在python中内置了很多函数或者类,比如:int,str,list,tuple,等。当然也可以自建函数,这个放在后文讨论。原理如下:
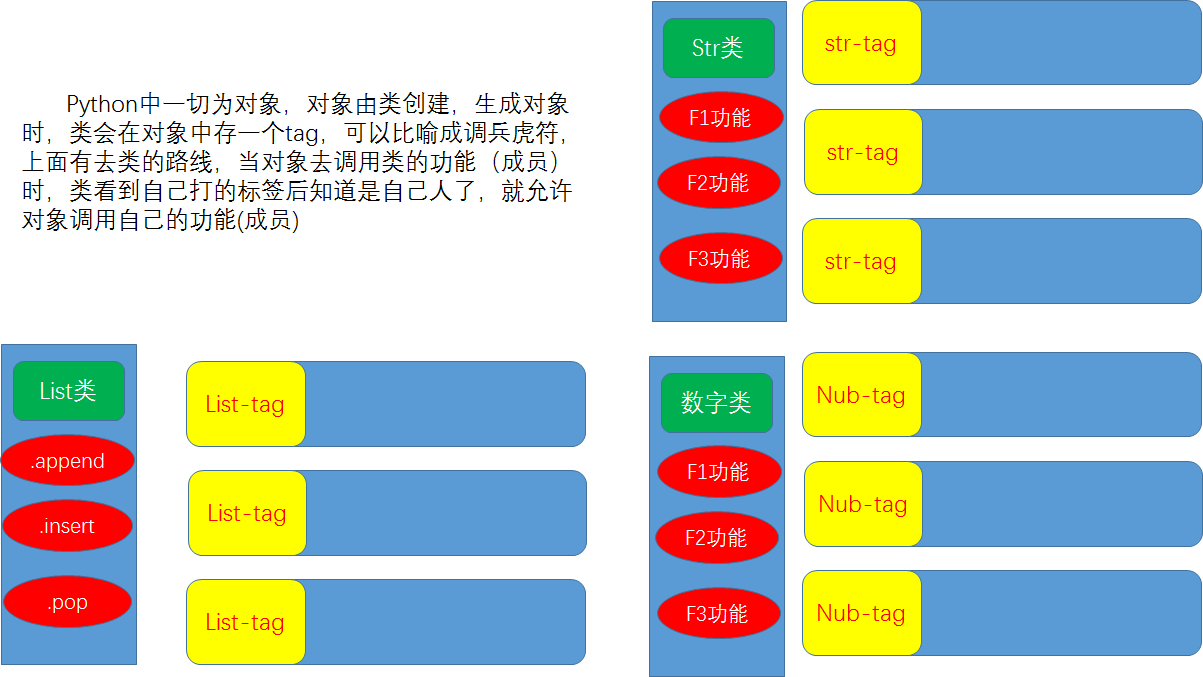
其实python中的类和方法非常非常多,这里只是以点带面,提供一个学习的方法。
(一)int
使用举例
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- age = -19 #其实是执行了一个__init__的过程。 print (type(age)) #打印age的类型 age = int(age) re = age.__float__() #将age的类型变成浮点类型,注,本来是int类型。 print(type(re)) #打印re的类型 reslutd = age.__abs__() #绝对值.(-19)=19。 <===>...reslutd=abs(age) reslut = reslutd.__divmod__(3) #divmod得出商和余数,19/4。在写扉页的时候会用到。<===>...reslutd=divmod(age) reslut_fan = reslutd.__rdivmod__(4) #反向求商和余数。4/19 print(reslutd,reslut_fan,reslut) #结果 ''' <class 'int'> <class 'float'> 19 (0, 4) (6, 1) '''
按住Ctrl,点击int,可以在builtins模块中看到int成员,其中int成员里大部分都是带下划线的,这一类的功能大多是通过内置方法就可以直接执行(例子参考上面abs,divmod和下文中add),请看:

def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ abs(self) """ pass #取绝对值 def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self+value. """ pass #相加,print(1+1)其实就是调用了“int”中内置的__add__这个函数,所以可以直接执行。但过程依然是:创建对象,调用方法,得到结果。 def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self&value. """ pass #融合 def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ self != 0 """ pass #变成波尔类型 def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return pow(self, value, mod). """ pass #取指数 .... def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. >>> bin(37) '0b100101' >>> (37).bit_length() 6 """ return 0 #返回用最少多少位可以表示当前数字 #举例: a= 59 result = a.bit_length() print(result) #结果 6
(二)str
先来个例题
#字符串。str如‘张洪震’‘zhang’。举例: name = 'zhang' name = str('zhang') #str执行时其本质是执行的.__init__方法.按住Ctrl,点击“str” ,查看有哪些成员 print(type(name)) #tpye.快速获取类 print(dir(name)) #dir.快速获取这个类里面有哪些成员 a = name.__contains__('ang') #a<=>b,a和b其实是一样的。 b = 'zh' in name print(a,b) #结果: ''' <class 'str'> ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] True True
来看下其他的成员:

