单链表:
1 2 3 4 5 6
1.设计节点
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct node
{
datatype data;
struct node *next;
}listnode,*linklist;
listnode a; === struct node a;
linklist p =malloc === struct node *p =malloc;
2.初始化空链表
1.linklist L =NULL;
2.
linklist init_list()
{
linklist L=malloc(sizeof(listnode))
L->next=NULL;
return L
}
3.插入(尾)
bool insert_node( int data,linklist L)
{
//产生新节点
linklist new=malloc(sizeof(listnode));
new->data=data;
new->next=NULL;
//定位
linklist p=L;
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
}
//新节点插入
p->next=new;
return true;
}
4.显示
show(linklist L)
{
p=L->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf( ,p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
-----------
void revert(linklist L)
{
//p指向要插入到排序好链的节点(也是未排序好的链表的第一节点)
//q 指向未排序好的链表的第二节点
linklist p,q;
p=L->next;
L->next=NULL;
while(p!=NULL)
{
q=p->next;
p->next=L->next;
L->next=p;
p=q;
}
}
================================================================================
int main()
{
linklist L;
L=init_list();
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
insert_node(i,L)
}
show(L);
revert(L)
show(L)
}
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef int datatype;
struct node
{
datatype data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *init_list(void)
{
struct node *p = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->next = NULL;
return p;
}
void insert(int n, struct node *head)
{
// 创建一个新节点
struct node *new = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new->data = n;
new->next = NULL;
// 找到单链表的最后一个节点
struct node *p = head;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
// 将最后这个节点的next指向新节点
p->next = new;
}
void show(struct node *head)
{
struct node *p = head->next;
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("
");
}
//单链表的逆序
void inverse(struct node *head)
{
struct node *p, *q;
p = head->next;
head->next = NULL;//将链表断成两个链表
while(p != NULL)
{
q = p->next;
p->next = head->next;
head->next = p;
p = q;
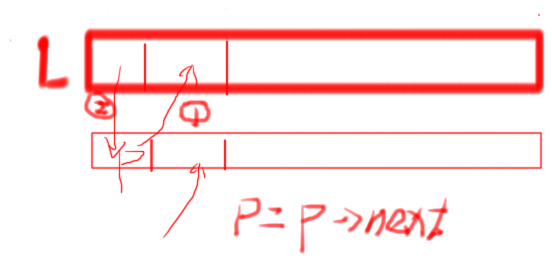
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct node *head;
head = init_list();
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int i;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
insert(i, head);
}
show(head);
inverse(head);
show(head);
return 0;
}