1. Node.js模块化开发
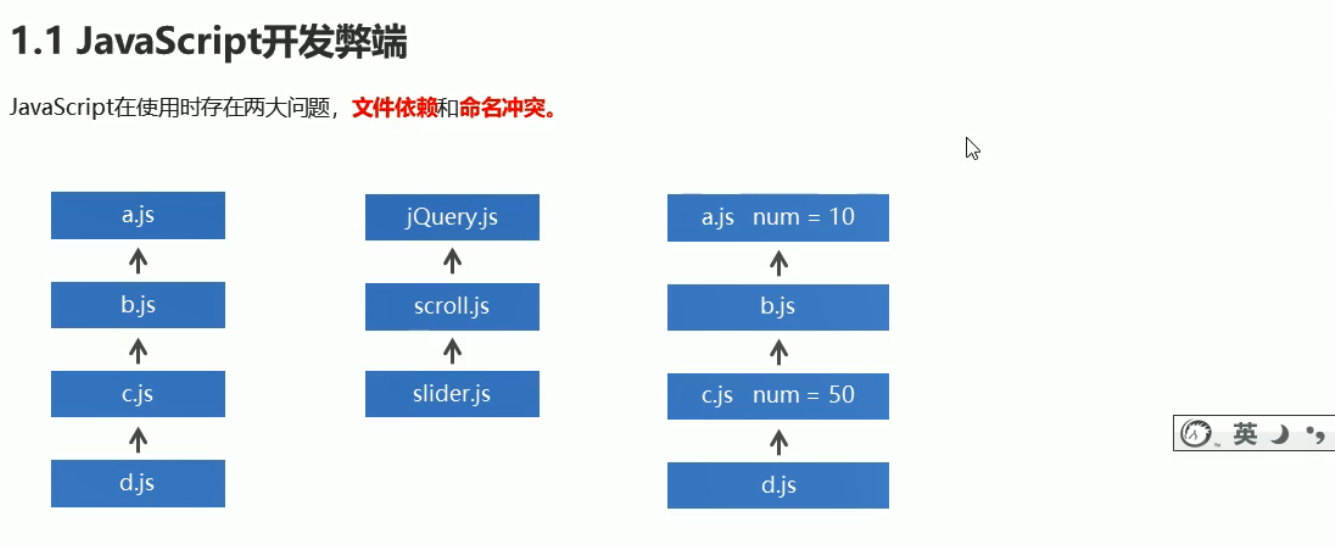


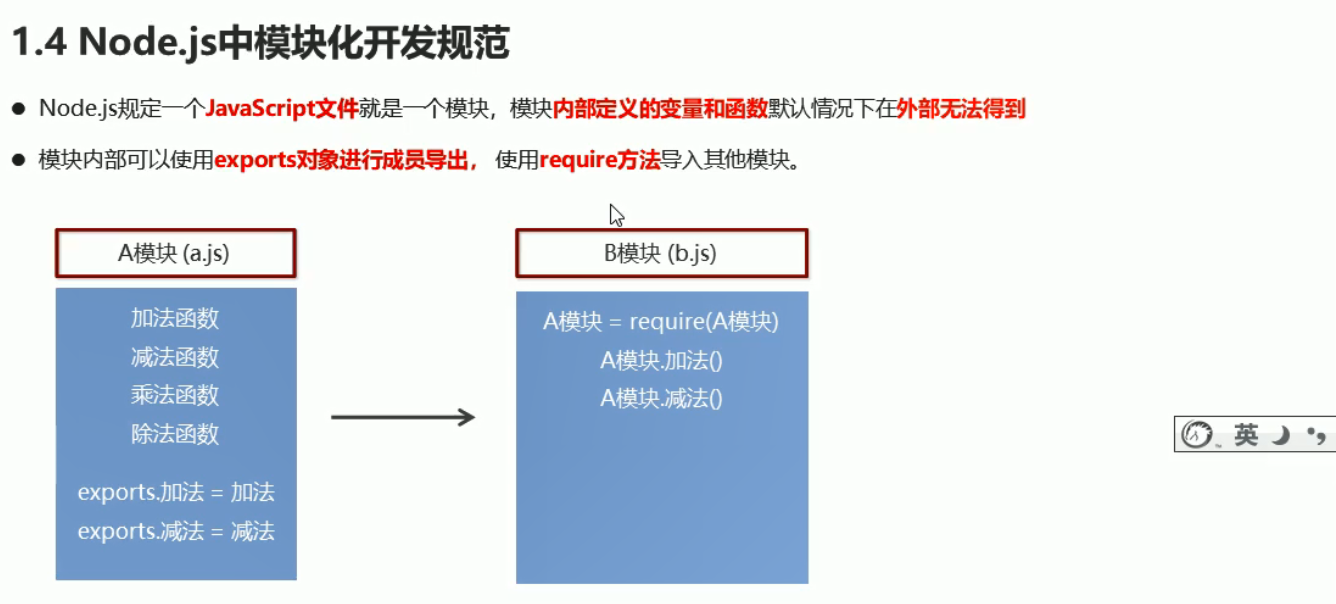

上述exports.version将version变成了exports的属性

上述导入模块时,后缀可以省略
//03.module-a.js
const add = (n1, n2) => n1 + n2;
exports.add = add;
//03.module-b.js
//const a = require('./03.module-a.js');
const a = require('./03.module-a'); // ./表示当前目录 ../表示上一级目录
console.log(a.add(10, 20));


//04.module.exports.js
const greeting = name => `hello ${name}`;
module.exports.greeting = greeting;
// 04.reguire.js
const a = require('./04.reguire.js');
console.log(a.greeting('zhangsan'));


写法1:exports.属性名=属性值
写法2:module.exports.属性名=属性值
这两种写法都是等价的,这两种方法指向的都是同一个对象
//04.module.exports.js
const greeting = name => `hello ${name}`;
const x = 100;
//导出方法1
exports.x = x;
//导出方法2
module.exports.greeting = greeting;
//04.require.js
const a = require('./04.module.exports.js');
console.log(a);

当exports对象和moudle.exports对象指向的不是同一个对象时 以module.exports为准
//04.module.exports.js
const greeting = name => `hello ${name}`;
const x = 100;
//导出方法1
exports.x = x;
//导出方法2
module.exports.greeting = greeting;
// 当exports对象和moudle.exports对象指向的不是同一个对象时 以module.exports为准
module.exports = {
name: 'zhangsan'
}
//04.require.js
const a = require('./04.module.exports.js');
console.log(a);

//04.module.exports.js
const greeting = name => `hello ${name}`;
const x = 100;
//导出方法1
exports.x = x;
//导出方法2
module.exports.greeting = greeting;
// 当exports对象和moudle.exports对象指向的不是同一个对象时 以module.exports为准
module.exports = {
name: 'zhangsan'
}
//不生效
exports = {
age: 20
}
//04.require.js
const a = require('./04.module.exports.js');
console.log(a);

