1 BST迭代器
注意点:1. 实际就是中序遍历的非递归写法,迭代器就是要用Stack存储数据,不过把不同的模块功能进行了分割,而不是一次完成中序遍历;
2. 可以把添加到Stack单独抽取成一个函数,面向对象,更容易理解。
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/binary-search-tree-iterator/#

1 public class BSTIterator { 2 //@param root: The root of binary tree. 3 TreeNode next = null; 4 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); 5 public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { 6 // write your code here 7 next = root; 8 } 9 10 //@return: True if there has next node, or false 11 public boolean hasNext() { 12 // write your code here 13 while(next != null) { 14 stack.push(next); 15 next = next.left; 16 } 17 if(stack.isEmpty()) return false; 18 return true; 19 } 20 21 //@return: return next node 22 public TreeNode next() { 23 // write your code here 24 if(!hasNext()) return null; 25 TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); 26 if(cur.right == null) next = null; 27 else next = cur.right; 28 return cur; 29 } 30 }
2 二叉查找树中搜索
注意点:见代码
不一定要完全遍历二叉树,可以在遍历前判断下来减少遍历的量。
if(root.val > k1) helper(root.left, result, k1, k2);
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/search-range-in-binary-search-tree/

1 //可以定义一个 ArrayList<Integer> result的成员变量,这样helper中就不需要resul作为参数一直传递添加了。 2 public ArrayList<Integer> searchRange(TreeNode root, int k1, int k2) { 3 ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer> (); 4 helper(root, result, k1, k2); 5 return result; 6 } 7 private void helper(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> result, int k1, int k2) { 8 if(root == null) return; 9 helper(root.left, result, k1, k2); 10 if(root.val >= k1 && root.val <= k2) result.add(root.val); 11 helper(root.right, result, k1, k2); 12 return; 13 }
3 二叉树中插入结点
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/insert-node-in-a-binary-search-tree/
注意点:非递归的插入方式

1 public TreeNode insertNode(TreeNode root, TreeNode node) { 2 // write your code here 3 if(root == null) { 4 root = node; 5 return root; 6 } 7 if(root.val <= node.val) { 8 root.right = insertNode(root.right, node); 9 10 } else { 11 root.left = insertNode(root.left, node); 12 } 13 return root; 14 } 15 //非递归 16 public TreeNode insertNode(TreeNode root, TreeNode node) { 17 // write your code here 18 if(root == null) { 19 root = node; 20 return root; 21 } 22 TreeNode last = null, temp = root; 23 while(temp != null) { 24 last = temp; 25 if(temp.val <= node.val) temp = temp.right; 26 else temp = temp.left; 27 } 28 if(last != null) { //可以不判断,last不可能为null 29 if(last.val <= node.val) last.right = node; 30 else last.left = node; 31 } 32 return root; 33 } 34
4 二叉树删除结点
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/remove-node-in-binary-search-tree/
注意点:见代码
结点的传递是地址传递,所以将待改变结点的引用传入函数,函数操作后,整个树是会发生变化的。
待删结点有两个子树的删除方式:
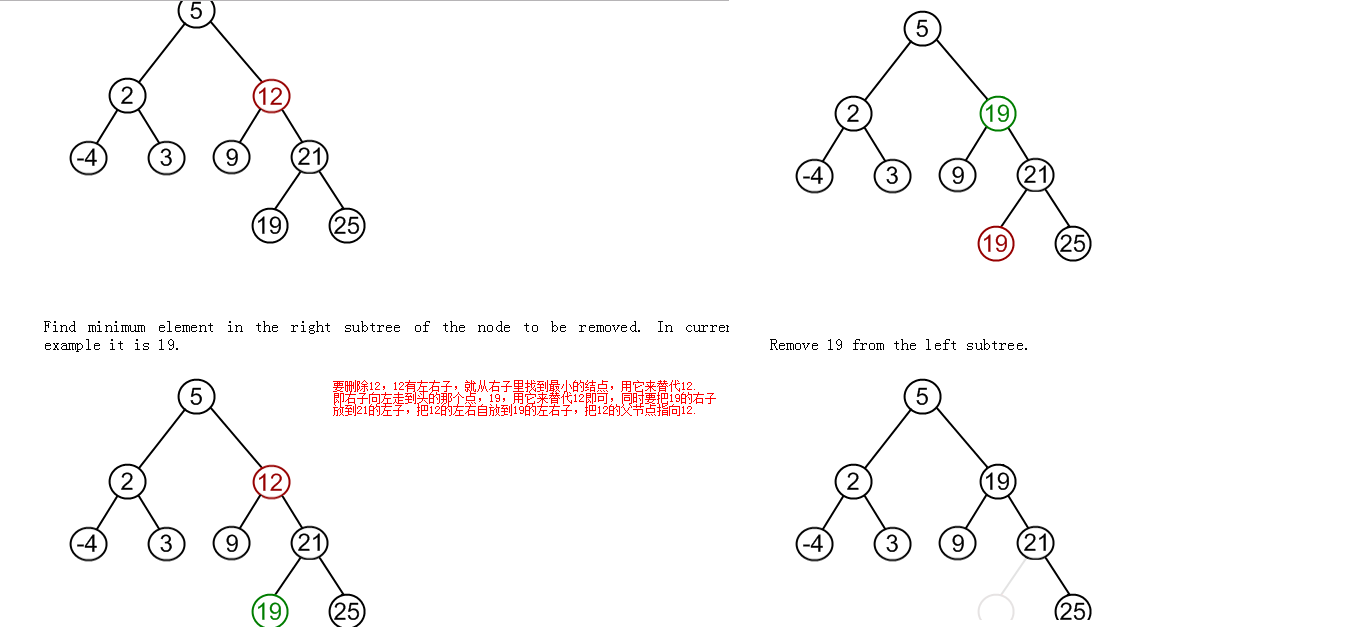

1 public TreeNode removeNode(TreeNode root, int value) { 2 TreeNode dummy = new TreeNode(0); //dummy的值随便取,反正不输出,为了仅仅是给root设个头 3 dummy.left = root; 4 5 TreeNode parent = findNode(dummy, root, value); 6 TreeNode node; //待删结点 7 if (parent.left != null && parent.left.val == value) { 8 node = parent.left; 9 } else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.val == value) { 10 node = parent.right; 11 } else { 12 return dummy.left ; //待删结点不存在 13 } 14 15 deleteNode(parent, node); 16 17 return dummy.left ; 18 } 19 20 private TreeNode findNode(TreeNode parent, TreeNode node, int value) { //返回待删结点的父节点,待删的不存在也返回父节点 21 if (node == null) { 22 return parent; 23 } 24 25 if (node.val == value) { 26 return parent; 27 } 28 if (value < node.val) { 29 return findNode(node, node.left, value); 30 } else { 31 return findNode(node, node.right, value); 32 } 33 } 34 35 private void deleteNode(TreeNode parent, TreeNode node) { 36 if (node.right == null) { 37 if (parent.left == node) { 38 parent.left = node.left; 39 } else { 40 parent.right = node.left; 41 } 42 } else { 43 TreeNode temp = node.right; 44 TreeNode father = node; 45 46 while (temp.left != null) { 47 father = temp; 48 temp = temp.left; 49 } 50 51 if (father.left == temp) { 52 father.left = temp.right; 53 } else { 54 father.right = temp.right; 55 } 56 57 if (parent.left == node) { 58 parent.left = temp; 59 } else { 60 parent.right = temp; 61 } 62 63 temp.left = node.left; 64 temp.right = node.right; 65 } 66 }
DP--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
满足下面三个条件之一:
● 求最大值最小值
● 判断是否可行
● 统计方案个数
则 极有可能 是使用动态规划求解
序列型dp 递推表达式f[] 里代表着含有0个~length个字符,所以数组的长度定义为length+1;
区间型dp 递推表达式f[] 里代表着坐标,所以数组的长度定义为length;
1 数字三角形
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/triangle/
疑问: 用HashMap怎么存?编译不通过?????
注意点:top- down 、down - top、 记忆化搜索
初始化三角形的顶点和两个侧边
错误点:

1 //搜索记忆,查找过的结点不需要再查一次,所以复杂度为O(n * n) 2 int[][] triangle = null; 3 int[][] sumMin = null; 4 int n; 5 public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) { 6 if(triangle == null || triangle.length == 0 || triangle[0].length == 0) return 0; 7 this.n = triangle.length; 8 this.triangle = triangle; 9 this.sumMin = new int[n][n]; 10 for(int i = 0; i< n; i++) { 11 for(int j = 0; j < n ; j++) sumMin[i][j] = Math.MAX_VALUE; 12 } 13 14 return helper(0, 0); 15 } 16 private int helper(int x, int y) { 17 if(x >= n) return 0; 18 if(sumMin[x][y] != Math.MAX_VALUE) return sumMin[x][y]; 19 sumMin[x][y] = Math.min(helper(x+1, y),helper(x+1,y+1)) + triangle[x][y]; 20 return sumMin[x][y]; 21 } 22 // 同上,用哈希表存查过的结点 23 int[][] triangle = null; 24 HashMap<int[], Integer> sumMin = new HashMap<int[], Integer>(); 25 int n; 26 public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) { 27 if(triangle == null || triangle.length == 0 || triangle[0].length == 0) return 0; 28 this.n = triangle.length; 29 this.triangle = triangle; 30 for(int i = 0; i< n; i++) { 31 for(int j = 0; j < n ; j++) sumMin[i][j] = Math.MAX_VALUE; 32 } 33 34 return helper(0, 0); 35 } 36 private int helper(int x, int y) { 37 if(x >= n) return 0; 38 if(sumMin.containsKey({x,y})) return sumMin.get({x,y}); 39 int value = Math.min(helper(x+1, y),helper(x+1,y+1)) + triangle[x][y]; 40 sumMin.put({x,y}, value); 41 return value; 42 } 43 //top - down 44 public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) { 45 if(triangle == null || triangle.length == 0 || triangle[0].length == 0) return 0; 46 int row = triangle.length; 47 for(int i =1; i < row; i++) { 48 triangle[i][0] += triangle[i-1][0]; 49 triangle[i][i] += triangle[i-1][i-1]; 50 } 51 for(int i = 2; i < row; i++) { 52 for(int j =1; j < i; j++) { 53 triangle[i][j] += Math.min(triangle[i-1][j],triangle[i-1][j-1]); 54 } 55 } 56 for(int i = 1; i < row; i++) { 57 triangle[row-1][0] = Math.min(triangle[row-1][i],triangle[row-1][0]); 58 } 59 return triangle[row-1][0]; 60 } 61 //down - top 62 public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) { 63 if(triangle == null || triangle.length == 0 || triangle[0].length == 0) return 0; 64 int row = triangle.length; 65 for(int i= row -2; i >=0; i--) { 66 for(int j=0; j<= i; j++) 67 triangle[i][j] += Math.min(triangle[i+1][j], triangle[i+1][j+1]); 68 } 69 return triangle[0][0]; 70 }
2 爬梯子
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/climbing-stairs/
注意点:类似斐波那契别超时~

1 public int climbStairs(int n) { 2 if(n == 0) return 1; 3 a = 1; 4 b = 1; 5 for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 6 int c = a+ b; 7 c= b; 8 a = b; 9 } 10 return c; 11 } 12 //--------------------- 13 public int climbStairs(int n) { 14 int[] f = new int[n+1]; 15 if(n == 0) return 1; 16 f[0] = 1; 17 f[1] = 1; 18 for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 19 f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; 20 } 21 return f[n]; 22 }

