开启、关闭、重启 Nginx
官方地址:http://wiki.nginx.org/CommandLine
开启:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
关闭,用信号控制,语法:
kill 信号名 pid
查看 Nginx 进程:
netstat -antp

或
ps aux|grep nginx

master process 表示主进程,用来管理子进程
关闭 Nginx:
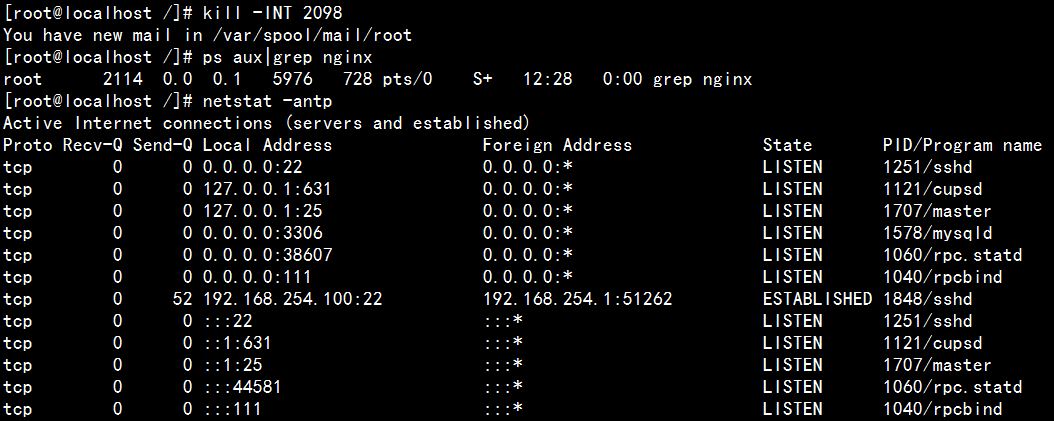
master process 和 worker process 这两个进程已经不存在了,同时 80 端口已经没有被占用了。
Nginx 的信号控制包括:
| TERM, INT | Quick shutdown(紧急关闭,轻易不要这样使用) |
| QUIT | Graceful shutdown(优雅地关闭进程,即等请求结束后再关闭) |
| KILL | Halts a stubborn process |
| HUP | Configuration reload Start the new worker processes with a new configuration Gracefully shutdown the old worker processes(改变配置文件,平滑地重读配置文件) |
| USR1 | Reopen the log files(重读日志,在日志按月/日分割时有用) |
| USR2 | Upgrade Executable on the fly(平滑地升级) |
| WINCH | Gracefully shutdown the worker processes(优雅地关闭旧的进程(配合USR2来进行升级)) |
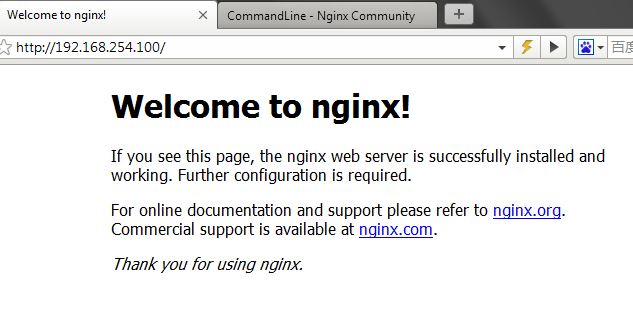
【测试 HUP】
① 访问 http://192.168.254.100/
② 更改配置文件:
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
在 index.html 前加上 test.html。此时 test.html 的优先级要高于 index.html

③ 在 nginx 的 html 目录下新建 test.html:
vim /usr/local/nginx/html/test.html

此时在 nginx 的 html 目录下就多了 test.html 文件:
ls /usr/local/nginx/html/

④ 平滑地重读配置文件:
首先查看 nginx 的进程号 pid:2192

平滑地重读配置文件:
kill -HUP 2192
重新访问 192.168.254.100:
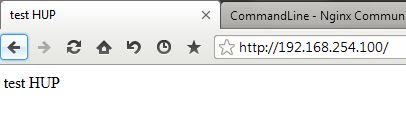
【另一个测试 HUP】
① 修改 test.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meat charset="utf-8">
<title>test HUP</title>
</head>
<body>
test HUP
<script>
window.location.href="/";
</script>
</body>
</html>

导致的结果是访问该页面,该页面会一直刷新:
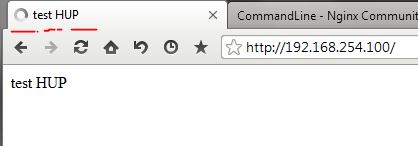
② 修改配置文件:
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
去掉 test.html
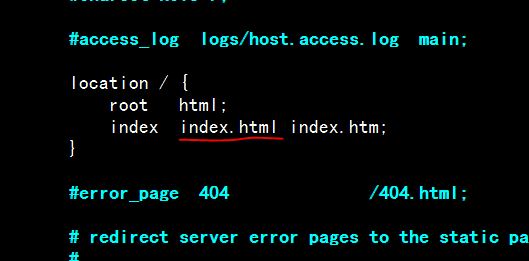
此时页面一直在刷新,而内容不变;
③ 再次平滑地重读配置文件:
kill -HUP 2192
内容在很短时间内改变为 Welcome to nginx!
或者
kill -HUP `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
因为
cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
输出的就是 nginx 的 pid:2192
进程文件 nginx.pid 是不会变的,而进程号 pid 是会变的。
【测试 USR1】
① 查看 nginx 的 logs 目录,有一个 access.log,它记录了所有对 Web 服务器的访问活动(例如上例中 js 不断刷新页面就会记录到 access.log 中,该文件会一直增涨):
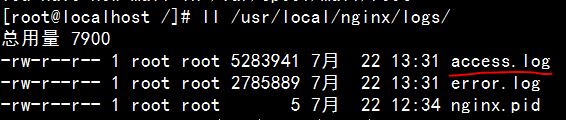
如果要把 access.log 按日期进行备份,不能简单地只把 access.log 更改为 access.log.20150722,然后新建一个 access.log。因为该文件的 inode 是不变的,access.log.20150722 还在继续增涨。
② 要想新的日志写进新的 access.log ,则需要使用 Nginx 信号控制中的 USR1:
kill -USR1 2192
此时新的日志都写进了新建的 access.log 中,access.log.20150722 的大小则保持不变,完成备份。