2. 系统模块
2.1 什么是系统模块
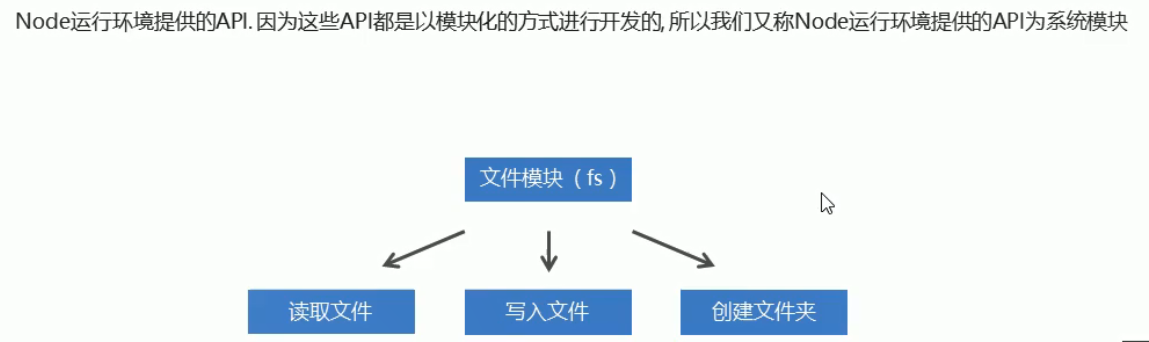
2.2 系统模块fs文件操作

读取文件是硬盘在读取,读取是需要时间的,所以不能直接通过readfile的返回值返回读取内容,而是需要通过回调函数得到文件内容(说明:硬盘在读取文件结束后,会调用回调函数,并将读取的结果doc通过参数的形式返回)
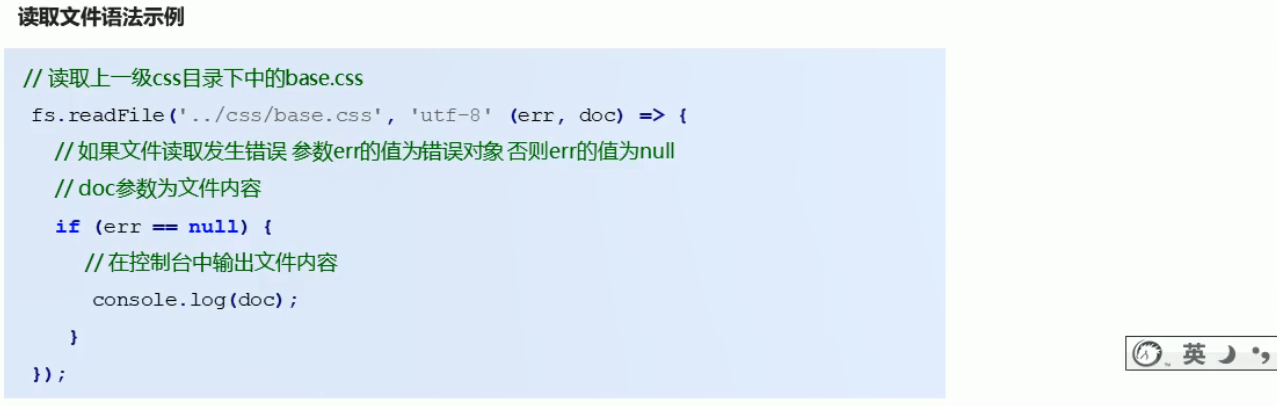
// 1.通过模块的名字fs对模块进行引用
const fs = require('fs');
// 2.通过模块内部的readFile读取文件内容
fs.readFile('./01.helloworld.js', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
// 如果文件读取出错err 是一个对象 包含错误信息
// 如果文件读取正确 err是 null
// doc 是文件读取的结果
console.log(err);
console.log(doc);
});

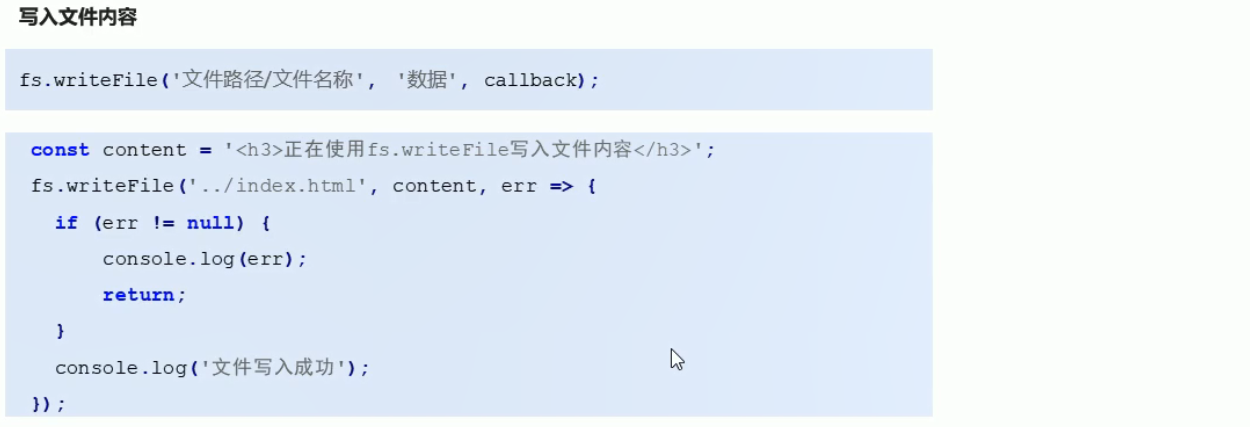
const fs = require('fs');
//向demo.txt文件中写入内容 如果没有demo.txt则会自动创建一个
fs.writeFile('./demo.txt', '即将要写入的内容', err => {
if (err != null) {
console.log(err);
return;
}
console.log('文件内容写入成功');
})

2.3 系统模块path路径操作

2.4 路径拼接语法

// public/uploads/avatar
//引入系统模块path
const path = require('path');
const finalPath = path.join('public', 'uploads','avatar');
console.log(finalPath);

