转载请注明出处:
http://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/5655957.html
参考网址:
http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/38560/gpu-usage-monitoring-cuda
http://blog.csdn.net/revolver/article/details/49682131
一 在终端中直接安装
说明:由于nvidia并未给出ubuntu16上面的cuda toolkit,本文方法不一定可行,我这边安装成功,感觉完全是瞎猫碰死耗子了。。。不过没有安装sample,只是其他程序可以使用显卡了。
1. 第一个网址,使用
sudo apt-get install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
安装cuda toolkit,要看网速,下载很慢。还有,网址中说重启ubuntu有问题(I can't log in to my computer and end up in infinite login screen)。我这边安装了之后,正常登陆了,没有出现问题。
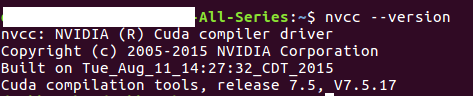
2. 安装完之后的信息:
装的是7.5.17,不是最新的7.5.18,但是能用就行。
3. 第二个网址中qed给出了在终端中持续显示GPU当前的使用率(仅限nvidia的显卡):
nvidia-smi -l 1
结果:
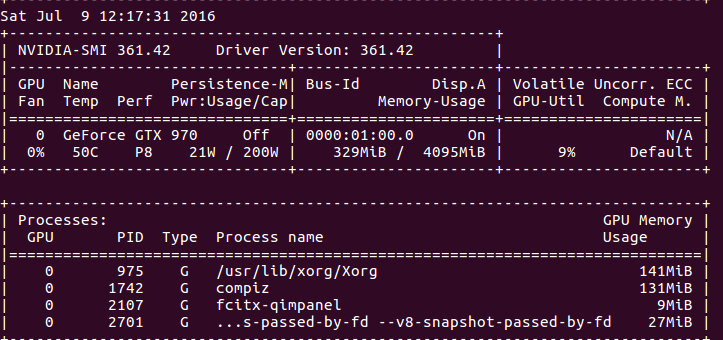
说明:上面的命令貌似要显卡支持才行。也可以使用Jonathan提供的命令(目前没测试):
watch -n0.1 "nvidia-settings -q GPUUtilization -q useddedicatedgpumemory"
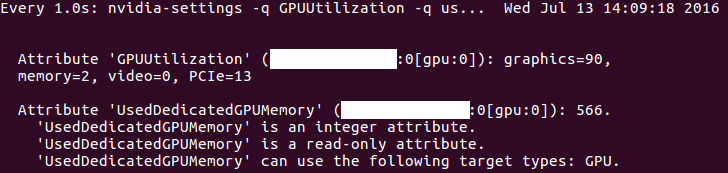
160713说明:a. 这条命令显示信息如下:
b. 其实这条命令就是在终端中显示‘NVIDIA X serve settings’中的一些信息,如下(NVIDIA X serve settings位置为/usr/share/applications,也可以直接打开该软件查看):
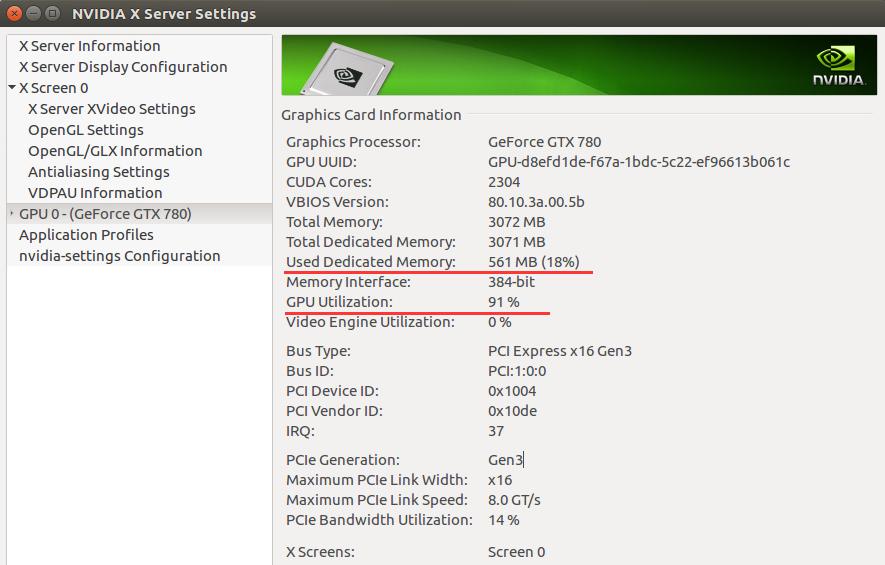
c. 由于这张图使用的GPU和之前使用的GPU不一样,因而参数不一致(比如显存)。
4. 安装完cuda之后,安装cutorch,之后安装cunn,都安装成功。使用GPU的程序也能正常运行。
5. 第三个参考网址中给出了测试程序,本处稍微进行了修改,打印出来每次循环执行的时间(CPU版本和GPU版本代码实际上差不多):
① CPU版本:
require 'torch' require 'nn' require 'optim' --require 'cunn' --require 'cutorch' mnist = require 'mnist' fullset = mnist.traindataset() testset = mnist.testdataset() trainset = { size = 50000, data = fullset.data[{{1,50000}}]:double(), label = fullset.label[{{1,50000}}] } validationset = { size = 10000, data = fullset.data[{{50001,60000}}]:double(), label = fullset.label[{{50001,60000}}] } trainset.data = trainset.data - trainset.data:mean() validationset.data = validationset.data - validationset.data:mean() model = nn.Sequential() model:add(nn.Reshape(1, 28, 28)) model:add(nn.MulConstant(1/256.0*3.2)) model:add(nn.SpatialConvolutionMM(1, 20, 5, 5, 1, 1, 0, 0)) model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2 , 2, 2, 0, 0)) model:add(nn.SpatialConvolutionMM(20, 50, 5, 5, 1, 1, 0, 0)) model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2 , 2, 2, 0, 0)) model:add(nn.Reshape(4*4*50)) model:add(nn.Linear(4*4*50, 500)) model:add(nn.ReLU()) model:add(nn.Linear(500, 10)) model:add(nn.LogSoftMax()) model = require('weight-init')(model, 'xavier') criterion = nn.ClassNLLCriterion() --model = model:cuda() --criterion = criterion:cuda() --trainset.data = trainset.data:cuda() --trainset.label = trainset.label:cuda() --validationset.data = validationset.data:cuda() --validationset.label = validationset.label:cuda()--[[]] sgd_params = { learningRate = 1e-2, learningRateDecay = 1e-4, weightDecay = 1e-3, momentum = 1e-4 } x, dl_dx = model:getParameters() step = function(batch_size) local current_loss = 0 local count = 0 local shuffle = torch.randperm(trainset.size) batch_size = batch_size or 200 for t = 1,trainset.size,batch_size do -- setup inputs and targets for this mini-batch local size = math.min(t + batch_size - 1, trainset.size) - t local inputs = torch.Tensor(size, 28, 28)--:cuda() local targets = torch.Tensor(size)--:cuda() for i = 1,size do local input = trainset.data[shuffle[i+t]] local target = trainset.label[shuffle[i+t]] -- if target == 0 then target = 10 end inputs[i] = input targets[i] = target end targets:add(1) local feval = function(x_new) -- reset data if x ~= x_new then x:copy(x_new) end dl_dx:zero() -- perform mini-batch gradient descent local loss = criterion:forward(model:forward(inputs), targets) model:backward(inputs, criterion:backward(model.output, targets)) return loss, dl_dx end _, fs = optim.sgd(feval, x, sgd_params) -- fs is a table containing value of the loss function -- (just 1 value for the SGD optimization) count = count + 1 current_loss = current_loss + fs[1] end -- normalize loss return current_loss / count end eval = function(dataset, batch_size) local count = 0 batch_size = batch_size or 200 for i = 1,dataset.size,batch_size do local size = math.min(i + batch_size - 1, dataset.size) - i local inputs = dataset.data[{{i,i+size-1}}]--:cuda() local targets = dataset.label[{{i,i+size-1}}]:long()--:cuda() local outputs = model:forward(inputs) local _, indices = torch.max(outputs, 2) indices:add(-1) local guessed_right = indices:eq(targets):sum() count = count + guessed_right end return count / dataset.size end max_iters = 5 do local last_accuracy = 0 local decreasing = 0 local threshold = 1 -- how many deacreasing epochs we allow for i = 1,max_iters do timer = torch.Timer() local loss = step() print(string.format('Epoch: %d Current loss: %4f', i, loss)) local accuracy = eval(validationset) print(string.format('Accuracy on the validation set: %4f', accuracy)) if accuracy < last_accuracy then if decreasing > threshold then break end decreasing = decreasing + 1 else decreasing = 0 end last_accuracy = accuracy print('Time elapsed: ' .. i .. 'iter: ' .. timer:time().real .. ' seconds') end end testset.data = testset.data:double() eval(testset)
② GPU版本:
