linux pwd指令的C实现
pwd指令的功能介绍
linux pwd命令用于显示工作目录
执行pwd命令可立刻得知当前所在工作目录的绝对路径名称。
示例:

查询系统手册
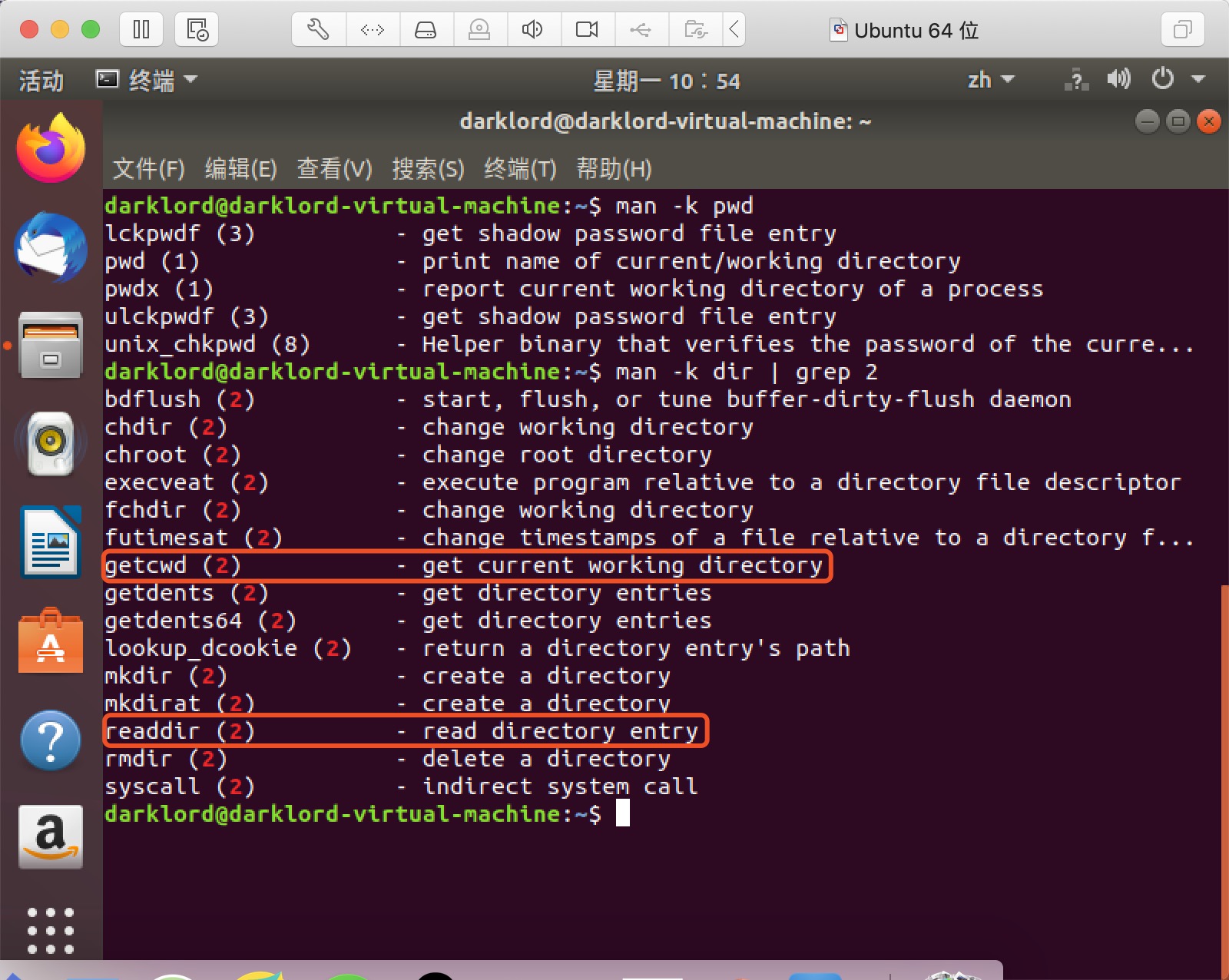
- 如图所示,
getcwd的描述是“get current working