1 // 递归调用会超时,因为有重复计算的过程 2 public int climbStairs(int n) { 3 if(n == 0) return 1; 4 if(n == 1) return 1; 5 return climbStairs(n-2)+climbStairs(n-1); 6 } 7 // 加入记忆化搜索,还超时 8 int[] result = null; 9 public int climbStairs(int n) { 10 result = new int[n]; 11 Arrays.fill(result, -1); 12 if(n == 0) return 1; 13 if(n == 1) return 1; 14 result[0] = 1, result[1] = 1; 15 return helper(n); 16 } 17 private int helper(n) { 18 if(result[n] != -1) return result[n]; 19 return helper(n-1) + helper(n-2); 20 } 21 // 22 public int climbStairs(int n) { 23 if(n <=1) return 1; 24 int last = 1, last_last = 1; 25 int now = 0; 26 for(int i=1 ; i< n;i++) { 27 now = last + last_last; 28 last_last = last; 29 last = now; 30 } 31 return now; 32 }
3 跳跃游戏
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/jump-game/
注意点:O(N * N)的时间复杂度
错误点:

1 // me 2 public boolean canJump(int[] A) { 3 // wirte your code here 4 if(A == null || A.length == 0) return false; 5 int n = A.length; 6 int pos =0; 7 while(pos <= n -1) { 8 if(A[pos] >= n - 1 - pos) return true; 9 else { 10 int temp = pos + A[pos]; 11 while(A[temp] == 0) { 12 temp--; 13 if(temp <= pos) return false; 14 } 15 pos = temp; 16 } 17 } 18 return false; 19 } 20 // greedy 21 public boolean canJump(int[] A) { 22 if(A == null || A.length == 0) return false; 23 int farthest = A[0]; 24 for(int i = 1; i< A.length; i++) { 25 if(farthest >= i && farthest < i+ A[i]) { 26 farthest = i + A[i]; 27 } 28 } 29 return farthest>= A.length - 1; 30 } 31 //dp 32 public boolean canJump(int[] A) { 33 if(A == null || A.length == 0) return false; 34 boolean[] can = new boolean[A.length]; 35 can[0] = true; 36 for(int i = 1; i < A.length; i++) { 37 for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 38 if(can[j] && A[j] + j >= i) { 39 can[i] = true; 40 break; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 return can[A.length - 1]; 45 }
4 跳跃游戏二
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/jump-game-ii/
注意点:
错误点:结果数组没有初始化,数组间的关系没搞清楚

1 public int jump(int[] A) { 2 // state 3 int[] steps = new int[A.length]; 4 5 // initialize 6 steps[0] = 0; 7 for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i++) { 8 steps[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 9 } 10 11 // function 12 for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i++) { 13 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 14 if (steps[j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && j + A[j] >= i) { 15 //steps[i] = Math.min(steps[i], steps[j] + 1); 16 steps[i] = steps[j] + 1; 17 break; //贪心 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 // answer 23 return steps[A.length - 1]; 24 }
5 two Sum
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/two-sum/
注意点: map里存需要的值和它的角标;

1 //dp 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { 3 // write your code here 4 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); 5 for(int i = 0 ; i< numbers.length; i++) { 6 if(map.get(numbers[i]) != null) { 7 int[] result = {map.get(numbers[i]) + 1, i+1}; 8 return result; 9 } 10 // if在前,put在后,一定要这样,先看有没有再放。 11 map.put(target - numbers[i], i); 12 } 13 int[] result = {}; 14 return result; 15 } 16 //--------------------------- 17 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { 18 // write your code here 19 if(numbers == null || numbers.length <= 1) return null; 20 for(int i = 0; i< numbers.length - 1; i++) { 21 for(int j = i+1; j< numbers.length; j++) { 22 if(numbers[i] == target - numbers[j]) return new int[]{i + 1, j + 1}; 23 } 24 } 25 return null; 26 }
6 k sum 不会
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/k-sum/
7 最长上升连续子序列
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-increasing-continuous-subsequence/
注意点:

1 public int longestIncreasingContinuousSubsequence(int[] A) { 2 if(A == null || A.length == 0) return 0; 3 int[] result = new int[A.length]; 4 Arrays.fill(result, 1); 5 int max = 1; 6 for(int i = 1; i< A.length; i++) { 7 if(result[i -1] == 1) { 8 result[i] =2; 9 if(max < result[i]) max = result[i]; 10 continue; 11 } 12 if(A[i-2] < A[i -1] && A[i-1] < A[i] || 13 A[i-2] > A[i-1] && A[i-1] > A[i]) 14 result[i] = result[i- 1]+1; 15 else result[i] = 2; 16 if(max < result[i]) max = result[i]; 17 } 18 return max; 19 } 20 //------------------------------------------------------------ 21 public int longestIncreasingContinuousSubsequence(int[] A) { 22 if(A == null || A.length == 0) return 0; 23 int max = 1; 24 int length =1; 25 for(int i = 1; i < A.length; i++) { 26 if(A[i] > A[i-1]) length++; 27 else length=1; 28 max= Math.max(length, max); 29 } 30 for(int i = A.length -2; i >=0; i--) { 31 if(A[i+1] < A[i]) length++; 32 else length=1; 33 max= Math.max(length, max); 34 } 35 return max; 36 }
8 最长连续序列
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-consecutive-sequence/
注意点: 求数组中连续序列个数的两种方式:
先排序,在求最长的递增序列长度;
把元素放到set里,之后遍历数组,查找是否包含连续序列,见代码。

1 public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) { 2 if(num == null || num.length == 0) return 0; 3 int[] sortArray = bucketSort(num); 4 int[] f= new int[sortArray.length]; 5 f[0] = 1; 6 int maxLen = 1; 7 for(int i = 1; i < sortArray.length; i++) { 8 f[i] = 1; 9 if(sortArray[i] == sortArray[i -1] + 1) { 10 f[i] = f[i - 1] + 1; 11 } else if(sortArray[i] == sortArray[i -1]) f[i] = f[i - 1]; 12 if(maxLen < f[i]) maxLen = f[i]; 13 } 14 return maxLen; 15 } 16 private int[] bucketSort(int[] num) { 17 if(num == null || num.length == 0) return null; 18 int max = 0, min = 0; 19 for(int i : num) { 20 if(max <= i) max = i; 21 if(min >= i) min = i; 22 } 23 long[] bucket = new long[max - min + 1]; 24 for(int i : num) { 25 //如果min= 3, 4应该放在1的位置 26 bucket[i - min]++; 27 } 28 int[] result = new int[num.length]; 29 int i = 0; 30 for(int j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) { 31 if(bucket[j] == 0) continue; 32 while(bucket[j] != 0) { 33 result[i] = j + min; 34 bucket[j] -= 1; 35 i++; 36 } 37 } 38 return result; 39 }

1 public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) { 2 if(num == null || num.length == 0) return 0; 3 Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); 4 for(int i : num) set.add(i); 5 int max = 0; 6 for(int i = 0; i< num.length; i++) { 7 int down = num[i]; 8 while(set.contains(down)) { 9 set.remove(down); 10 down--; 11 } 12 int up = num[i] + 1; 13 while(set.contains(up)) { 14 set.remove(up); 15 up++; 16 } 17 max = Math.max(max, up-down - 1); 18 } 19 return max; 20 }

1 public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) { 2 if(num == null || num.length == 0) return 0; 3 int max = 1; 4 Arrays.sort(num); 5 HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); 6 for(int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) { 7 if(map.get(num[i]) != null) { 8 map.put(num[i] + 1, map.get(num[i]) + 1); 9 } else map.put(num[i] + 1, 1); 10 max = Math.max(max, map.get(num[i] + 1)); 11 } 12 return max; 13 } 14 //用set存放,while循环找顺序序列,而不需要提前排序 15 public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) { 16 if(num == null || num.length == 0) return 0; 17 HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); 18 for(int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) { 19 set.add(num[i]); 20 } 21 int max = 1; 22 for(int i=0;i< num.length; i++) { 23 int down = num[i] - 1; 24 while(set.contains(down)) { 25 set.remove(down); 26 down--; 27 } 28 int up = num[i] + 1; 29 while(set.contains(up)) { 30 set.remove(up); 31 up++; 32 } 33 max = Math.max(max, up - down -1); 34 } 35 return max; 36 }
9 最大子数组 部分答案看不懂,还是不懂~~~
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/maximum-subarray/
注意点:

1 public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { 2 //错误点: 没有考虑到 4,-1,2,1 这种情况,应该是6,目前结果时4. 3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; 4 int[] f = new int[nums.length]; 5 int max = f[0] = nums[0]; 6 for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { 7 if(nums[i] >= 0) { 8 if(f[i - 1] >=0) f[i] = f[i-1] + nums[i]; 9 else f[i] = nums[i]; 10 } else { 11 if(f[i - 1] < nums[i]) f[i] = nums[i]; 12 else f[i] = nums[i]; 13 14 } 15 max = Math.max(max, f[i]); 16 } 17 return max; 18 } 19 public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { 20 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; 21 int max = nums[0], sum = 0; 22 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 23 sum +=nums[i]; 24 max = Math.max(sum, max); 25 sum = Math.max(sum, 0); 26 } 27 return max; 28 }

1 public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { 2 int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, sum = 0; 3 if(nums == null || nums.length ==0) return 0; 4 for(int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) { 5 sum += nums[i]; 6 max = Math.max(sum, max); //用max记录每次sum后现阶段遇到的最大sum和。 7 sum = Math.max(0, sum); //每次sum的和一定要大于0,否则之前sum的数字就不要了。 8 } 9 return max; 10 } 11 //--------------------------------------------------------------- 12 public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { 13 int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, sum = 0; 14 if(nums == null || nums.length ==0) return 0; 15 int[] partMax = new int[nums.length]; 16 int[] globalMax = new int[nums.length]; 17 partMax[0] = globalMax[0] = nums[0]; 18 19 for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { 20 partMax[i] = Math.max(partMax[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]); 21 globalMax = Math.max(partMax[i], globalMax[i-1]); 22 } 23 return globalMax[nums.length - 1]; 24 }
10 分割回文串2
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/palindrome-partitioning-ii/#
注意点:

1 private boolean[][] getInstance(String s) { 2 boolean[][] str = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()]; 3 for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { 4 str[i][i] = true; 5 } 6 for(int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) { 7 str[i][i+1] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i+1); 8 } 9 for(int len = 2;len <s.length(); len++) { 10 for(int i = 0; i + len < s.length(); i++) { 11 str[i][i+len] = str[i + 1][i+len -1] && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i+len); 12 } 13 } 14 return str; 15 } 16 public int minCut(String s) { 17 if(s==null || s.length() ==0) return 0; 18 boolean[][] str = getInstance(s); 19 int[] f = new int[s.length() + 1]; 20 for(int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) { 21 f[i] = i - 1; 22 } 23 for(int i= 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { 24 for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 25 if(str[j][i-1]) { 26 f[i]= Math.min(f[i], f[j] + 1); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 return f[f.length -1]; 31 }

