1.例如:
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring.xml"));
User user = (User) bf.getBean("user");
new ClassPathResource("spring.xml") 根据 xml通过不同参数构建Resource,
/** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); } /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); //XmlBeanDefinitionReader } 2. reader加载Bean public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); } /** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); ...... 3. 根据XML真正加载Bean /** * Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource); Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument( inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware()); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); ..... /** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by <code>loadBeanDefinitions</code>. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * <code>registerBeanDefinitions</code> on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//记录加载前BeanDefinition的加载个数 int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; } protected XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) { if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) { this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(); } return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener, this.sourceExtractor, this, this.namespaceHandlerResolver); } /** * {@inheritDoc} * <p>This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD * (or DTD, historically). * <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings * specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions. */ public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); } 4.注册Bean /** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. * @throws IllegalStateException if {@code <beans profile="..."} attribute is present * and Environment property has not been set * @see #setEnvironment */ protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { Assert.state(this.environment != null, "environment property must not be null"); String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { return; } } // any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parent); preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; } /** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); //默认标签解析 <bean id="test" class=""> } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);//<tx:annotation-driven> } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } } /** * Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types first, * before we start to process the bean definitions. This method is a natural * extension point for any other custom pre-processing of the XML. * <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to * convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example. * Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the * underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors. * @see #getReaderContext() */ protected void preProcessXml(Element root) { } /** * Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types last, * after we finished processing the bean definitions. This method is a natural * extension point for any other custom post-processing of the XML. * <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to * convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example. * Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the * underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors. * @see #getReaderContext() */ protected void postProcessXml(Element root) { }
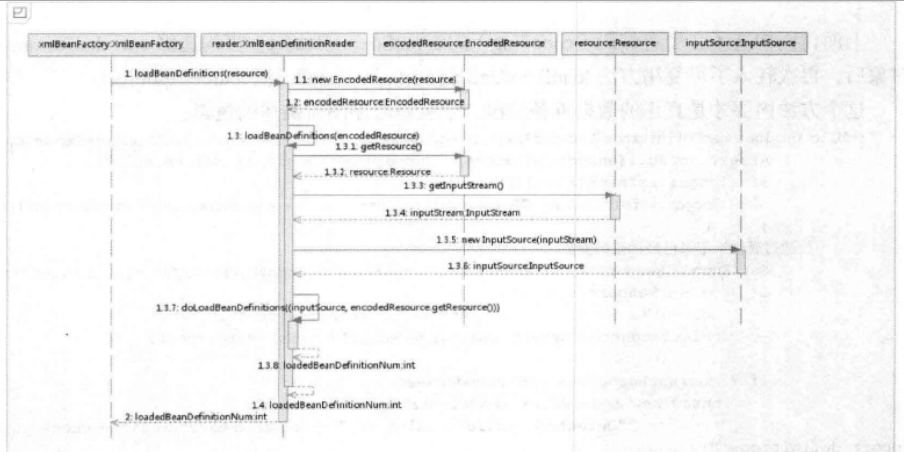
时序图:
下一篇解析默认标签