directory”,这与我们要实现的pwd命令的功能非常相近,于是我继续查询getcwd
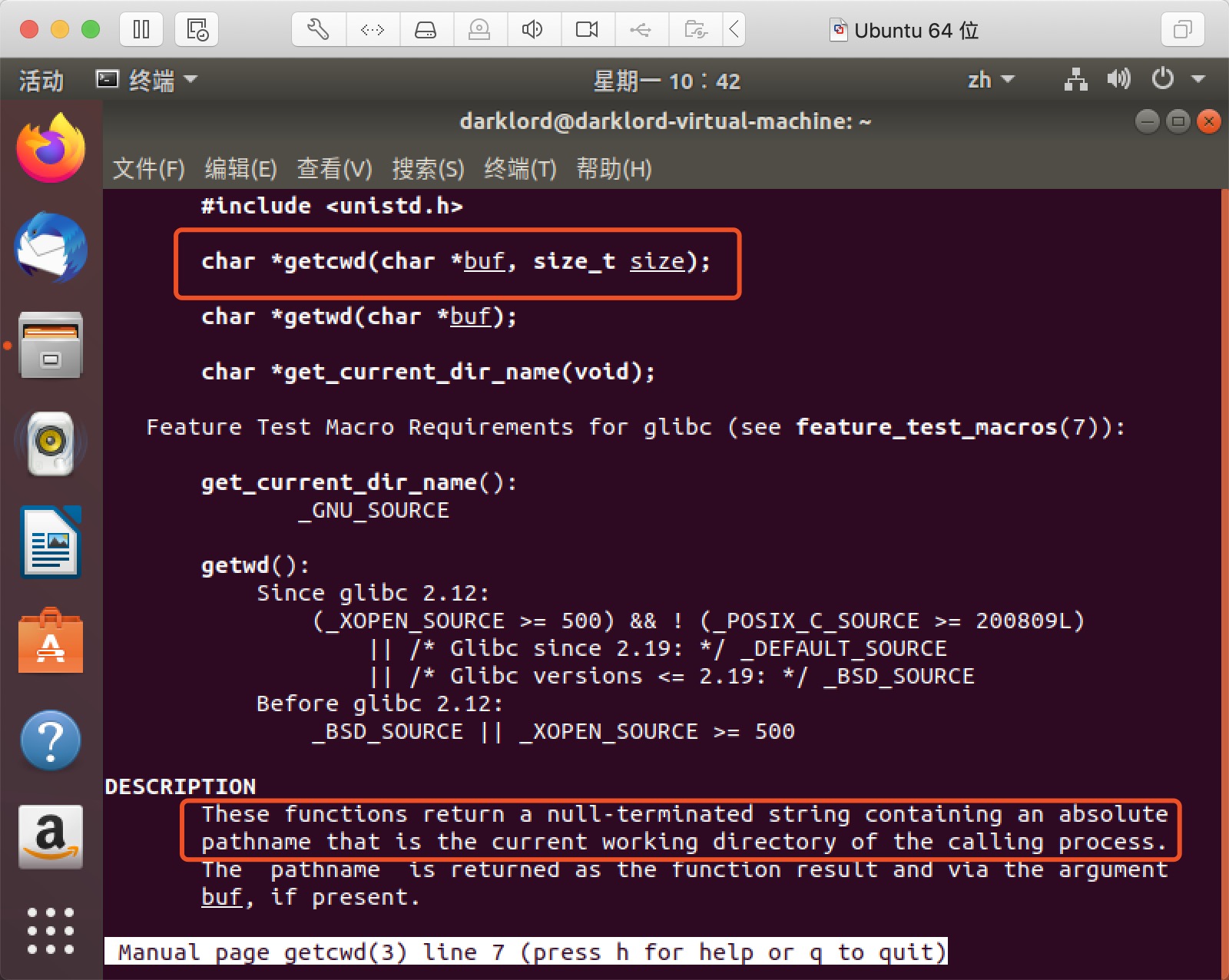
- 如图所示,有关getcwd的用法及描述中提到它的功能是返回一个包含调用程序所在位置绝对路径的以空字符为结尾的字符串,这显然正是我们需要实现的功能!