1 for(int i = 0; i<f.length; i++) { 2 f[i] = i - 1; //i长度的字符串,最多分割i-1刀可以构成回文串,设为Integer.MAX_VALUE也行,关键是f[0]=-1,f[1]=0 3 } 4 for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { //长度为i的字符串 5 for(int j = 0; j< i; j++) { //两个子串: 0~j-1, j~i-1,判断是否是回文串。 6 if(str[j][i-1]) { 7 f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j] + 1); //f[j]已经在之前求出来了,表示0~j-1这j个字符至少分几刀可以形成回文串 8 } 9 } 10 }

1 private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) { 2 for(int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++,j--) { 3 if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) return false; 4 } 5 return true; 6 } 7 private boolean[][] getPalindromeInstance(String s) { 8 boolean[][] str = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()]; 9 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++) { 10 str[i][i] = true; 11 } 12 for(int i = 0; i<s.length() - 1; i++) { 13 str[i][i+1] = isPalindrome(s, i, i+1); 14 } 15 for(int len = 2; len < s.length(); len++) { //长度是len+1的子串 16 for(int i = 0; i + len < s.length(); i++) { //len+i代表尾角标位置 17 str[i][i+len] = isPalindrome(s, i + 1, i+len - 1) && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i+len); 18 } 19 } 20 return str; 21 } 22 public int minCut(String s) { 23 if(s==null || s.length() == 0) return 0; 24 boolean[][] str = getPalindromeInstance(s); 25 26 int[] f = new int[s.length() + 1]; 27 for(int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) { //长度为i的字符串最多分割i-1次就可以都是回文串,也可以将f[i]设为Integer.MAX_VALUE; 28 f[i] = i - 1; 29 } 30 for(int i = 1; i<= s.length(); i++) {//i个字符构成回文串 31 for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 32 if(str[j][i -1]) { 33 f[i] = Math.min(f[i],f[j] + 1); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 return f[f.length - 1]; 38 }
11 单词分割
http://www.lintcode.com/problem/word-break

1 public boolean wordBreak(String s, Set<String> dict) { 2 if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return true; 3 if(dict == null ||dict.size() == 0) return false; 4 int wordLen = 0; 5 for(String s1 : dict) { 6 wordLen = Math.max(wordLen, s1.length()); 7 } 8 boolean f[] = new boolean[s.length() + 1]; 9 f[0] = true; 10 for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { //i表示包含i个单词,j表示最后一个单词的长度 11 f[i] = false; 12 //0~i-1 0~i-j-1,i-j~i-1 13 for(int j=1;j<=wordLen && j<=i; j++) { 14 if(f[i-j]) { 15 if(dick.contains(s.subString(i-j, i-1))) { 16 f[i] = true; 17 break; 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 return f[f.length - 1]; 23 }

1 public boolean wordBreak(String s, Set<String> dict) { 2 if(s == null || dict == null) return false; 3 if(dict.size() == 0) { 4 if(s.length() == 0 ) return true; 5 return false; 6 } 7 int maxLen = 0; 8 for(String s1 : dict) { 9 maxLen = Math.max(s1.length(), maxLen); 10 } 11 boolean[] canBreak = new boolean[s.length() + 1]; 12 canBreak[0] = true; 13 for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { 14 canBreak[i] = false; 15 for(int lastWordLen = 1; lastWordLen <=i && lastWordLen <= maxLen; lastWordLen++) { 16 if(canBreak[i - lastWordLen]) { //最后一个单词的下标是 [i - lastWordLen, i) 左开右闭,包含的字符个数为lastWordLen 17 String word = s.substring(i - lastWordLen, i); 18 if(dict.contains(word)) { 19 canBreak[i] = true; 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 return canBreak[s.length()]; 26 }
12 最长公共子序列 LCS
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-common-subsequence/#

1 public int longestCommonSubsequence(String A, String B) { 2 if(A == null || B == null || A.length() == 0 || B.length() == 0) { 3 return 0; 4 } 5 int m = A.length(), n = B.length(); 6 int[][] f = new int[m+1][n+1]; 7 for(int i = 1; i <=m; i++) { 8 f[i][0] = 0; 9 } 10 for(int i = 0; i <=n; i++) { 11 f[0][i] = 0; 12 } 13 for(int i = 1; i<=m; i++) { 14 for(int j =1; j<=n; j++) { 15 if(A.charAt(i-1) == B.charAt(j-1)) { 16 f[i][j] = f[i-1][j-1]+1; 17 } else { 18 f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j-1],f[i-1][j]); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 return f[m][n]; 23 }

1 public int longestCommonSubsequence(String A, String B) { 2 if(A == null || B == null || A.length() == 0 || B.length() == 0) return 0; 3 int[][] lcs = new int[A.length() + 1][B.length() + 1]; 4 for(int i = 0; i <= A.length(); i++) { 5 lcs[i][0] = 0; 6 } 7 for(int j = 0; j <= B.length(); j++) { 8 lcs[0][j] = 0; 9 } 10 for(int i = 1; i <= A.length(); i++) { 11 for(int j = 1; j <= B.length(); j++) { 12 if(A.charAt(i-1) == B.charAt(j-1)) { 13 lcs[i][j] = Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j - 1]+1, Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j], lcs[i][j - 1])); //只写lcs[]][]+1即可,不用判断的 14 } else { 15 lcs[i][j] = Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j - 1]+0, Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j], lcs[i][j - 1])); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 return lcs[A.length()][B.length()]; 20 }
13 最长公共子串
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-common-substring/#
问题: contains复杂度O(n)???
注意点:
错误点: f[i][j]的含义搞不太懂,想一想递归关系之间的具体实现过程。在循环过程中,公共子串中的每一个字符都会作为最后一个字符去进行比较。

1 public int longestCommonSubstring(String A, String B) { 2 if(A == null || B == null || A.length() == 0 || B.length() == 0) return 0; 3 int max = 0; 4 for(int i = 0; i < A.length(); i++) { 5 for(int j= i + 1; j <= A.length(); j++) { 6 if(B.contains(A.substring(i,j))) max = Math.max(max, j- i); 7 } 8 } 9 return max; //O(n * n * n) 10 } 11 //---------------------------------------------------- 12 public int longestCommonSubstring(String A, String B) { 13 if(A == null || B == null || A.length() == 0 || B.length() == 0) return 0; 14 15 int[][] lcs = new int[A.length() + 1][B.length() + 1]; 16 for(int i = 1; i <= A.length(); i++) { 17 for(int j = 1; j <= B.length(); j++) { 18 if(A.charAt(i-1) == B.charAt(j-1)) { 19 lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1]+1; 20 } else { 21 lcs[i][j] = 0; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 26 int max = 0; 27 for(int i = 1; i <= A.length(); i++) { 28 for(int j = 1; j <= B.length(); j++) { 29 max = Math.max(max, lcs[i][j]); 30 } 31 } 32 return max; 33 }
14 编辑距离
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/edit-distance/#

1 // 为什么要死记公式啊,先求lcs再去匹配一致,考虑并不周全 abc cab 2 public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) { 3 if(word1 == null || word2 == null) { 4 if(word1 != null) return word1.length(); 5 if(word2 != null) return word2.length(); 6 return 0; 7 } 8 int[][] lcs = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1]; 9 for(int i = 1; i <= word1.length(); i++) { 10 for(int j = 1; j <= word2.length(); j++) { 11 if(word1.charAt(i-1) == word2.charAt(j-1)) { 12 lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1]+1; 13 } else { 14 lcs[i][j] = 0; 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 int max = 0; 19 for(int i = 1; i <= word1.length(); i++) { 20 for(int j = 1; j <= word2.length(); j++) { 21 max = Math.max(max, lcs[i][j]); 22 } 23 } 24 return Math.max(word1.length()-max, word2.length() - max); 25 } 26 //---------------------- 27 public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) { 28 if(word1 == null || word2 == null) { 29 if(word1 != null) return word1.length(); 30 if(word2 != null) return word2.length(); 31 return 0; 32 } 33 int[][] f = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1]; 34 for(int i = 0; i <= word1.length(); i++) f[i][0] = i; 35 for(int j = 0; j <= word2.length(); j++) f[0][j] = j; 36 37 for(int i = 1; i <=word1.length(); i++) { 38 for(int j = 1; j <= word2.length(); j++) { 39 if(word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) { 40 f[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(f[i-1][j] + 1, f[i][j-1]+1),f[i- 1][j - 1]); 41 } else { 42 f[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(f[i-1][j] + 1, f[i][j-1]+1),f[i- 1][j - 1] + 1); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 return f[word1.length()][word2.length()]; 47 }
链表----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意事项: 调用node.next时,一定要确保node非null,否则空指针异常。
链表的head 和head.next是否为空先判断下,类似二叉树root要单独拿出来考虑一样。

1 链表的基本操作 2 1. Insert a Node in Sorted List 3 2. Remove a Node from Linked List 4 3. Reverse a Linked List 5 4. Merge Two Linked Lists 6 5. Middle of a Linked List 7 8 1. // 最简单的方法 9 private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { 10 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 11 ListNode prev = null; 12 while(head!= null ) { 13 ListNode temp = head.next; 14 head.next = prev; 15 prev = head; 16 head = temp; 17 } 18 return prev; 19 } 20 //另一种写法 21 private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { 22 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 23 ListNode tail = head; 24 ListNode next =tail.next; 25 while(next != null) { 26 ListNode temp = next.next; 27 next.next =tail; 28 tail = next; 29 next =temp; 30 } 31 head =tail; 32 tail.next = null; 33 return head; 34 } 35 4. private ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) { 36 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy; 37 while(left != null && right != null) { 38 tail.next = left; 39 left = left.next; 40 tail = tail.next; 41 tail.next = right; 42 right.next = right; 43 tail = tail.next; 44 } 45 if(left != null) tail.next = left; 46 else tail.next = right; 47 return dummy.next; 48 } 49 5. 快慢指针 50 private ListNode getMid(ListNode head) {} 51 //12345 要找到3 52 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 53 ListNode slow = head, fast = head; 54 while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 55 slow = slow.next; 56 fast = fast.next.next; 57 } 58 return slow; 59 //查找倒数第n个结点 60 private ListNode find(ListNode head) { 61 ListNode slow = head, fast = head; 62 // 1 2 3 4 5 找4,倒数第2个,需要在fast走第二步的时候,slow开始走第一步 63 int i = 0; 64 while(fast.next != null) { 65 i++; 66 fast = fast.next; 67 if(i < 2) coutinue; 68 slow = slow.next; 69 } 70 return slow; 71 }
1 删除排序链表2
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/

1 //----------------运行超时 2 public static ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { 3 // write your code here 4 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 5 ListNode prev = null; 6 ListNode curr = head; 7 Map<ListNode,Integer> map = new HashMap<ListNode,Integer>(); 8 int value = 0; 9 while(curr != null) { 10 if(map.get(curr) != null) { 11 map.put(curr,map.get(curr) + 1); 12 } else { 13 map.put(curr,1); 14 } 15 } 16 prev.next = head; 17 curr = head; 18 ListNode currNext = curr.next; 19 while(currNext != null) { 20 if(map.get(currNext) != 1) { 21 curr = currNext; 22 currNext.next = currNext.next; 23 } 24 } 25 return prev.next; 26 } 27 //-------------------------------------------------- 28 public static ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { 29 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 30 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 31 dummy.next = head; 32 //只要不用next操作,引用再怎么换也不会影响链表。 33 head = dummy; 34 while(head.next != null && head.next.next != null) { 35 if(head.next.val == head.next.next.val) { 36 int val = head.next.val; 37 while(head.next != null && head.next.val == val) { 38 head.next = head.next.next; 39 } 40 } else { 41 head = head.next; 42 } 43 } 44 return dummy.next; 45 }
2 删除排序链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/#
注意点:引入dummy的目的是为了不用将头结点删除与否分情况讨论。这里头结点肯定不用删除,所以可以不引入dummy。
也可以沿用删除链表2的解法,稍微改改。

