在"C#中,什么时候用yield return"中,我们了解到:使用yield return返回集合,不是一次性加载到内存中,而是客户端每调用一次就返回一个集合元素,是一种"按需供给"。本篇来重温yield return的用法,探秘yield背后的故事并自定义一个能达到yield return相同效果的类,最后体验yield break的用法。
□ 回顾yield return的用法
以下代码创建一个集合并遍历集合。
class Program{static Random r = new Random();static IEnumerable<int> GetList(int count){List<int> list = new List<int>();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){list.Add(r.Next(10));}return list;}static void Main(string[] args){foreach(int item in GetList(5))Console.WriteLine(item);Console.ReadKey();}}
使用yield return也能获得同样的结果。修改GetList方法为:
通过断点调试发现:客户端每显示一个集合中的元素,都会到GetList方法去获取集合元素。static IEnumerable<int> GetList(int count){for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){yield return r.Next(10);}}
□ 探密yield
使用yield return获取集合,并遍历。
class Program{public static Random r = new Random();static IEnumerable<int> GetList(int count){for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){yield return r.Next(10);}}static void Main(string[] args){foreach(int item in GetList(5))Console.WriteLine(item);Console.ReadKey();}}
生成项目,并用Reflector反编译可执行文件。在.NET 1.0版本下查看GetList方法,发现该方法返回的是一个GetList类的实例。原来yield return是"语法糖",其本质是生成了一个GetList的实例。
那GetList实例是什么呢?点击Reflector中<GetList>链接查看。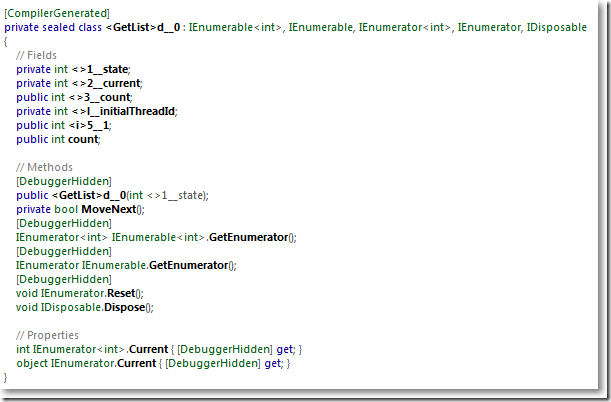
○ 原来GetList类实现了IEnumerable和IEnumerator的泛型、非泛型接口
○ yield return返回的集合之所以能被迭代、遍历,是因为GetList内部有迭代器
○ yield return之所以能实现"按需供给",是因为GetList内部有一个_state字段记录这上次的状态
接下来,就模拟GetList,我们自定义一个GetRandomNumbersClass类,使之能达到yield return相同的效果。
using System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace ConsoleApplication2{class Program{public static Random r = new Random();static IEnumerable<int> GetList(int count){GetRandomNumbersClass ret = new GetRandomNumbersClass();ret.count = count;return ret;}static void Main(string[] args){foreach(int item in GetList(5))Console.WriteLine(item);Console.ReadKey();}}class GetRandomNumbersClass : IEnumerable<int>, IEnumerator<int>{public int count;//集合元素的数量public int i; //当前指针private int current;//存储当前值private int state;//保存遍历的状态#region 实现IEnumerator接口public int Current{get { return current; }}public bool MoveNext(){switch (state){case 0: //即为初始默认值i = 0;//把指针调向0goto case 1;break;case 1:state = 1;//先设置原状态if (!(i < count))//如果指针大于等于当前集合元素数量{return false;}current = Program.r.Next(10);state = 2; //再设置当前状态return true;break;case 2: //再次遍历如果state值为2i++;//指针再移动一位goto case 1;break;}return false;}//被显式调用的属性object IEnumerator.Current{get { return Current; }}public void Reset(){throw new NotImplementedException();}public void Dispose(){}#endregion#region 实现IEnumerable的泛型和非泛型public IEnumerator<int> GetEnumerator(){return this;}//被显式调用的属性IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator(){return GetEnumerator();}#endregion}}
关于GetRandomNumbersClass类:
○ count表示集合的长度,可以在客户端赋值。当调用迭代器的MoveNext方法,需要把count和当前位置比较,以决定是否可以再向前移动。
○ 字段i相当于索引,指针每次移动一位,i需要自增1
○ current表示当前存储的值,外部通过IEnumerator.Current属性访问
迭代器的MoveNext方法是关键:
○ state字段是整型,表示产生集合过程中的3种状态
○ 当state为0的时候,说明是初始状态,把索引位置调到0,并跳转到state为1的部分
○ 当state为1的时候,首先把状态设置为1,然后判断索引的位置有没有大于或等于集合的长度,接着产生集合元素,把state设置为2,并最终返回true
○ 当sate为2的时候,也就是迭代器向前移动一位,再次执行MonveNext方法的时候,跳转到state为2的语句块部分,把索引位置自增1,再跳转到state为1的语句块中,产生新的集合元素
○ 如此循环
□ yield break的用法
假设在一个无限循环的环境中获取一个int类型的集合,在客户端通过某个条件来终止循环。
class Program{static Random rand = new Random();static IEnumerable<int> GetList(){while (true){yield return rand.Next(100);}}static void Main(string[] args){foreach (int item in GetList()){if (item%10 == 0){break;}Console.WriteLine(item);}Console.ReadKey();}}
以上,当集合元素可以被10整除的时候,就终止循环。终止循环的时机是在循环遍历的时候。
如果用yield break,就可以在获取集合的时候,当符合某种条件就终止获取集合。
class Program{static Random rand = new Random();static IEnumerable<int> GetList(){while (true){int temp = rand.Next(100);if (temp%10 == 0){yield break;}yield return temp;}}static void Main(string[] args){foreach (int item in GetList()){Console.WriteLine(item);}Console.ReadKey();}}
总结:
○ yield return能返回一个"按需供给"的集合
○ yield return是"语法糖",其背后是一个实现了IEnuerable,IEnumerator泛型、非泛型接口的类,该类维护着一个状态字段,以保证yield return产生的集合能"按需供给"
○ yield break配合yield return使用,当产生集合达到某种条件的时候使用yield break,以终止继续创建集合