实现pwd命令(一)
到此为止,第一代mypwd就已经成型了,只要在程序中使用getcwd()函数就可以实现获得绝对路径的功能了。
以下为实现mypwd的C语言代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
char buf[1024];
char *cwd =getcwd(buf, sizeof(buf));
if (NULL == cwd) {
perror("Get cerrent working directory fail.
");
exit(-1);
} else {
printf("%s
", cwd);
}
return 0;
}
测试结果
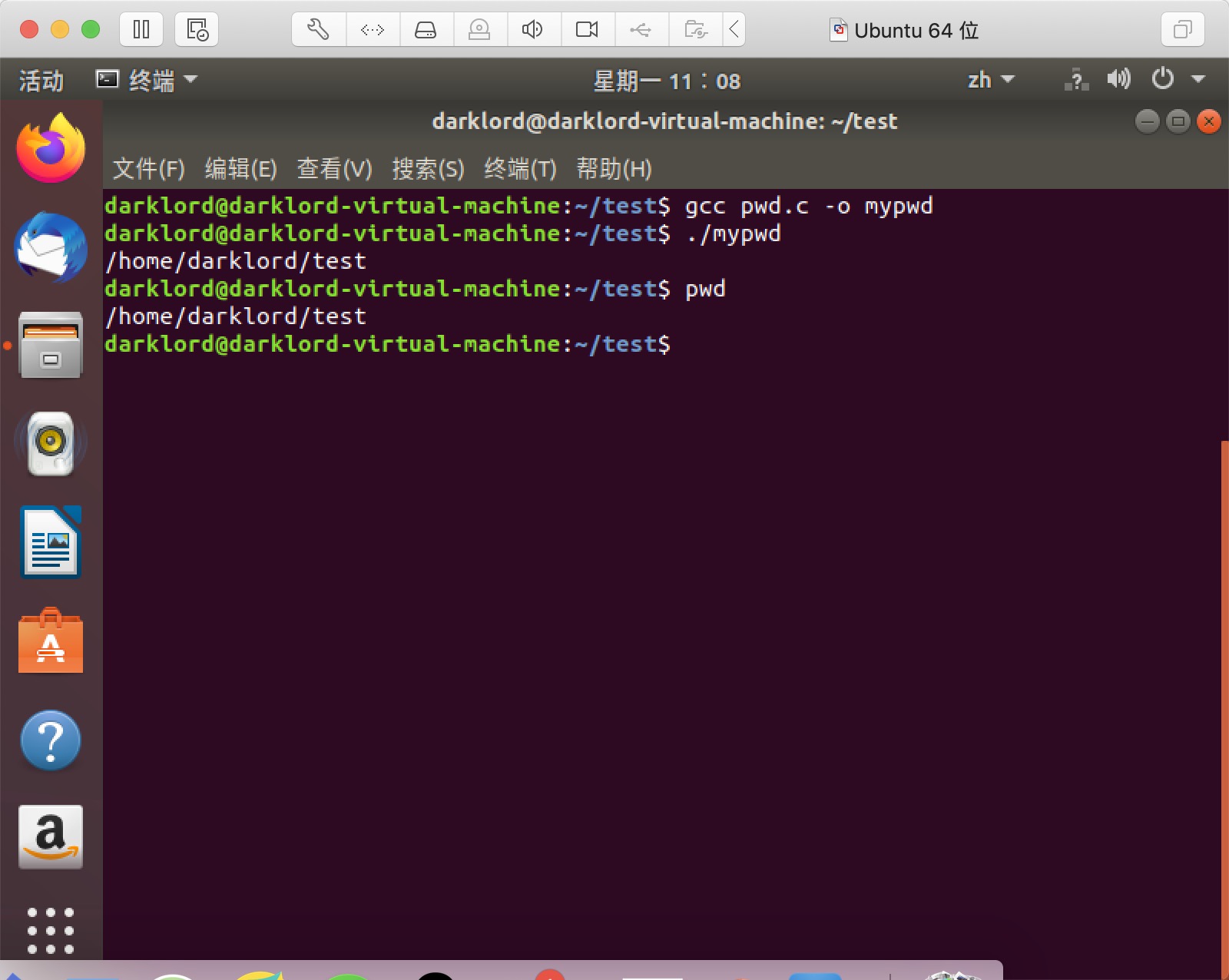
实现pwd命令(二)
第一代mypwd命令其实已经实现了pwd的功能,但这显然只能实现其功能,而不能了解其工作原理,过于耍流氓,因此我继续参考有关linux的目录的资料
linux中目录的文件组织方式
在一个文件系统中,一个inode代表一个文件,并使用一个整数值来表示该inode,称为inode-number,该值对于一个文件系统而言是唯一的,即通过该值可以找到其对应的inode。一般情况下,一个文件只有一个inode信息来描述它。
本学期的学习中,我们一直在强调一个概念,“linux系统下,一切皆文件”,因此毫无疑问,目录也是文件,也必定是由inode组织的。
因此,我们通常所说的目录a“包含”文件b,其实现层面上的意思是,目录a的内容列表里有一个关于文件b的列表项,即“b的inode-number+b的filename”。综上,Linux中,一个文件(包括目录)的文件名,及文件名与inode的对应关系,都是由包含该文件的目录所描述的。
伪代码