#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- a = 'abc' def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.capitalize() -> str #让第一个字母大写 """ return "" a1 = a.capitalize() print(a1) #结果 #Abc def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ #width宽度;fillchar=None,填充字符,默认为空格 """ S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space默认为空格) """ return "" a2 = a.center(10) #让a这个字符串宽度为10.且abc位于中央。 print(a2) # abc a3 = a.center(10,'@') #以@为填充符。 print(a3) #@@@abc@@@@ def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ #统计子序列出现的次数。 #sub附属的,起始位置,结束为止 S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. """ return 0 a4 = a.count('a',0,2) #计算从0-2之间有几个a。 print(a4) #1 def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ #转码,encoding是编码方式;默认转成utf-8。errors是错误处理方式。 S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes """ return b"" #返回为b"",就是以b开头。 A = '张洪震' a5 = A.encode('gbk',errors='ignore') #转成gbk编码,忽略错误。注:其实内部还是从utf-8转为Unicode,再从Unicode转为gbk。 print(a5) #b'xd5xc5xbaxe9xd5xf0' def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool #suffix后缀, suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.#后缀也可以是一个元组。 """ return False #返回正误 a6 = a.endswith('c',0,3) #这里注意一下,是0<=suffix position.<3, #a6 = a.endswith('c',0,2),这样写会报错。 print(a6) #True def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise. With optional start, test S beginning at that position. With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try. 判断是否是以“。。”开头,可以指定开头和结尾的位置, """ return False def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str Return a copy#副本of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces. If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed. #返回一个用空格代替tab键的副本。 """ return "" B = 'zhan g' b7 = B.expandtabs() print(b7) #zhan g def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ #查找出sub所在的位置。 S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return -1 on failure.#如果失败的话返回-1. """ return 0 a8 =a.find('c',0,3) #在0-2的位置找c。 a9 =a.index('b') #index和find都是找,index找不到的话会直接报错。 print(a8,a9) #2 1 def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format """ S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs. 返回一个格式化的字符串,用替换的来自于传参。 The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). 被替换的东西用{}来定义 """ pass C ='zhen,{0},{1}' a10 = C.format('是四个字母','对') #传参为“是四个字母” print(a10) #zhen,是四个字母,对 D ='zhen,{dd},{ddd}' a10 = D.format(dd='是四个字母',ddd='对') #做一个动态对应 print(a10) #zhen,是四个字母,对 #以is开头的大都是判断,举一个例子 def isalnum(self): # 判断是否是文字数字 return False def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ #主要用来做拼接 S.join(iterable) -> str Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable. The separator between elements is S.元素之间的分隔符是S.。 """ return "" E=['ni hao','zhang','chi le ma'] #定义一个列表 a11= ",".join(E) #让“E”中的字符串以“,”为分割符相连。 print(a11) #ni hao,zhang,chi le ma def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str 左对齐。参数为宽度,填充字段.默认为空 """ return "" def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str 右对齐。参数为宽度,填充字段,默认为空 """ return "" F = 'abc' a12=F.ljust(7,'#') #让F的宽度为7个字符,如果不够7个,那么在字符串的右边填充上“#”把字符串“挤”至左对齐。 print(a12) a13=F.rjust(6,'$') #让F的宽度为6个字符,如果不够6个,那么在字符串的左边填充上“#”把字符串“挤”至右对齐。 print(a13) #结果 ''' abc#### $$$abc ''' def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.lower() -> str Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase. 返回一个字符串的小写副本。 """ return "" def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.upper() -> str 大写 Return a copy of S converted to uppercase. """ return "" def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.strip([chars]) -> str Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 删除开头和结尾空格,如果给定字符或不是空的,那么删除给定字符 """ return "" def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.lstrip([chars]) -> str Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 返回一个去掉字符串的开头空格的副本 如果给定字符而不是空的,则删除给定字符。 """ return "" a14=a.lstrip('a') print(a14) def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.rstrip([chars]) -> str Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 返回一个去掉字符串的结尾空格的副本 如果给定字符而不是空的,则删除给定字符。 """ return "" a15=a.rstrip('c') print(a15) def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return S and two empty strings. 在字符串中搜索分隔符,并返回它前面的部分、分隔符本身和后面的部分。如果找不到分隔符,返回s和两个空字符串。 """ pass a16= a.partition('b') #以b为分隔符 print(a16) #('a', 'b', 'c') a17= a.partition('d') #以d为分割符 print(a17) #('abc', '', '') def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is given, only the first count occurrences are replaced. """ return "" h='aaaaaaa' h1= h.replace('a','b',3) #用b替换a,个数为3 h2=h.replace('a','9',2) print(h1,h2) #bbbaaaa 99aaaaa def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings 分割。 """ i='zhang hong z hen' i1=i.split('h',2) #指定h为分隔符,i中有3个h,指定最大为2个,所以,只有两个作为分割符了 i2=i.split() #没有指定,则以空格为分割符并删除空格 print(i1,i2) #['z', 'ang ', 'ong z hen'] ['zhang', 'hong', 'z', 'hen'] def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.swapcase() -> str Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase and vice versa. 如果是大写,那么给它换成小写,反之亦然。 """ return "" def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.title() -> str Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case. """ return ""
通过上面可以看出其实python的解释很清晰简洁,真的难懂的话可以通过翻译软件翻译出来,一般情况下是可以看懂的。
(三)list列表
如:['zhang']、[11,'hong','zhen']

