
//如果文件不存在则新建36
if (!file.exists()) {37
try {38
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);39
Workbook workbook = isOlderEdition(file) ? new HSSFWorkbook() : new XSSFWorkbook();40
workbook.write(os);41
log.debug("文件不存在,新建该Excel文件");42
os.close();43
44
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {45
e.printStackTrace();46
} catch (IOException e) {47
e.printStackTrace();48
}49
}50
51
try {52
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);53
return isOlderEdition(file) ? new HSSFWorkbook(is) : new XSSFWorkbook(is);54
55
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {56
e.printStackTrace();57
} catch (IOException e) {58
e.printStackTrace();59
}60
61
return null;62
}63
64
/**65
* 判断某个Excel文件是否是2003-2007通用旧版66
*/67
private static boolean isOlderEdition(File file) {68
return file.getName().matches(".+\.(?i)xls");69
}70
71
/**72
* 判断文件是否是一个Excel文件73
*/74
private static boolean isExcel(File file) {75
String fileName = file.getName();76
String regXls = ".+\.(?i)xls";77
String regXlsx = ".+\.(?i)xlsx";78
return fileName.matches(regXls) || fileName.matches(regXlsx);79
}80
81
/**82
* 将某个对象的List转换为Excel工作簿83
*/84
public static <E> Workbook createExcel(List<E> list, File file) {85
String sheetName = "default";86
if (list.size() == 0) {87
return null;88
}89
90
Workbook workbook = null;91
try {92
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();93
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();94
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Excel.class)) {95
Excel excel = (Excel) clazz.getAnnotation(Excel.class);96
sheetName = excel.name();97
}98
99
workbook = gainWorkbook(file);100
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(sheetName);101
//创建首行102
Row line = sheet.createRow(0);103
for (int k = 0; k < fields.length; k++) {104
Cell cell = line.createCell(k);105
String columnName = fields[k].getName();106
if (fields[k].isAnnotationPresent(Excel.class)) {107
Excel excel = fields[k].getAnnotation(Excel.class);108
columnName = excel.name();109
}110
cell.setCellValue(columnName);111
}112
//创建数据113
for (int i = 1; i <= list.size(); i++) {114
Row row = sheet.createRow(i);115
for (int j = 1; j <= fields.length; j++) {116
Cell cell = row.createCell(j - 1);117
String fieldName = fields[j - 1].getName();118
String fieldFirstLetterUpper = fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase();119
String prefix = "get";120
if ("boolean".equals(fields[j - 1].getType().getName())) {121
prefix = "is";122
}123
String methodName = prefix + fieldFirstLetterUpper + fieldName.substring(1);124
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName);125
cell.setCellValue(String.valueOf(method.invoke(list.get(i - 1))));126
}127
}128
log.debug("List读入完毕");129
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);130
workbook.write(os);131
os.close();132
133
} catch (ExcelException e) {134
e.printStackTrace();135
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {136
e.printStackTrace();137
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {138
e.printStackTrace();139
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {140
e.printStackTrace();141
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {142
e.printStackTrace();143
} catch (IOException e) {144
e.printStackTrace();145
}146
return workbook;147
}148
}