现在我们了解了可以实现工作目录与上级目录inode值的比对来判断是否追溯到根目录,为了实现这个上溯目录的功能,我们可以使用如图所示这个函数:

chdir("..")即可实现向上级目录跳转
定义用来存储路径的字符数组
通过特殊文件名“.”获得当前工作目录名称
chdir()返回上级目录
if(本目录inode-number和上级inode-number不同),本目录不是根目录,继续向上查找
else
是根目录,可以输出绝对路径了
详细代码
有了上述的思路,我们可以写出详细代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
ino_t get_inode(char*);
void printpathto(ino_t);
void inum_to_name(ino_t,char*,int);
int main()
{
printpathto(get_inode(".")); //打印当前目录绝对路径
putchar('
');
return 0;
}
void printpathto(ino_t this_inode)
{
ino_t my_inode;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
/*如果本目录的inode-number与上级目录不同,即本目录不是根目录*/
if (get_inode("..")!=this_inode)
{
chdir(".."); //进入上级目录
inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ);
my_inode = get_inode(".");
printpathto(my_inode);
printf("/%s",its_name);
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find,char* namebuf,int buflen) //找到inode-number节点对应的文件名,并放在字符数组里
{
DIR* dir_ptr;
struct dirent* direntp;
dir_ptr = opendir(".");
if (dir_ptr == NULL)
{
perror(".");
exit(1);
}
while((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
{
if(direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find)
{
strncpy(namebuf,direntp->d_name,buflen);
namebuf[buflen-1] = '�';
closedir( dir_ptr);
return;
}
}
fprintf( stderr , "error looking for inum % d
" ,inode_to_find);
exit (1) ;
}
ino_t get_inode(char* fname) //根据文件名,返回inode-number
{
struct stat info;
if ( stat( fname, &info) == -1){
fprintf( stderr , "Cannot stat ");
perror(fname);
exit (1);
}
return info.st_ino;
}
测试结果
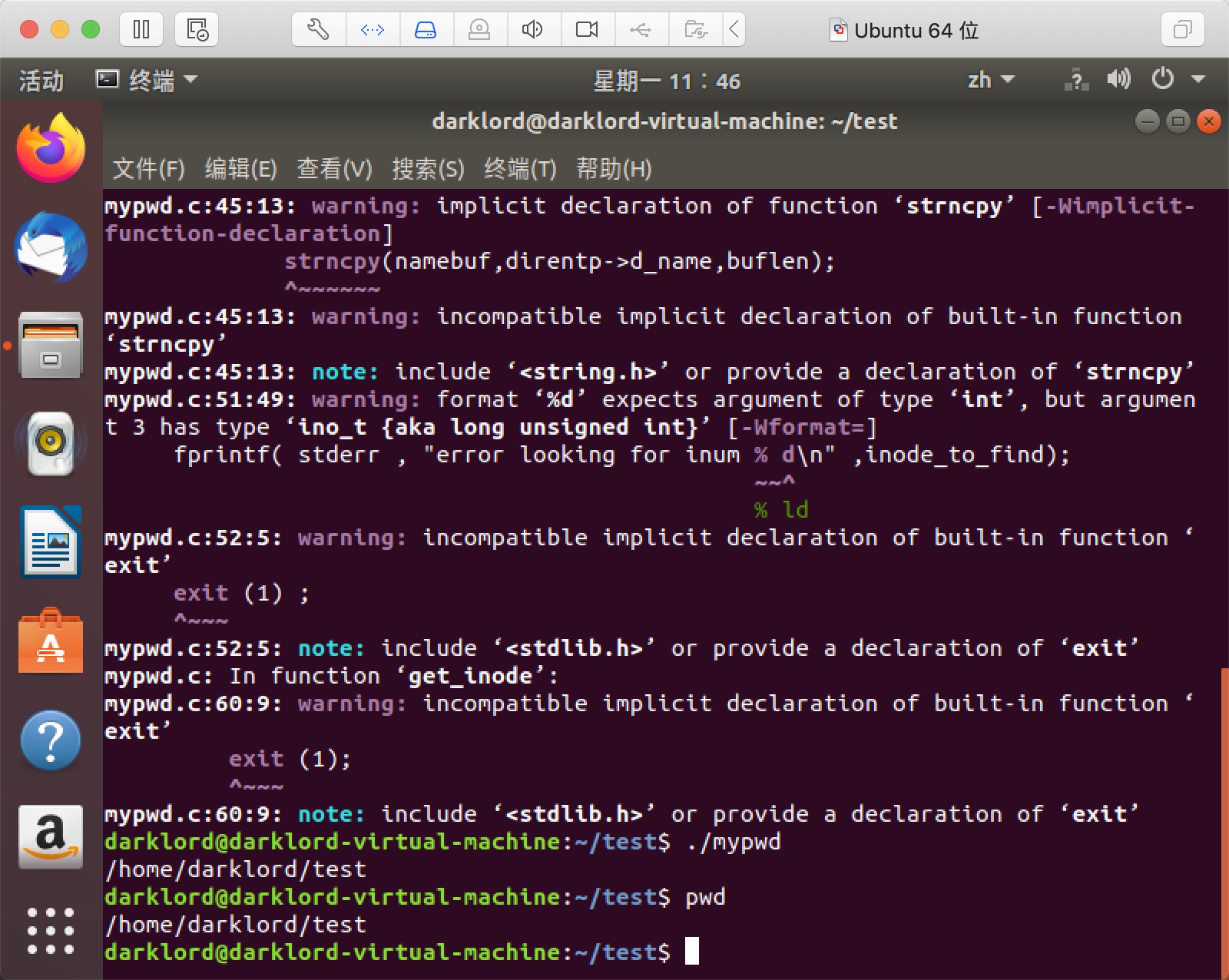
参考资料
《Unix环境高级编程》
博客园连接