2.5 绝对路径VS相对路径

相对路径大多数情况下,不是相对于当前文件,而是相对于命令行中的当前工作目录,比如上述文件读取操作API,在这个API中写相对路径,相对的是命令行中的当前工作目录,证明如下:
const fs = require('fs');
//写入相对路径
fs.readFile('./01.helloworld.js', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
console.log(err);
console.log(doc);
});
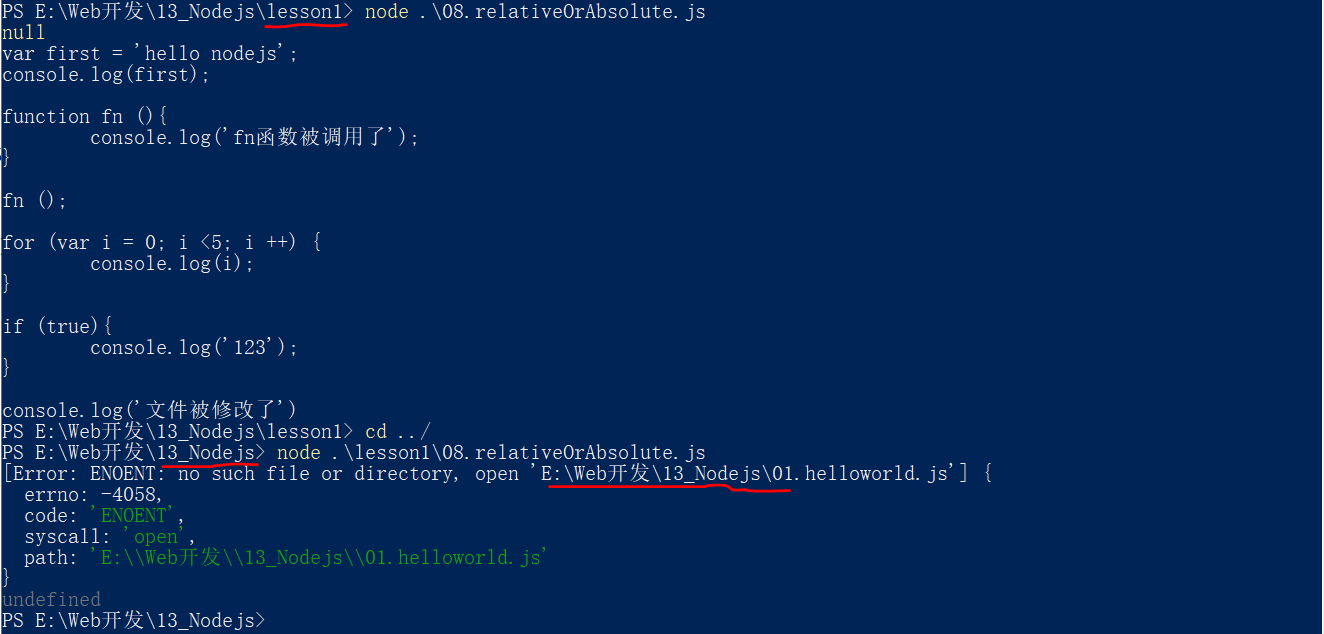
由于命令行中的当前目录是可变的,所以写相对路径是不安全的,一般选用绝对路径

const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
//观察
console.log(__dirname);//E:Web开发13_Nodejslesson1
console.log(path.join(__dirname, '01.helloworld.js'))//E:Web开发13_Nodejslesson1�1.helloworld.js

const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
// 将绝对路径拼接上要执行的文件
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, '01.helloworld.js'), 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
console.log(err)
console.log(doc)
});
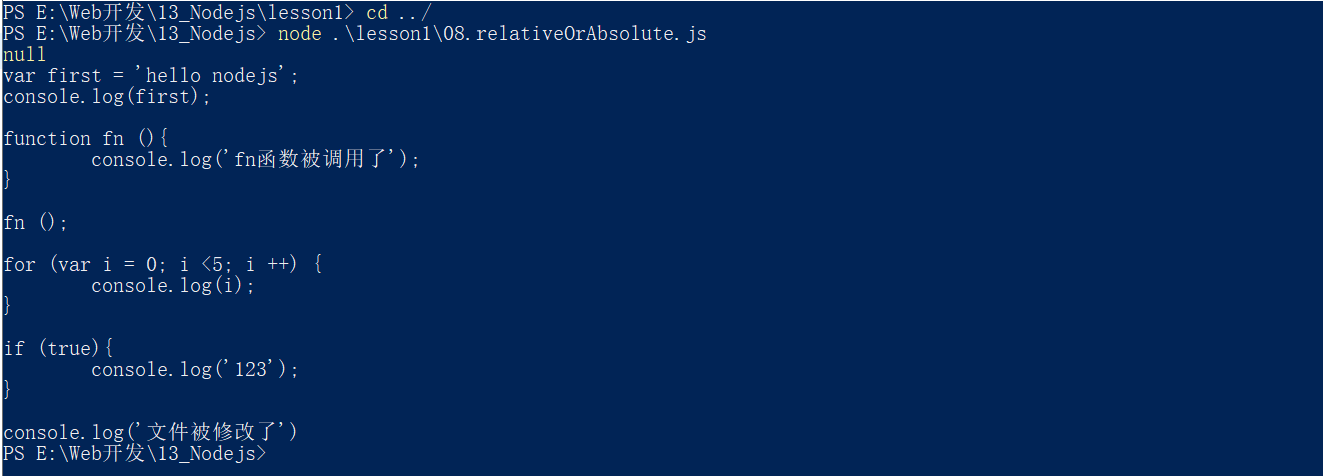
注意:require里面也有相对路径,该方法里的相对路径相对的就是当前文件,所以在使用require的时候是可以使用相对路径的