1 public static ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { 2 // write your code here 3 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 4 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 5 dummy.next = head; 6 head = dummy; 7 while(head.next != null && head.next.next != null) { 8 if(head.next.val == head.next.next.val) { 9 head.next = head.next.next; 10 } else head = head.next; 11 } 12 return dummy.next; 13 }
3 反转链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/reverse-linked-list/
注意点: 死记解法,四步骤

1 public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { 2 // write your code here 3 ListNode prev = null; 4 while(head != null) { 5 ListNode temp = head.next; 6 head.next = prev; 7 prev = head; 8 head = temp; 9 } 10 return prev; 11 }
4 反转链表2
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/reverse-linked-list-ii/
错误点: 第二个for循环里写成了if(nPost.next== null) return null;
注意点: 第二个for循环里,n~m ,共n-m+1个数字,需要nNode走n-m次,i=m+1时,n移动了一次,所以i最后出了循环需要等于m+n-m = n

1 public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m , int n) { 2 if(head == null || m >= n) return head; 3 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 4 dummy.next = head; 5 head = dummy; 6 for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) { 7 if(head != null) head = head.next; 8 else return null; 9 } 10 ListNode mprev = head; 11 ListNode mNode = mprev.next; 12 ListNode nNode = mNode; 13 ListNode nPost = nNode.next; 14 for(int i = m; i < n;i++) { 15 if(nPost == null) return null; 16 ListNode temp = nPost.next; 17 nPost.next = nNode; 18 nNode = nPost; 19 nPost = temp; 20 } 21 mprev.next = nNode; 22 mNode.next = nPost; 23 return dummy.next; 24 25 }
5 链表划分
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/partition-list/
注意点: 将链表分成两个子链,左链放比指定数小的,右链连比指定数大的,最后再将他们合并。
leftDummy和rightDummy保持不动,作为头指针,然后从它们的位置发出left和right指针,作为尾指针,依次移动记录当前子链表的最后一个位置。
头指针.next=头结点,尾指针=尾结点

1 public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { 2 if(head == null) return head; 3 ListNode leftDummy = new ListNode(0); 4 ListNode rightDummy = new ListNode(0); 5 ListNode left = leftDummy, right = rightDummy; 6 while(head != null) { 7 if(head.val < x) { 8 left.next = head; 9 left = head; 10 } else { 11 right.next = head; 12 right = head; 13 } 14 head = head.next; 15 } 16 right.next = null; 17 left.next = rightDummy.next; 18 return leftDummy.next; 19 }
6 链表排序
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/sort-list/#
注意点:
错误点: sortList(ListNode head) 里if(head == null )而不判断head.next会报错,为啥??????

1 private ListNode findMid(ListNode head) { 2 ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next; 3 while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 4 fast = fast.next.next; 5 slow = slow.next; 6 } 7 return slow; 8 // 12345 return 2; 9 } 10 private ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { 11 //dummy是合并后主链表的头,tail是尾。head1或head2中每当有一个结点链入主链,那链入的那个结点就可以 12 //在原先的链表中删除了,同时把原先的链表的头往后移。因为主链中加入了一个结点,所以主链的tail后移一次。 13 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy; 14 while(head1 != null && head2 != null) { 15 if(head1.val < head2.val) { 16 tail.next = head1; 17 head1 = head1.next; 18 } else { 19 tail.next = head2; 20 head2 = head2.next; 21 } 22 tail = tail.next; 23 } 24 //head1或head2有一个都链入主链后,把另一个非空的原先链表在链到主链尾部 25 //(这时原先链表中的后面位置的结点并没有进行排序。) 26 //最后返回的结果只是将head1或者head2进行排序了。(head1为空,则代表它完成排序了) 27 //要保证最后都有序,则head1和head2必须先有序。 28 if(head1 != null) { 29 tail.next = head1; 30 } else { 31 tail.next = head2; 32 } 33 return dummy.next; 34 } 35 36 public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { 37 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 38 ListNode mid = findMid(head); 39 ListNode right = sortList(mid.next); 40 mid.next = null; 41 ListNode left = sortList(head); 42 return merge(left, right); 43 }
7 重排链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/reorder-list/#

1 public void reorderList(ListNode head) { 2 if(head == null || head.next == null) return; 3 ListNode mid = getMid(head); 4 ListNode right = reverse(mid.next); 5 mid.next = null; 6 head = merge(head, right); 7 } 8 9 private ListNode getMid(ListNode head) {} 10 //12345 15243 要找到3 11 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 12 ListNode slow = head, fast = head; 13 while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 14 slow = slow.next; 15 fast = fast.next.next; 16 } 17 return slow; 18 } 19 private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { 20 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 21 22 ListNode prev = null; 23 while(head!= null ) { 24 ListNode temp = head.next; 25 head.next = prev; 26 prev = head; 27 head = temp; 28 } 29 return prev; 30 } 31 private ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) { 32 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy; 33 while(left != null && right != null) { 34 tail.next = left; 35 left = left.next; 36 tail = tail.next; 37 tail.next = right; 38 right = right.next; 39 tail = tail.next; 40 } 41 if(left != null) tail.next = left; 42 else tail.next = right; 43 return dummy.next; 44 }
8 带环链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/linked-list-cycle-ii/#
注意点:快慢指针

1 public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { 2 if(head == null || head.next == null) return null; 3 ListNode slow1 = head, fast = head; 4 while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 5 slow1= slow1.next; 6 fast = fast.next.next; 7 if(slow1 == fast) { 8 ListNode slow2 = head; 9 while(true) { 10 if(slow1 == slow2) return slow1; 11 slow2 = slow2.next; 12 slow1 = slow1.next; 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 return null; 17 }
9 旋转链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/rotate-list/#

1 public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { 2 if(head == null || head.next == null || k == 0) return head; 3 int len = 0; 4 ListNode temp = head; 5 while( temp != null ) { 6 len++; 7 temp = temp.next; 8 } 9 k = k % len; 10 if(k == 0) return head; 11 ListNode tail= head; 12 int i = 1; 13 while( len - k != i) { 14 i++; 15 tail = tail.next; 16 } 17 ListNode newHead = tail.next, temp1 = newHead; 18 tail.next = null; 19 while(temp1.next != null) { 20 temp1 = temp1.next; 21 } 22 temp1.next = head; 23 return newHead; 24 } 25 //---------------------------------------------------- 26 private int getLength(ListNode head) { 27 int length = 0; 28 while (head != null) { 29 length ++; 30 head = head.next; 31 } 32 return length; 33 } 34 35 public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int n) { 36 if (head == null) { 37 return null; 38 } 39 40 int length = getLength(head); 41 n = n % length; 42 43 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 44 dummy.next = head; 45 head = dummy; 46 47 ListNode tail = dummy; 48 //寻找倒数第n个结点(类似快慢指针实现的) 49 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 50 head = head.next; 51 } 52 while (head.next != null) { 53 tail = tail.next; 54 head = head.next; 55 } 56 57 head.next = dummy.next; 58 dummy.next = tail.next; 59 tail.next = null; 60 return dummy.next; 61 }
10 合并k个排序链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/merge-k-sorted-lists/

1 //两两合并---------------------------------------------- 2 public ListNode mergeKLists(List<ListNode> lists) { 3 if(lists == null || lists.size() == 0) return null; 4 5 while(lists.size() > 1) { 6 List<ListNode> newList = new ArrayList<ListNode>(); 7 for(int i = 0; i + 1< lists.size() ; i+=2) { 8 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 9 dummy.next = mergeTwo(lists.get(i), lists.get(i+1)); 10 newList.add(dummy.next); 11 } 12 if(lists.size() % 2 != 0) newList.add(lists.get(lists.size() - 1)); 13 lists = newList; 14 } 15 return lists.get(0); 16 } 17 18 private ListNode mergeTwo(ListNode node1, ListNode node2) { 19 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy; 20 while(node1 != null && node2 != null) { 21 if(node1.val < node2.val) { 22 tail.next = node1; 23 node1 = node1.next; 24 } else { 25 tail.next = node2; 26 node2 = node2.next; 27 } 28 tail = tail.next; 29 } 30 if(node1 != null) { 31 tail.next = node1; 32 } else { 33 tail.next = node2; 34 } 35 return dummy.next; 36 } 37 //分治------------------------------------------------- 38 public ListNode mergeKLists(List<ListNode> lists) { 39 if(lists == null || lists.size() == 0) return null; 40 return mergeHelper(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1); 41 } 42 private ListNode mergeHelper(List<ListNode> lists, int start , int end) { 43 if(start == end) return lists.get(start); 44 int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; 45 ListNode left = mergeHelper(lists, start, mid); 46 ListNode right = mergeHelper(lists, mid+1, end); 47 return mergeTwo(left, right); 48 } 49 50 private ListNode mergeTwo(ListNode node1, ListNode node2) { 51 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy; 52 while(node1 != null && node2 != null) { 53 if(node1.val < node2.val) { 54 tail.next = node1; 55 node1 = node1.next; 56 } else { 57 tail.next = node2; 58 node2 = node2.next; 59 } 60 tail = tail.next; 61 } 62 if(node1 != null) { 63 tail.next = node1; 64 } else { 65 tail.next = node2; 66 } 67 return dummy.next; 68 }
11 复制随机指针链表
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/copy-list-with-random-pointer/#
注意点:传入head并在另一个函数中操作时,并不会引起传入前的head的变化。
见答案,不需要返回值 http://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/copy-list-with-random-pointer/

1 public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { 2 if(head == null) return head; 3 head = insert(head); 4 RandomListNode dummy = new RandomListNode(0); 5 dummy.next = head; 6 while(head != null) { 7 if(head.random == null) { 8 head.next.random = null; 9 } else { 10 head.next.random = head.random.next; 11 } 12 head = head.next.next; 13 } 14 dummy.next = remove(dummy.next); 15 return dummy.next; 16 17 } 18 private RandomListNode insert(RandomListNode head) { 19 if(head == null) return head; 20 RandomListNode dummy = new RandomListNode(0); 21 dummy.next = head; 22 while(head != null) { 23 RandomListNode temp = new RandomListNode(head.label); 24 temp.next = head.next; 25 head.next = temp; 26 head = head.next.next; 27 } 28 return dummy.next; 29 } 30 private RandomListNode remove(RandomListNode head) { 31 RandomListNode dummy = new RandomListNode(0); 32 dummy.next = head.next; 33 while(head.next.next != null) { 34 RandomListNode temp = head.next.next; 35 head.next.next = head.next.next.next; 36 head = temp; 37 } 38 return dummy.next; 39 }
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Arrays 拿到数组先排序,最快需要nlogn.(快排,归并,堆排),然后看看排序是否有助于问题解决,是否满足复杂度要求。
数组和的问题,排序后,收尾指针依次中间移动,可以以O(n)的代价,遍历一次就能判断是否满足。
1 合并排序数组
注意点:可以从头开始合并,也可以从尾开始合并
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/merge-sorted-array/