1 require 'torch' 2 require 'nn' 3 require 'optim' 4 require 'cunn' 5 require 'cutorch' 6 mnist = require 'mnist' 7 8 fullset = mnist.traindataset() 9 testset = mnist.testdataset() 10 11 trainset = { 12 size = 50000, 13 data = fullset.data[{{1,50000}}]:double(), 14 label = fullset.label[{{1,50000}}] 15 } 16 17 validationset = { 18 size = 10000, 19 data = fullset.data[{{50001,60000}}]:double(), 20 label = fullset.label[{{50001,60000}}] 21 } 22 23 trainset.data = trainset.data - trainset.data:mean() 24 validationset.data = validationset.data - validationset.data:mean() 25 26 27 model = nn.Sequential() 28 model:add(nn.Reshape(1, 28, 28)) 29 model:add(nn.MulConstant(1/256.0*3.2)) 30 model:add(nn.SpatialConvolutionMM(1, 20, 5, 5, 1, 1, 0, 0)) 31 model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2 , 2, 2, 0, 0)) 32 model:add(nn.SpatialConvolutionMM(20, 50, 5, 5, 1, 1, 0, 0)) 33 model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2 , 2, 2, 0, 0)) 34 model:add(nn.Reshape(4*4*50)) 35 model:add(nn.Linear(4*4*50, 500)) 36 model:add(nn.ReLU()) 37 model:add(nn.Linear(500, 10)) 38 model:add(nn.LogSoftMax()) 39 40 model = require('weight-init')(model, 'xavier') 41 42 criterion = nn.ClassNLLCriterion() 43 44 model = model:cuda() 45 criterion = criterion:cuda() 46 trainset.data = trainset.data:cuda() 47 trainset.label = trainset.label:cuda() 48 validationset.data = validationset.data:cuda() 49 validationset.label = validationset.label:cuda()--[[]] 50 51 sgd_params = { 52 learningRate = 1e-2, 53 learningRateDecay = 1e-4, 54 weightDecay = 1e-3, 55 momentum = 1e-4 56 } 57 58 x, dl_dx = model:getParameters() 59 60 step = function(batch_size) 61 local current_loss = 0 62 local count = 0 63 local shuffle = torch.randperm(trainset.size) 64 batch_size = batch_size or 200 65 for t = 1,trainset.size,batch_size do 66 -- setup inputs and targets for this mini-batch 67 local size = math.min(t + batch_size - 1, trainset.size) - t 68 local inputs = torch.Tensor(size, 28, 28):cuda() 69 local targets = torch.Tensor(size):cuda() 70 for i = 1,size do 71 local input = trainset.data[shuffle[i+t]] 72 local target = trainset.label[shuffle[i+t]] 73 -- if target == 0 then target = 10 end 74 inputs[i] = input 75 targets[i] = target 76 end 77 targets:add(1) 78 local feval = function(x_new) 79 -- reset data 80 if x ~= x_new then x:copy(x_new) end 81 dl_dx:zero() 82 83 -- perform mini-batch gradient descent 84 local loss = criterion:forward(model:forward(inputs), targets) 85 model:backward(inputs, criterion:backward(model.output, targets)) 86 87 return loss, dl_dx 88 end 89 90 _, fs = optim.sgd(feval, x, sgd_params) 91 92 -- fs is a table containing value of the loss function 93 -- (just 1 value for the SGD optimization) 94 count = count + 1 95 current_loss = current_loss + fs[1] 96 end 97 98 -- normalize loss 99 return current_loss / count 100 end 101 102 eval = function(dataset, batch_size) 103 local count = 0 104 batch_size = batch_size or 200 105 106 for i = 1,dataset.size,batch_size do 107 local size = math.min(i + batch_size - 1, dataset.size) - i 108 local inputs = dataset.data[{{i,i+size-1}}]:cuda() 109 local targets = dataset.label[{{i,i+size-1}}]:long():cuda() 110 local outputs = model:forward(inputs) 111 local _, indices = torch.max(outputs, 2) 112 indices:add(-1) 113 local guessed_right = indices:eq(targets):sum() 114 count = count + guessed_right 115 end 116 117 return count / dataset.size 118 end 119 120 max_iters = 5 121 122 do 123 local last_accuracy = 0 124 local decreasing = 0 125 local threshold = 1 -- how many deacreasing epochs we allow 126 for i = 1,max_iters do 127 timer = torch.Timer() 128 129 local loss = step() 130 print(string.format('Epoch: %d Current loss: %4f', i, loss)) 131 local accuracy = eval(validationset) 132 print(string.format('Accuracy on the validation set: %4f', accuracy)) 133 if accuracy < last_accuracy then 134 if decreasing > threshold then break end 135 decreasing = decreasing + 1 136 else 137 decreasing = 0 138 end 139 last_accuracy = accuracy 140 141 print('Time elapsed: ' .. i .. 'iter: ' .. timer:time().real .. ' seconds') 142 end 143 end 144 145 testset.data = testset.data:double() 146 eval(testset)
==================================================================================
17012更新:
今天重新试了一下上面的程序,提示下面的错误:
Epoch: 1 Current loss: 0.652170 /home/XXX/torch/install/bin/luajit: testGPU.lua:113: invalid arguments: CudaLongTensor CudaTensor expected arguments: [*CudaByteTensor*] CudaLongTensor long | *CudaLongTensor* CudaLongTensor long | [*CudaByteTensor*] CudaLongTensor CudaLongTensor | *CudaLongTensor* CudaLongTensor CudaLongTensor stack traceback: [C]: in function 'eq' testGPU.lua:113: in function 'eval' testGPU.lua:131: in main chunk [C]: in function 'dofile' ...gram/torch/install/lib/luarocks/rocks/trepl/scm-1/bin/th:150: in main chunk [C]: at 0x00405d50
在GPU代码第113行加上下面一句话,就可以成功运行了:
indices=indices:cuda()
真是见鬼了。。。
170121更新结束
==================================================================================
6. CPU和GPU使用率
① CPU版本
CPU情况:

GPU情况:
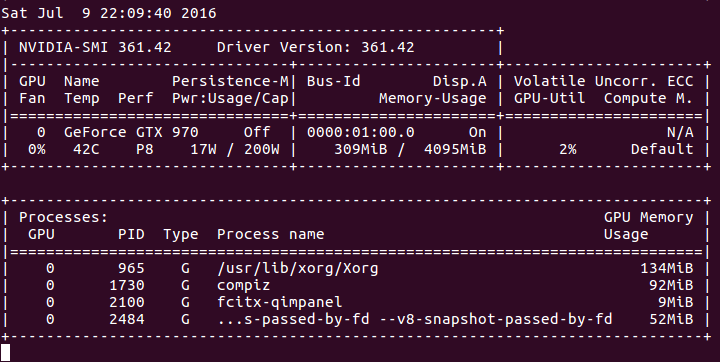
② GPU版本
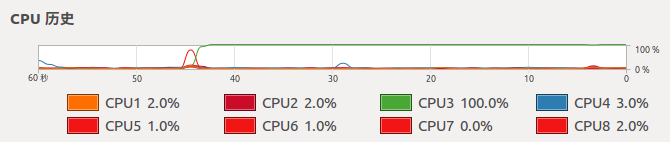
CPU情况:
GPU情况:
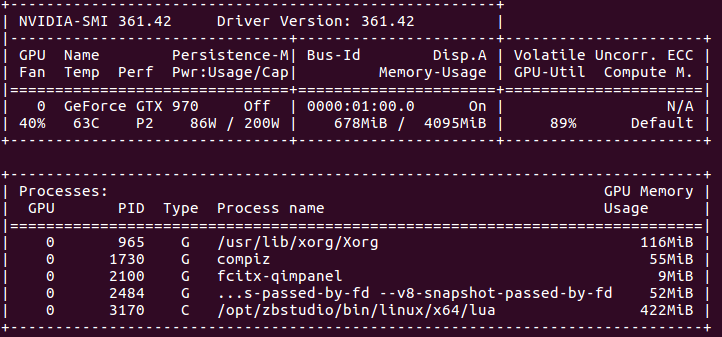
7. 可以看出,CPU版本的程序,CPU全部使用上了,GPU则基本没用。GPU版本,只有一个核心(线程)的CPU完全是用上了,其他的则在围观。。。而GPU使用率已经很高了。
8. 时间比较
CPU版本:
