SpringBoot默认是将Tomcat作为嵌入式的servlet容器。
问题:
-
如何修改嵌入式的servlet容器?
1)在配置文件中设置对应的属性值
server.port=8081 # Tomcat access日志的编码格式 server.tomcat.accesslog.encoding=UTF-8 # 最小的空闲线程个数 server.tomcat.min-spare-threads=11
- 在spring1.x版本时,编写一个配置类,将EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer加入到容器中,EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer接口中的customize方法可以修改servlet的配置。
@Bean //一定要将这个定制器加入到容器中
public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer embeddedServletContainerCustomizer(){
return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer() {
//定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) {
container.setPort(8083);
}
};
}
到了springboot2.x,上面那个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer已经被WebServerFactoryCustomizer取代,
package org.springframework.boot.web.server;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface WebServerFactoryCustomizer<T extends WebServerFactory> {
void customize(T factory);
}
所以编写一个config实现这个接口,T是ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory
@Component
public class EmbeddedTomcatConfig implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
((TomcatServletWebServerFactory)factory).addConnectorCustomizers(new TomcatConnectorCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
protocol.setMaxConnections(200);
protocol.setMaxThreads(200);
protocol.setSelectorTimeout(3000);
protocol.setSessionTimeout(3000);
protocol.setConnectionTimeout(3000);
}
});
}
}
-
springboot能不能支持其他的servlet容器?
支持Jetty,Undertow服务器。
这里了解一下两者的一些特点,undertow是一款红帽旗下的开源容器,是轻量级的,它是一个 内嵌Web 服务器, 由两个核心 Jar 包组成,它支持IO/NIO,在多款同类产品的压测中,在高并发情况下表现出色, 它还提供了对 Servlet4.0 的支持,WebSocket的支持。用以满足 Web 应用巨大数量的客户端。jetty也是轻量级别的服务器,它更加灵活,可扩展性强,作为嵌入式服务器在自动测试环境下不需要外部环境的支持,且运行速度较快。首先去除Tomcat相关依赖,然后引入undertow的依赖,pom.xml依赖的变化
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!--去除Tomcat的依赖-->
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入undertow服务器的依赖-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>
同样替换成jetty也是一样
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!--去除Tomcat的依赖-->
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入jetty服务器的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
使用外置的servlet容器
嵌入式tomcat容器的优缺点:
优点:简单,便携
缺点:默认不支持JSP、优化定制比较复杂(使用定制器【ServerProperties、自定义EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】,自己编写嵌入式Servlet容器的创建工厂【EmbeddedServletContainerFactory】);
外置的Servlet容器:外面安装的Tomcat—应用打成war包
步骤
-
必须创建一个war的项目,
-
将嵌入式的Tomcat制定成provided;
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>-
编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,这件事idea在我们创建好项目的时候就已经帮我们做好了。
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer { @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) { return application.sources(Springboot04JspApplication.class); } }
-
-
启动服务器就可以使用(注意这时候就不要再使用SpringBoot默认的主类的main方法启动服务器了,这样做是启动不了的)
原理:
jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法。启动IOC容器,创建嵌入式的servlet容器;
war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用【ServletInitializer】这个也就是idea创建的时候帮我们生成的类是SpringBootServletInitializer的子类。再启动IOC容器
规则:
1)服务器启动会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包的ServletContainerInitializer实例;
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现会放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为
javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的全类名
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣的类;
流程:首先启动Tomcat,这时orgspringframeworkspring-web5.2.3.RELEASEspring-web-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar!META-INFservicesjavax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer路径下的ServletContainerInitializer类就会起作用,打开这个类,查看他的实现,发现他上面@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class}),也就是说WebApplicationInitializer这个接口同样也创建出了实例对象。
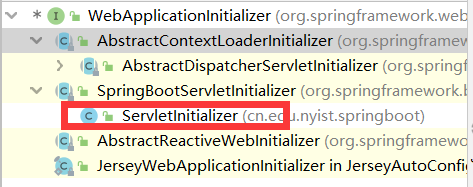
打开继承树,发现他就是idea帮我们自动创建的那个类的父类所实现的接口,并且创建完WebApplicationInitializer后有调用了他们的onStartup方法.
while(var4.hasNext()) {
WebApplicationInitializer initializer = (WebApplicationInitializer)var4.next();
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
但是我们的idea帮我们生成的ServletInitializer类并没有这个onStartup方法,所以看他的父类SpringBootServletInitializer,果然,SpringBootServletInitializer实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口,重写了onStartup方法。
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
//下面这个创建了IOC容器,点进去查看其实,方法就在本类中实现
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = this.createRootApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (rootAppContext != null) {
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext) {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
}
});
} else {
this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
createRootApplicationContext方法;
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = this.createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(this.getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = this.getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, (Object)null);
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)});
}
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)});
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
//调用config方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot主程序类传了进来
builder = this.configure(builder);
builder.listeners(new ApplicationListener[]{new SpringBootServletInitializer.WebEnvironmentPropertySourceInitializer(servletContext)});
//创建spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getAllSources().isEmpty() && MergedAnnotations.from(this.getClass(), SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY).isPresent(Configuration.class)) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(this.getClass()));
}
Assert.state(!application.getAllSources().isEmpty(), "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class));
}
//启动spring
return this.run(application);
}
run方法的定义在SpringApplication类中找到
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}