1 public void mergeSortedArray(int[] A, int m, int[] B, int n) { 2 int index = m+n-1, i = m - 1, j = n - 1; 3 while(i >=0 && j >=0) { 4 if(A[i] > B[j]) { 5 A[index--] = A[i--]; 6 7 } else { 8 A[index--] = B[j--]; 9 } 10 } 11 while(i >= 0) { 12 A[index--] = A[i--]; 13 } 14 while(j >= 0) { 15 A[index--] = B[j--]; 16 } 17 18 }
2 两个排序数组的中位数
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/
注意点:找中点,就是找第k个数,依次剔除k/2, k/4,......1个数,剩下的就是要找的数。
如果k个排序数组找中位数,则二分答案,判断此答案是否位于中间。
错误点: 需要double,则return时除的时候要 /2.0 而不是 /2

1 // A = 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 // B = 1 3 // 找中点,第k = 4大的数,则先去掉 k/2 = 2 个数,之后再从剩下的数中找第k-k/2 = 2大的数。 4 // 去2个数时,由于B不包含2个数,所以把A的前2个数去掉,剩下: 4 5 6 7 和 1; 5 // 从它们中找第2大的数就是结果。去掉的数不一定非要是A,B中最小的前几个数,只要保证去掉的数比要找的数小,那要找的数的相对位置就不会变。 6 // 在4 5 6 7 和 1中找第2个大的数时,先去掉1个数,在从剩下的里面找第一个大的数就是结果。所以把1去掉,剩下了4 5 6 7 。这时第1个大的数是4,也就是最后结果。 7 8 public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] A, int[] B) { 9 int len = A.length + B.length; 10 if(len % 2 == 1) return findKth(A, 0, B, 0, len/2+1); 11 else return (findKth(A, 0, B, 0, len/2) + findKth(A, 0, B, 0, len/2+1)) / 2.0; 12 } 13 //函数含义:A数组从AStart角标开始,B从BStart开始,寻找A,B中第k个大的数 14 private int findKth(int[] A, int AStart, int[] B, int BStart, int k) { 15 if(AStart >= A.length) return B[BStart + k - 1]; 16 if(BStart >= B.length) return A[AStart + k - 1]; 17 18 if(k == 1) { 19 return Math.min(A[AStart], B[BStart]); 20 } 21 22 //找第k个,先去掉前k/2个数,AValue和BValue不可能都是MAX_VALUE 23 int AValue = AStart + k/2 - 1 < A.length ? A[AStart + k/2 - 1] : Integer.MAX_VALUE; 24 int BValue = BStart + k/2 - 1 < B.length ? B[BStart + k/2 - 1] : Integer.MAX_VALUE; 25 if(AValue <= BValue) { 26 //去A的前k/2个数,则去掉后的角标从AStart+k/2开始 27 return findKth(A, AStart+k/2, B, BStart, k - k/2); //递归的终止条件是k-k/2=1,一定会走到1,因为1+2+...+ k/2 = k - 1 k是偶数,1+1+2+...+ k/2 = k - 1 k是奇数 28 } else { 29 return findKth(A, AStart, B, BStart + k/2, k - k/2); 30 } 31 }
3 最大子数组2
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/maximum-subarray-ii/
衍生:最小子数组 http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/minimum-subarray/# 把数组取反,求出最大子数组,再把结果取反即可。
最大子数组差 http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/maximum-subarray-difference/ 左右求出最大最小子数组,因为不许重叠,所以找分割线依次比较。
错误点:a=1,b=2;错,要写成a=1;b=2;
int a =1, b = 2; 可以
注意点:见答案

1 //最大子数组答案 http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/maximum-subarray/ 2 public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { 3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; 4 int sum = 0, preFixSum = 0, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 5 //理解不了的话,只需要知道这个操作能实现功能就行,死记代码 6 for(int i = 0; i< nums.length; i++) { 7 sum+= nums[i]; 8 max = Math.max(max, sum - preFixSum); 9 preFixSum = Math.min(preFixSum, sum); 10 } 11 return max; 12 } 13 14 public int maxTwoSubArrays(List<Integer> nums) { 15 if(nums == null || nums.size() <= 1) return 0; 16 // i是分割线位置,i+1就是分割线之后的第一个位置的坐标 17 int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 18 for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) { 19 int max1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max2 = max1; 20 int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, preFix1 = 0, preFix2 = 0; 21 for(int j = 0; j <=i; j++) { 22 sum1+=nums.get(j); 23 max1 = Math.max(max1, sum1 - preFix1); 24 preFix1 = Math.min(preFix1, sum1); 25 } 26 for(int j = i+1; j < nums.size(); j++) { 27 sum2+=nums.get(j); 28 max2 = Math.max(max2, sum2 - preFix2); 29 preFix1 = Math.min(preFix2, sum2); 30 } 31 result = Math.max(result, max1+max2); 32 } 33 return result; 34 } 35 //O(n)--------------------------------------------- 36 public int maxTwoSubArrays(List<Integer> nums) { 37 int[] left = new int[nums.size()]; 38 int[] right = new int[nums.size()]; 39 int sum = 0, preFixSum = 0, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 40 for(int i = 0; i< nums.size(); i++) { 41 sum+= nums[i]; 42 max = Math.max(max, sum - preFixSum); 43 preFixSum = Math.min(preFixSum, sum); 44 left[i] = max; 45 } 46 sum = 0, preFixSum = 0, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 47 for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 48 sum+= nums[i]; 49 max = Math.max(max, sum - preFixSum); 50 preFixSum = Math.min(preFixSum, sum); 51 right[i] = max; 52 } 53 int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 54 for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) { 55 result = Math.max(result, left[i] + right[i+1]); 56 } 57 return result; 58 }
4 买卖股票的最佳时机
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/#
注意点:包含DP
错误点: ①profit = Math.max(profit, i - min);
②min = Math.min(min, i); 一二前后顺序的区别是是否每一轮至少要包含一个数。此题中盈利的计算,一开始是买入,没有盈利,所以也即一个数都不能包含,
所以要先②后①。

1 //错误逻辑,思路都理不清,代码更写不出来。 2 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 3 if(prices == null || prices.length <= 1) return 0; 4 int profit = 0, min = 0; 5 for(int i : prices) { 6 min = Math.min(min, i); 7 profit + = i - min; 8 } 9 return profit; 10 } 11 // 当天有盈利,代表着当天卖出和前一天买入。连续三天盈利,每隔天的买入卖出正好合下来是三天前买入,三天后卖出的情况。 1 2 3 4 12 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 13 int profit = 0; 14 for(int i = 0; i < prices.length- 1; i++) { 15 int diff = prices[i + 1] - prices[i]; 16 if(diff > 0) profit += diff; 17 } 18 return profit; 19 }

1 //----------------------------------------------------------- 2 // 暴力破解 3 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 4 if(prices == null || prices.length == 0) return 0; 5 int max =0 ; 6 for(int i = 1; i< prices.length; i++) { 7 int sum = 0; 8 for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 9 max= Math.max(max, prices[i] - prices[j]); 10 } 11 } 12 return max; 13 } 14 //------------------------------------------------------ 15 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 16 if(prices == null || prices.length == 0) return 0; 17 int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, profit = 0; 18 for(int i : prices) { 19 min = Math.min(i, min); // min = i < min ? i : min; 20 profit = Math.max(i - min, profit); 21 } 22 return profit; 23 } 24 25 //股票二------------------------------------------ 26 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 27 int profit = 0; 28 for(int i = 0; i < prices.length- 1; i++) { 29 int diff = prices[i + 1] - prices[i]; 30 if(diff > 0) profit += diff; 31 } 32 return profit; 33 } 34 35 //股票三----------------------------------------------- 36 public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { 37 if (prices == null || prices.length <= 1) { 38 return 0; 39 } 40 41 int[] left = int[prices.length]; 42 int[] right = int[prices.length]; 43 44 //从左往右看,不依赖于右侧,能卖出的最大利润。通过更新买入的最小值(min)来计算 DP 45 int min = prices[0], left[0] = 0; 46 for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { 47 min = math.min(min, prices[i]); 48 left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], prices[i] - min); 49 } 50 51 //从右往左看,不依赖于左侧,能卖出的最大利润。通过更新卖出的最大值(max)来计算 52 int max = prices[prices.length - 1], right[prices.length - 1] = 0; 53 for(int i = prices.length -2; i>=0; i--) { 54 max = Math.max(prices[i], max); 55 right[i] = Math.max(right[i + 1], max - prices[i]); 56 } 57 58 //类似分割线,left和right不交叉 59 int maxProfit = 0; 60 for(int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) { 61 maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, left[i] + right[i]); 62 } 63 return maxProfit; 64 }
5 两数和
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/two-sum/
衍生: 三数和 http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/3sum/
4数 http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/4sum/
注意点:时间复杂度的计算:
排序模块的最优复杂度nlogn,找两数和的复杂度n,所以合并的复杂度是nlogn,即用这种方法的复杂度为nlogn。
如果放入map中,遍历一次数组,复杂度n,判断map是否包含,n,所以最后合并的复杂度n。

1 //O(n * n)--------------------------------------------------------------- 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { 3 if(numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) return new int[]{-1, -1}; 4 for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length - 1; i++) { 5 for(int j = i +1; j < numbers.length; j++) { 6 if(numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) return new int[]{i +1, j+1}; 7 } 8 } 9 return new int[]{-1, -1}; 10 11 //O(nlogn)-------------------------- 12 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { 13 //先排序,获得排序数组nlogn,下面的操作是O(n),最后总体的时间复杂度nlogn. 14 if(numbers == null || numbers.length <=1) return new int[]{-1, -1}; 15 for(int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1; i < j;) { 16 if(numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) return new int[]{i + 1,j + 1}; 17 else if ( numbers[i] + numbers[j] < target) i++; 18 else j--; 19 } 20 return new int[]{-1, -1}; 21 22 } 23 //O(n)------------------------------ 24 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { 25 if(numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) return null; 26 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); 27 for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { 28 if(map.containsKey(numbers[i])) { 29 return new int[] {map.get(numbers[i]) + 1, i+1}; 30 } 31 map.put(target - numbers[i], i); 32 } 33 return null;
6 数组划分 (类似快排)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/partition-array/#
衍生: http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/sort-letters-by-case/ Character.isUpperCase()
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/sort-colors/
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/sort-colors-ii/ (相当于给定k个不同的数的快排)