class list(object): """ list() -> new empty list list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items """ def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end """ #从列表末尾加入元素 pass def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L """ #清除所有 pass def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L """ #浅拷贝 return [] def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """ #计数 return 0 def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable """ #扩展,将新列表元素加到老列表中 pass def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. #下标,也就是索引号 """ return 0 def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index """ #指定位置插入元素 pass def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last). Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. #移除,参数为指定位置 """ pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. #移除,参数为指定的值 """ pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """ #反转,即倒序。 pass def sort(self, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE* """ #排序。 pass
(四)tuple元组
如:(11,22,)('zhang',[11,22,33],)

class tuple(object): """ tuple() -> empty tuple tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. """ def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """#计数 return 0 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.#返回一个索引 Raises ValueError if the value is not present. """ return 0 #例: a=(('zhang'),[11,22,33],) re=a.index('zhang') print(type(a),re) #<class 'tuple'> 0
(五)dict字典
如:{'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','123':'abc'}
使用:
name1=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99]
name2=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
dict['k1']=name1 #<=>dic=dict(k1=name1)
dict['k2']=name2 #<=>dic2=dict(k2=name2)

dict dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','123':'abc'} class dict(object): """ dict() -> new empty dictionary dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's (key, value) pairs dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: d = {} for k, v in iterable: d[k] = v dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) """ def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """ pass def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """ pass @staticmethod # known case def fromkeys(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns a new dict with keys from iterable and values equal to value. """ pass def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. 如果key在D中就是key,否则就是设置的d。d默认是空""" pass #例 dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','123':'abc'} kk= dd.get('li','sorry,meiyouzhaodao') print(kk) #sorry,meiyouzhaodao def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items 输出所有的字典对儿""" pass def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys 输出所有的key值""" pass def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values 输出所有的value值。""" pass def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.给定k值,删除相应的value If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised如果key没有找到,如果给了d的话d会输出。否则,报错, """ pass #例: dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','123':'abc'} aa= dd.pop('li','sorry,meiyouzhaodao') bb=dd.pop() print(aa,bb) #sorry,meiyouzhaodao #bb=dd.pop() #TypeError: pop expected at least 1 arguments, got 0 def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty. #随机删除一个对儿,如果参数是空的话会报错 """ pass def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D 给设置一个默认值""" pass def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update """ D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F. If E is present and has a .keys() method, then does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k] If E is present and lacks a .keys() method, then does: for k, v in E: D[k] = v In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k] """ pass def __contains__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ True if D has a key k, else False. """ pass def __delitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Delete self[key]. """ pass def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self==value. """ pass def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return getattr(self, name). """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>=value. """ pass def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>value. """ pass def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__ """ dict() -> new empty dictionary dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's (key, value) pairs dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: d = {} for k, v in iterable: d[k] = v dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Implement iter(self). """ pass def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return len(self). """ pass def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<=value. """ pass def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<value. """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ pass def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self!=value. """ pass def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return repr(self). """ pass def __setitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Set self[key] to value. """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """ pass __hash__ = None