1 //报错,rainb里不设置startColo会排序出问题,所以这种换位的快排操作到底会产生什么结果?---------------------------------------------- 2 public void sortColors2(int[] colors, int k) { 3 if (colors == null || colors.length == 0) { 4 return; 5 } 6 rainbowSort(colors, 0, colors.length - 1); 7 8 } 9 10 private void rainbowSort(int[] colors, int start, int end) { 11 if(colors == null || colors.length <= 1) return; 12 if(start >= end) return; 13 int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; 14 int k = colors[mid]; 15 int i = start, j = end; 16 while(i <= j) { 17 while(i <=j && colors[i] < k) i++; 18 while(i <=j && colors[j] >= k) j--; 19 if(i <= j) { 20 int temp = colors[i]; 21 colors[i] = colors[j]; 22 colors[j] = temp; 23 i++; 24 j--; 25 } 26 } 27 rainbowSort(colors, start, i - 1); 28 rainbowSort(colors,i + 1, end); 29 } 30 //能用--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 31 public void sortColors2(int[] colors, int k) { 32 if (colors == null || colors.length == 0) { 33 return; 34 } 35 rainbowSort(colors, 0, colors.length - 1, 1,k); 36 37 } 38 39 private void rainbowSort(int[] colors, int start, int end, int startColor, int endColor) { 40 if (startColor == endColor) { 41 return; 42 } 43 if(colors == null || colors.length <= 1) return; 44 if(start >= end) return; 45 int midColor = (startColor + endColor)/2; 46 int i = start, j = end; 47 while(i <= j) { 48 //为啥?????????????? 49 //这里必须 <= midColor, 不能是< 50 while(i <=j && colors[i] <= midColor) i++; 51 while(i <=j && colors[j] > midColor) j--; 52 if(i <= j) { 53 int temp = colors[i]; 54 colors[i] = colors[j]; 55 colors[j] = temp; 56 i++; 57 j--; 58 } 59 } 60 //这里必须是midColor,不能是midColor+1 61 rainbowSort(colors, start, i, startColor, midColor); 62 rainbowSort(colors,i,end, midColor+1, endColor); 63 }
注意点: 两个指针一首一尾遍历数组
死记住程序,条件统一写成 i <= j :这样返回的 i 始终是第一个大于等于k的位置,也正是题目所求。
if(i <= j) 调制完顺序后,i++,j--一下,减少下一次while里的操作。
 数组划分
数组划分
1 public int partitionArray(int[] nums, int k) { 2 if(nums == null | nums.length <= 0) return -1; 3 int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1; 4 while(i <= j) { 5 while(nums[i] < k) i++; 6 while(nums[j] >= k) j--; 7 if(i <= j) { 8 int temp = nums[j]; 9 nums[j] = nums[i]; 10 nums[i] = temp; 11 } 12 } 13 return i; 14 }
7 最接近零的子数组和
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/subarray-sum-closest/
问题:最后利用减前缀和求结果的时候,怎么知道这样的结果就离0最近? 难道是因为后一个肯定比前一个大,所以相减的结果一定大于0,最小的那个就是最接近0的?确实是这样。
-1,-3, -3,-2,1,4,;
-1位置补0 -1,-3, -3,-2,1,4, 前缀和 -1,-4,-7,-9,-8,-4,排序后:-9,-8,-7,-4,-4,-1。
子数组一共有O(n * n)个,这里两两相减也就O(n)个,不能全覆盖啊?
注意点: 实现Comparator比较器接口时,虽然接口中有俩抽象方法,但只需要实现compare方法就行,equals方法不用覆盖。
此题对应的解法,在数组中有0时,会返回两次0的角标作为返回结果。
错误点: new int[]{0,1} ,不要写错new int[2]{}

1 class Pair { 2 //记录前几个数的和 3 int sum; 4 int index; 5 public Pair(int s, int i) { 6 this.sum = s; 7 this.index = i; 8 } 9 } 10 11 public class Solution { 12 13 public int[] subarraySumClosest(int[] nums) { 14 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null; 15 if(nums.length == 1) return new int[]{0, 0}; 16 //结果集数组 17 int[] res = new int[2]; 18 19 int len = nums.length; 20 //遍历一次nums,获得Pair数组,其中,前0个数的和是0 21 Pair[] sums = new Pair[len + 1]; 22 sums[0] = new Pair(0,0); 23 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++) { 24 sums[i] = new Pair(sums[i - 1].sum + nums[i - 1], i); 25 } 26 27 Arrays.sort(sums, new Comparator<Pair>(){ 28 public int compare(Pair p1, Pair p2) { 29 return p1.sum - p2.sum; 30 } 31 }); 32 33 //排序完成后,遍历sums数组,找到离0最近的子数组,从角标1开始。 34 int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //answer 35 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++) { 36 if(ans > sums[i].sum - sums[i - 1].sum) { 37 ans = sums[i].sum - sums[i - 1].sum; 38 //Pair 记录的是前几个数的和,前0,1,2个等等,对应nums中的角标需要-1; 39 int[] temp = new int[]{sums[i].index - 1, sums[i - 1].index - 1}; 40 Arrays.sort(temp); 41 //前5个数的和-前3个数的和离0最近,则需要返回的是第4,第5个的角标,所以temp[0]+1; 42 res[0] = temp[0] + 1; 43 res[1] = temp[1]; 44 } 45 } 46 return res; 47 } 48 }
8 子数组之和(求子数组,先写出来前缀和,sum(i,j) = sum(j) - sum(i - 1),然后看它和所求的关系)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/subarray-sum/
注意点:子数组和为0,代表存在位置,sum(j) 等于sum(i-1)。
既然需要sum(i - 1),那为了求0位置的和同时能用到上面的递推关系,所以在-1位置放一个0;
两sum相等,相当于去重,hash表天然就是实现是否存在,相等问题的,所以使用hashMap存放数据。

1 public ArrayList<Integer> subarraySum(int[] nums) { 2 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null; 3 ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 4 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap(); 5 map.put(0, -1); 6 int sum = 0; 7 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 8 sum += nums[i]; 9 if(map.get(sum) != null) { 10 res.add(map.get(sum) + 1); 11 res.add(i); 12 return res; 13 } 14 map.put(sum, i); 15 } 16 return null; 17 }
数据结构
1 带最小值操作的栈
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/min-stack/#
注意点: 用另一个栈依次记录最小值。

1 public class MinStack { 2 3 //minStack的构造放到构造函数中比较好。 4 Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<Integer>(); 5 Stack<Integer> s ; 6 7 public MinStack() { 8 // do initialize if necessary 9 s = new Stack<Integer>(); 10 } 11 12 public void push(int number) { 13 // write your code here 14 s.push(number); 15 if(minStack.isEmpty() || minStack.peek() >= number) minStack.push(number); 16 } 17 18 public int pop() { 19 // write your code here 20 int number = s.pop(); 21 if(number == minStack.peek()) minStack.pop(); 22 return number; 23 } 24 25 public int min() { 26 // write your code here 27 28 return minStack.peek(); 29 } 30 }
2 用栈实现队列
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/implement-queue-by-two-stacks/#
3 直方图最大矩形覆盖(栈)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/#
注意点: 递增栈,每次角标出栈时才计算对应角标高度的直方图面积。(while循环里,栈内弹出一个数需要O(1),弹出n个数需要O(n),所以while的平均时间为O(1),所以
总体时间就只是for的时间,O(n))。
高度中找左边和右边第一个比他小的位置,然后就是此高度对应的宽度。

1 public int largestRectangleArea(int[] height) { 2 if(height == null || height.length == 0) return 0; 3 Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>(); 4 int max = 0; 5 for(int i = 0; i <= height.length; i++) { 6 int currHeight = (i == height.length)?-1:height[i]; 7 while(!s.isEmpty() && currHeight <= height[s.peek()]) { 8 int h = height[s.pop()]; 9 int w = s.isEmpty()? i: i - s.peek() - 1; 10 max = Math.max(max, h*w); 11 } 12 s.push(i); 13 } 14 return max; 15 }
4 哈希表原理(增删查的复杂度O(1),二叉查找树logn)
Cache (一个大的哈希表):memory级别的访问, ns级别,500M/b
数据库:文件系统访问,硬盘,微秒级别,500k/b

1 public void hashFunc(String key) { 2 //hash本身就是杂乱无章的表示。所以不要去理解表达的含义,大概类似于把key按33进制表示出来,同时让他最后的值处于HASH_TABLE_SIZE的范围中。 3 int sum = 0; 4 for(int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++ ) { 5 sum = sum * 33 + (int)key.charAt(i); 6 sum = sum % HASH_TABLE_SIZE; //如果不包含这一步,则相当于把key当成33进制数表示出来。 1234 按十进制表达: ((1*10 + 2)*10+3)*10 + 4; 7 //HASH_TABLE_SIZE 表示开辟的数组大小,实际存储的数据size/HASH_TABLE_SIZE = 1/10 最好,否则size再大, 8 //产生冲突的概率会增大。每一次操作都保证sum在HASH_TABLE_SIZE的范围内。 9 10 } 11 return sum; 12 }
5 重哈希(需要把所有的数重新计算插入一遍,很麻烦,所以尽量避免重哈希的出现,开始定义hash大小时数组开的空间大点。)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/rehashing/
注意点: 增加链表时,一定要new,而且是· .next = new ListNode,不然赋值不过来。不知道地址传递到底是怎么传的。

1 public ListNode[] rehashing(ListNode[] hashTable) { 2 if(hashTable == null || hashTable.length == 0) return hashTable; 3 ListNode[] newHash = new ListNode[hashTable.length * 2]; 4 int len = newHash.length; 5 for(int i = 0; i < hashTable.length; i++) { 6 ListNode node = hashTable[i]; 7 int index = 0; 8 while(node != null ) { 9 index = (node.val%len + len) % len; 10 if(newHash[index] == null) { 11 newHash[index] = new ListNode(node.val); 12 node = node.next; 13 continue; 14 } 15 ListNode head = newHash[index]; 16 while( head.next != null) { 17 head = head.next; 18 } 19 head = new ListNode(node.val); 20 21 node = node.next; 22 } 23 } 24 return newHash; 25 }
6 快乐数(hash)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/happy-number/
注意点: 注意按位取元素的方法

1 private int getNextHappy(int n) { 2 int sum = 0; 3 while (n != 0) { 4 sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10); 5 n /= 10; 6 } 7 return sum; 8 } 9 10 public boolean isHappy(int n) { 11 HashSet<Integer> hash = new HashSet<Integer>(); 12 while (n != 1) { 13 if (hash.contains(n)) { 14 return false; 15 } 16 hash.add(n); 17 n = getNextHappy(n); 18 } 19 return true; 20 }
7 LRU缓存策略
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/lru-cache/
注意点: node结点写在主类里面,因为它只需要在此类里暴露,不需要对外显示。
一共有两种存储的数据结构,map存放指定容量的key,value数据,LinkedList存放各种数据的前后放入关系。所以操作数据时,要同时维护这两种数据结构,get方法只需要维护链表,set方法两个都需要维护。
(堆相关)
8 数据流中位数 优先队列/heap :O(log N) Add O(log N) Remove O(1) Min/Max 二叉树实现的,根节点是最值,每次移除根节点,都需要从剩下的结点中找到最值
再移到根上,所以remove是O(logn)。堆排序只能保证根是最大(最小),不能保证整体是按照顺序来排序的。
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/data-stream-median/
注意点: offer poll方法
maxHeap里存放小于等于中位数的数字,minHeap里放大于中位数的数字。 中位数,则 maxHeap.size() == minHeap.size() 或者maxHeap.size() == minHeap.size()+1

1 public int[] medianII(int[] nums) { 2 // write your code here 3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null; 4 PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(); 5 PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(1, new Comparator<Integer>(){ 6 //@Override 可以不写,但是compare方法参数必须是Integer,不能是int 7 public int compare(Integer x, Integer y) { 8 return y - x; 9 } 10 }); 11 int[] res = new int[nums.length]; 12 res[0] = nums[0]; 13 maxHeap.offer(nums[0]); 14 for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { 15 if(nums[i] <= maxHeap.peek()) { 16 maxHeap.offer(nums[i]); 17 } else { 18 minHeap.offer(nums[i]); 19 } 20 21 //开始进入两个元素时,size上,maxHeap = minHeap 或者 maxHeap = minHeap +2,经过下面的if语句,转变成maxHeap = minHeap 22 // 每一轮进来后,只会出现maxHeap = minHeap 或者maxHeap = minHeap +1两种情况。(类似一种递推的关系) 23 if(maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size() + 1) { 24 minHeap.offer(maxHeap.poll()); 25 } else if( maxHeap.size() < minHeap.size()) { 26 maxHeap.offer(minHeap.poll()); 27 } 28 res[i] = maxHeap.peek(); 29 } 30 return res; 31 }
9 堆化 (有点堆排序的意思)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/heapify/
注意点: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 原序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 原序列元素对应的子树角标。
A[0]肯定是最小值。
siftdown的O(n)遍历方式很独特,从中间开始遍历。

1 // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 len = 8, mid = 3 对于位置i,两个子树2i+1,2i+2;对于位置i-1,子树2(i-1) +1, 2(i-1) +2,即2i-1和2i。 2 //也就是说 i-1,i-1恰好能连续覆盖掉2i-1,2i,2i+1,2i+2; 3 // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 len = 9, mid = 4 4 5 public void heapify(int[] A) { 6 // write your code here 7 //O(n)完成,只遍历一次,但是遍历的方式不是简单的从头到尾,而是从中间往左。 8 int mid = (A.length - 1)/2; 9 for(int i = mid; i >=0; i--) { 10 siftdown(A, i); 11 } 12 13 } 14 15 private void siftdown(int[] A, int k) { 16 int son = 0; 17 while(2*k+1 < A.length) { //从后往前保证 两个子树比根小,即有一定顺序。如果靠前的位置发生过swap,那也要保证swap之后,后面的位置还是有序 18 //所以有k = son 19 son = 2*k+1; 20 if(2*k+2 < A.length && A[2*k+2] <= A[son] ) son = 2*k+2; //son是两个子树中的较小的一个 21 22 if(A[son] < A[k]) { 23 swap(A, son, k); 24 k = son; 25 } else { 26 break; 27 } 28 } 29 30 } 31 private void swap(int[] A, int x, int y) { 32 int temp = A[x]; 33 A[x] = A[y]; 34 A[y] = temp; 35 }
10 丑数
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/ugly-number/
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/ugly-number-ii/#
注意点: 不理解丑数2的话看代码里的解释。

1 public int nthUglyNumber(int n) { 2 int[] uglyArr = new int[n]; 3 uglyArr[0] = 1; 4 //p2,p3,p5代表三个指针,指向uglyArr数组的索引。 5 int p2 = 0, p3=0, p5 = 0; 6 for(int i= 1; i < n; i++) { 7 // <= 说明此索引位置的丑数已经乘以过2了,即已有的丑数数组中已经包含由此位置丑数*2所对应的丑数了, 8 // 那么下一轮再乘的时候,就不能用此位置的丑数*2了,要用下一个丑数来乘。 9 // 所以p2表示:当前待乘以2来候选作为下一个丑数的数的角标 10 //为啥不是用uglyArr[i - 1]来乘2呢,比如1, 2,,3 用 3 *2 显然比 2* 2大,所以下一个丑数不是3*2。 11 //所以应该记录的是之前的丑数,1,2,3是否乘过2,3,5,p2= 1,p3= 1, p5 = 0表示5还没有乘过角标0的数,2没有乘过角标1的数,3没有乘过角标1的数。 12 if(uglyArr[p2] * 2 <= uglyArr[i - 1]) p2++; 13 if(uglyArr[p3] * 3 <= uglyArr[i - 1]) p3++; 14 if(uglyArr[p5] * 5 <= uglyArr[i - 1]) p5++; 15 16 //这一轮最小值是乘的2,3还是5会在下一轮通过if判断出来,判断出来后,p2,p3,p5中有且只有一个指针会移动1个位置。 17 uglyArr[i] = Math.min(uglyArr[p2] * 2, 18 Math.min(uglyArr[p3] * 3, uglyArr[p5] * 5)); 19 } 20 return uglyArr[n - 1]; 21 }
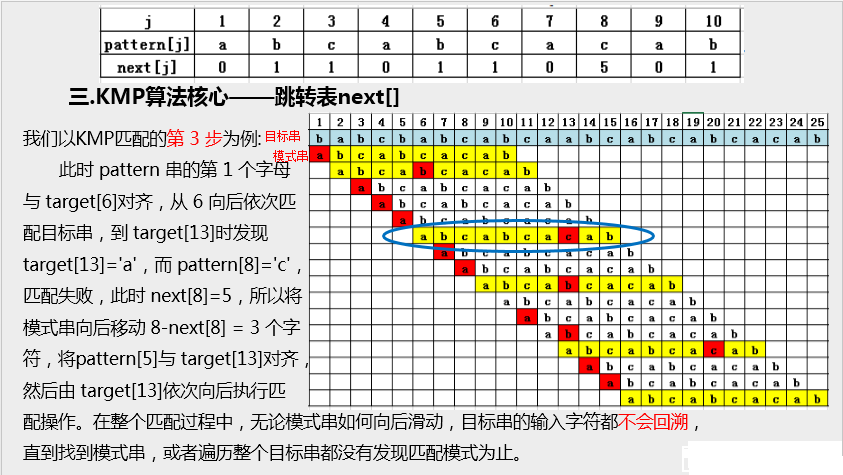
11.字符串查找
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/strstr/
注意点: O(n)实现 Rabin-Karp算法
1234 : 234=10(123-100)+4 = 123*10+4-1000 此处用的是后面的计算方式
(a+b)%b= (a%b+b%b)%b= a%b 这正是当hashcode<0时采取的做法,也就是对它取模,hashcode%HASH_SIZE=(hashcode+HASH_SIZE)%HASH_SIZE

1 /** 验证下面的结论是否普遍成立: 2 * 1%11*10%11*10%11=100%11=1 power 3 * 5%11*10%11*10%11= 5 =1 * 5 4 * 结论是:成立 5 */ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 int HASH_SIZE=1000000; 8 for(int numberSize = 2; numberSize < 10; numberSize++) { 9 int power = 1; 10 for(int i = 0; i <4; i++) { 11 power = (power*31)%HASH_SIZE; 12 } 13 for(int i =1; i < 10; i++) { 14 int count = 0; 15 int num = i; 16 int count0 = (num* power)%HASH_SIZE; 17 for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { 18 if(j != 0) num = 0; 19 count = (count*31+num)%HASH_SIZE; 20 } 21 if(count != count0){ 22 System.out.println(i); 23 break; 24 } 25 } 26 System.out.println(numberSize+"::finish"); 27 } 28 }

1 private int HASH_SIZE = 1000000; 2 3 public int strStr(String source, String target) { 4 // Write your code here 5 if (source == null || target == null) { 6 return -1; 7 } 8 int m = source.length(); 9 int n = target.length(); 10 if (n == 0) { 11 return 0; 12 } 13 if (m == 0) { 14 return -1; 15 } 16 int targetCode = 0; 17 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 18 targetCode = (targetCode * 31 + target.charAt(i)) % HASH_SIZE; 19 } 20 int power = 1; 21 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 22 power = (power * 31) % HASH_SIZE; 23 } 24 int hashCode = 0; 25 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { 26 //只有一开始i = n-1 时hashCode记录的是n个数的hash值, 27 //之后一直记录的是n+1个数的值,所以power才要乘31^n 而不是31^(n-1) 28 hashCode = (hashCode * 31 + source.charAt(i)) % HASH_SIZE; 29 if (i < n - 1) { 30 continue; 31 } 32 if (i >= n) { 33 hashCode = hashCode - (source.charAt(i - n) * power)% HASH_SIZE ; 34 //为啥可能出现hashcode<0? 因为新添加的一位导致hashcode的值>HASH_SIZE,出现了取模的情况, 35 // 而 a%b = (a+b)%b,所以<0的情况,原本的hashcode计算方式应该是: 36 // hashcode = hashCode + HASH_SIZE - (source.charAt(i - n) * power)% HASH_SIZE ; 37 // 所以如果遇到<0的情况,加HASH_SIZE就好了。 38 if (hashCode < 0) { 39 hashCode += HASH_SIZE; 40 } 41 } 42 // 0~n-1 i=n-1, 0 = i - n+1 43 // 1~n i=n, 1 = i - n+1 44 if (hashCode == targetCode) { 45 if (source.substring(i - n + 1, i + 1).equals(target)) { 46 return i - n + 1; 47 } 48 49 } 50 } 51 return -1; 52 }
graph and search
1 克隆图
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/clone-graph/#
拓扑排序
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/topological-sorting/#
注意点:图肯定要用hashMap
遍历完图的方式:while(start < res.size()) { start++} res动态增长,size变化,所有结点都加入进去后,就不变了,而start也增长,实现遍历完全的目的。

1 public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode node) { 2 //图的BFS,类似二叉树的BFS,不过需要统计邻居关系,避免已经访问过的邻居重复访问,所以用Map+ Queue实现。 3 //Queue可以用ArrayList + 头索引的位置来表示 4 if(node == null) return node; 5 ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> list = new ArrayList(); //放原先的结点 6 Map<UndirectedGraphNode,UndirectedGraphNode> map = new HashMap(); //放复制节点和原先结点的映射关系 7 int start = 0; 8 9 list.add(node); 10 map.put(node, new UndirectedGraphNode(node.label)); 11 while(start < list.size()) { 12 UndirectedGraphNode curr = list.get(start++); 13 for(int i = 0; i < curr.neighbors.size(); i++) { 14 if(!map.containsKey(curr.neighbors.get(i))) { 15 list.add(curr.neighbors.get(i)); 16 map.put(curr.neighbors.get(i), new UndirectedGraphNode(curr.neighbors.get(i).label)); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 // copy edge 22 for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 23 UndirectedGraphNode curr = list.get(i); 24 for(int j = 0; j < curr.neighbors.size(); j++) { 25 map.get(curr).neighbors.add(map.get(curr.neighbors.get(j))); 26 } 27 } 28 return map.get(node); 29 }
2 全排列(DFS)
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/permutations/
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/subsets/ 子集
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/subsets-ii/#
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/permutations-ii/#
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/combination-sum/# list里add一个元素,再做dfs,然后再remove掉
注意点: 写递归,想清楚两件事:
1.递归是做了一件什么样的事情,和参数的关系是什么
2.想清楚递归在什么时候return
3.想清楚递归关系,把大问题化解成小问题解决。
错误点: 返回 List<List<Integer>>,则声明为:List<List<Integer>> rst = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
返回ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>, 声明为:ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> rst = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 按上面的声明无法通过编译

1 public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { 2 // write your code here 3 if(nums == null) return null; 4 List<List<Integer>> rst = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); 5 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 6 if(nums.length == 0) { 7 rst.add(list); 8 return rst; 9 } 10 helper(rst, list, nums ); 11 return rst; 12 } 13 14 public void helper(List<List<Integer>> rst, ArrayList<Integer> list, int[] nums){ 15 if(list.size() == nums.length) { 16 //不能rst.add(list) 地址传递,最后内容都没了 17 rst.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); 18 return; 19 } 20 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { //假设nums={1,2,3,4},最外的循环进来,for4次对应四种情况: [ ] 21 // |--[1] 22 // |--[2] 23 // |--[3] 24 // |--[4] 25 //对于每一种情况,比如[1],又分为了三种 [1] 26 // |--[2] 27 // |--[3] 28 // |--[4] 29 //......最后直到list.size()==nums.length,所有元素都放进去了,才作为一次结果返回。 30 31 if(list.contains(nums[i])) { 32 continue; 33 } 34 list.add(nums[i]); 35 helper(rst, list, nums); 36 list.remove(list.size() - 1); 37 } 38 }
3 N皇后问题
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/n-queens/#
注意点:分成4块,每块函数各司其职
错误点: (cols.get(i) == j)?sb.append('Q'):sb.append('.'); (错) sb.append(j == cols.get(i) ? 'Q' : '.');(对) 三目表达式,一个整体

1 ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> solveNQueens(int n) { 2 if(n <= 0) return null; 3 ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> rst = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); 4 search(rst, new ArrayList<Integer>(), n); 5 return rst; 6 7 } 8 9 private void search(ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> rst, ArrayList<Integer> cols, int n) { 10 if(cols.size() == n) { 11 rst.add(drawChess(cols)); 12 return; 13 } 14 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 15 if(!isValid(cols, i)) { 16 continue; 17 } 18 cols.add(i); 19 search(rst, cols, n); 20 cols.remove(cols.size() - 1); 21 } 22 } 23 //查看第cols.size()行的第colIndex 列是否合法 24 //根据cols元素的放法的定义,不可能出现同一行,只可能有同一列或者同一斜行的情况。 25 private boolean isValid(ArrayList<Integer> cols, int colIndex) { 26 int rowIndex = cols.size(); 27 for(int i = 0; i < rowIndex; i++) { 28 if(cols.get(i) == colIndex) return false; 29 // right-top to left-down 30 // 。Q 。 。 31 // 。。 Q 。 左上到右下情况下的相同斜线: (0, 1) (1,2) 行序号-列序号的值相等。 32 33 // 。。 。 Q 34 // 。。 Q 。 右上到左下情况下的相同斜线: (0, 3) (1,2) 行序号+列序号的值相等。 35 if(cols.get(i) + i == rowIndex + colIndex) return false; 36 if(cols.get(i) - i == colIndex - rowIndex ) return false; 37 } 38 return true; 39 } 40 private ArrayList<String> drawChess(ArrayList<Integer> cols) { 41 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 42 for(int i = 0; i < cols.size(); i++) { 43 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 44 for(int j = 0; j < cols.size(); j++) { 45 //(cols.get(i) == j)?sb.append('Q'):sb.append('.'); 46 sb.append(j == cols.get(i) ? 'Q' : '.'); 47 } 48 list.add(sb.toString()); 49 } 50 return list; 51 }
4 单词接龙
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/word-ladder/ BFS 找最短路
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/word-ladder-ii/# 找所有方案,需要DFS,同时也要找最短路对应的所有方案,所以是DFS+BFS
注意点: BFS,因为每次只变一步,可以画出一张单词变化图出来, lot-log-pog
第一种方法超时了,差别主要在找下一个合法单词的方式上,一种是遍历dict,依次判断每个单词是否是合法的单词,另一种是先写出当前单词的所有的合法
改变单词来,然后判断它是否在dict中。结果是第二种方式更优,为啥??

1 public int ladderLength(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { 2 // 超时了,dict很大的时候,isValidChange 用时过长。 3 if(start == null || end == null || dict == null) return 0; 4 if(isValidChange(start,end)) return 2; 5 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 6 list.add(start); 7 return searchValidChange(list, dict, end); 8 } 9 private int searchValidChange(List<String> list, Set<String> dict,String end) { 10 int level = 1; 11 int pos = 0; 12 while(list.size() < dict.size() + 1) { 13 int len = list.size(); 14 while(pos < len) { 15 for(String s1 : dict) { 16 if(list.contains(s1)) continue; 17 if(isValidChange(list.get(pos), s1)) { 18 if(isValidChange(s1, end)) return level+2; 19 list.add(s1); 20 } 21 } 22 pos++; 23 } 24 level++; 25 } 26 return 0; 27 } 28 private boolean isValidChange(String s1, String s2) { 29 if(s1.length() != s2.length()) return false; 30 int count = 0; 31 for(int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) { 32 if(s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(i)) continue; 33 count++; 34 //if(count > 1) return false; 35 } 36 return count == 1; 37 } 38 //---------------------------------------------------- 39 public int ladderLength(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { 40 if (dict == null) { 41 return 0; 42 } 43 44 if (start.equals(end)) { 45 return 1; 46 } 47 48 dict.add(start); 49 dict.add(end); 50 51 HashSet<String> hash = new HashSet<String>(); 52 Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); 53 queue.offer(start); 54 hash.add(start); 55 56 int length = 1; 57 while(!queue.isEmpty()) { 58 length++; 59 int size = queue.size(); 60 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 61 String word = queue.poll(); 62 for (String nextWord: getNextWords(word, dict)) { 63 if (hash.contains(nextWord)) { 64 continue; 65 } 66 if (nextWord.equals(end)) { 67 return length; 68 } 69 70 hash.add(nextWord); 71 queue.offer(nextWord); 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 return 0; 76 } 77 78 // replace character of a string at given index to a given character 79 // return a new string 80 private String replace(String s, int index, char c) { 81 char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); 82 chars[index] = c; 83 return new String(chars); 84 } 85 86 // get connections with given word. 87 // for example, given word = 'hot', dict = {'hot', 'hit', 'hog'} 88 // it will return ['hit', 'hog'] 89 private ArrayList<String> getNextWords(String word, Set<String> dict) { 90 ArrayList<String> nextWords = new ArrayList<String>(); 91 for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) { 92 for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { 93 if (c == word.charAt(i)) { 94 continue; 95 } 96 String nextWord = replace(word, i, c); 97 if (dict.contains(nextWord)) { 98 nextWords.add(nextWord); 99 } 100 } 101 } 102 return nextWords; 103 }

1 //懒得看了,bfs写的就问题很大。用一个队列就能解决的问题,套了半天map,死循环,还绕。 2 private Map<String, Integer> map; 3 private int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 4 private List<List<String>> rsts; 5 private Set<String> dict; 6 public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { 7 // write your code here 8 if(start == null || end == null) return null; 9 rsts = new ArrayList<>(); 10 List<String> rst = new ArrayList<String>(); 11 rst.add(start); 12 if(start.equals(end)) { 13 rsts.add(new ArrayList<String>(rst)); 14 return rsts; 15 } 16 if(dict == null) return null; 17 map = findShortestLen(dict, end); 18 this.dict = dict; 19 dict.add(end); 20 //dict.add(start); 21 dfs(rst, start, end); 22 return rsts; 23 } 24 //dfs 25 private void dfs(List<String> rst,String start, String end) { 26 if(map.get(start) != null && map.get(start) == 2 && rst.size() + 1 == minLen) { 27 List<String> addRst = new ArrayList<String>(rst); 28 addRst.add(end); 29 rsts.add(addRst); 30 } 31 List<String> list = findNextWords(dict, start); 32 for(String s : list) { 33 //List<String> addList = new ArrayList<String>(); 34 if(!map.containsKey(s)) continue; 35 if(minLen < rst.size() + map.get(s)) continue; 36 else { 37 minLen = rst.size() + map.get(s); 38 rst.add(s); 39 dfs(rst, s, end ); 40 rst.remove(rst.size() - 1); 41 } 42 43 } 44 return; 45 } 46 //bfs 47 private Map<String, Integer> findShortestLen(Set<String> dict, String end) { 48 Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 49 map.put(end, 1); 50 int len = 1; 51 while(map.size() < dict.size()) { ///zzz, abc, abd, zzz永远也放不进map,死循环,先不管。 52 Map<String, Integer> temp = new HashMap<>(); 53 for(String s1 : map.keySet()) { 54 if(map.get(s1) != len) continue; 55 List<String> list = findNextWords(dict, s1); 56 if(list == null) continue; 57 for(String s2 : list) { 58 if(map.containsKey(s2) || temp.containsKey(s2)) continue; 59 temp.put(s2, len + 1); 60 } 61 } 62 len++; 63 map.putAll(temp); 64 } 65 return map; 66 } 67 private List<String> findNextWords(Set<String> dict, String end) { 68 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 69 for(int i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) { 70 for(int j = 0; j < end.length(); j++) { 71 if(i == end.charAt(j)) continue; 72 String s = replaceOneChar(end, j, (char)i); 73 if(dict.contains(s)) list.add(s); 74 } 75 } 76 return list; 77 } 78 private String replaceOneChar(String end, int pos, char c) { 79 char[] chars = end.toCharArray(); 80 chars[pos] = c; 81 return Arrays.toString(chars); 82 }

1 public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { 2 List<List<String>> rsts = new ArrayList<>(); 3 List<String> rst = new ArrayList<String>(); 4 Map<String,List<String>> map = new HashMap(); 5 Map<String, Integer> distance = new HashMap(); 6 dict.add(start); 7 dict.add(end); //避免dict中有无start和end造成的分类讨论 8 bfs(map, distance, start , end, dict); 9 dfs(rsts,map, distance,rst, end, start); 10 return rsts; 11 } 12 //从end开始添加 13 private void dfs(List<List<String>> rsts, Map<String,List<String>> map, Map<String, Integer> distance, List<String> rst, String curr, 14 String start) { 15 rst.add(curr); 16 if(curr.equals(start)) { 17 Collections.reverse(rst); 18 rsts.add(new ArrayList(rst)); 19 Collections.reverse(rst); 20 return; 21 } 22 /* 不要这样取元素 23 List<String> nexts = findNexts(dict, curr); 24 for(String next : nexts) { 25 if(distance.get(next) +1 == distance.get(curr)) { 26 dfs(rsts,map, distance, rst, next, start, dict); 27 } 28 }*/ 29 /* 这样只能取出一种结果来 30 List<String> list = map.get(curr); 31 dfs(rsts,map, distance, rst, list.get(list.size() - 1) , start, dict);*/ 32 List<String> list = map.get(curr); 33 for(String s : list) { 34 if(distance.get(s) +1 == distance.get(curr)) { 35 dfs(rsts,map, distance, rst, s , start); 36 } 37 } 38 rst.remove(rst.size() - 1); 39 40 } 41 //计算每一个字符串到start的路径距离 42 private void bfs(Map<String,List<String>> map, Map<String, Integer> distance, String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { 43 Queue<String> q = new LinkedList(); 44 q.offer(start); 45 distance.put(start, 0); 46 for(String s : dict) { 47 map.put(s, new ArrayList()); 48 } 49 while(!q.isEmpty()) { 50 String curr = q.poll(); 51 List<String> nexts = findNexts(dict, curr); 52 for(String next : nexts) { 53 /* 这样只能取出一种接过来 54 if(distance.containsKey(next)) continue; 55 distance.put(next, distance.get(curr) + 1); 56 map.get(next).add(curr); 57 q.offer(next);*/ 58 map.get(next).add(curr); 59 if(!distance.containsKey(next)) { 60 distance.put(next, distance.get(curr) + 1); 61 q.offer(next); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 private List<String> findNexts(Set<String> dict, String curr) { 67 List<String> nexts = new ArrayList(); 68 for(char ch = 'a'; ch <='z'; ch++) { 69 for(int i = 0; i < curr.length(); i++) { 70 if (ch == curr.charAt(i)) continue; 71 String s = curr.substring(0, i) + ch + curr.substring(i+1); 72 if(dict.contains(s)) { 73 nexts.add(s); 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 return nexts; 78 }