Epoch: 1 Current loss: 0.619644 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.924800 Time elapsed: 1iter: 895.69850516319 seconds Epoch: 2 Current loss: 0.225129 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.949000 Time elapsed: 2iter: 914.15352702141 seconds
GPU版本:
Epoch: 1 Current loss: 0.687380 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.925300 Time elapsed: 1iter: 14.031280994415 seconds Epoch: 2 Current loss: 0.231011 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.944000 Time elapsed: 2iter: 13.848378896713 seconds Epoch: 3 Current loss: 0.167991 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.959800 Time elapsed: 3iter: 14.071791887283 seconds Epoch: 4 Current loss: 0.135209 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.963700 Time elapsed: 4iter: 14.238609790802 seconds Epoch: 5 Current loss: 0.113471 Accuracy on the validation set: 0.966800 Time elapsed: 5iter: 14.328102111816 seconds
说明:① CPU为4790K@4.4GHZ(8线程全开时,应该没有这么高的主频,具体多少没注意);GPU为nvidia GTX 970。
② 由于CPU版本的执行时间实在太长,我都怀疑程序是否有问题了。。。但是看着CPU一直100%的全力工作,又不忍心暂停。直到第一次循环结束,用了将近900s,才意识到,原来程序应该木有错误。。。等第二次循环结束,就直接停止测试了。。。GPU版本的程序,每次循环则只用14s,时间上差距。。。额,使用CPU执行时间是GPU执行时间的64倍。。。
160727更新:
用了780和k80测试了一下,780要用18s迭代一次epoch,k80。。。额,迭代一次要23s(使用一个核心)。当然,只针对我这里的程序是这个结果,其他的,不太清楚。
============================================================================================
170121更新
使用笔记本的1060显卡测试了一下上面的程序,迭代一次用时10s(不保证其他条件完全一致,目前使用的是cuda8.0),不过即便是移动端的1060(虽说10系列移动端已经没有m标志了,但是参数和桌面版还是不完全一样),也还是比桌面版的970要强一点。
170121更新结束
============================================================================================
170505更新
重新配置了torch,使用1080Ti的显卡。但是测试上面的程序,迭代一次用时9s(不保证其他条件完全一致,目前使用的是cuda8.0)。理论上1080Ti比1060性能强一倍应该是有的,但是上面的程序迭代时,差距没有体现出来。累觉不爱。。。/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
170505更新结束
============================================================================================
170613更新
使用tensorflow进行训练,同样的程序,迭代一次,k80单核要1.2s多,1080Ti要0.36s。性能差距体现出来了。之前性能差距无法体现出来的原因是,上面的测试程序过于简单(和程序有关,和torch及tensorflow无关。如果torch上复杂的程序,这两个卡性能差距也差不多这样),不能完全发挥1080Ti的性能(不清楚上面的程序,k80是否完全发挥出来了)。新的测试程序,1080Ti和K80的GPU utilization基本上都是在90%——100%,这种情况下,才能真正考验这两个显卡的性能差距。
170613更新结束
============================================================================================
二 在官网下载安装
170121更新
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads中可以下载cuda。
1. 若下载deb文件
然后使用如下命令安装:
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-8-0-local_8.0.44-1_amd64.deb sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install cuda
之后编辑.bashrc:
gedit .bashrc
输入:
export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin:$PATH export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
之后终端中输入:
source ~/.bashrc
之后再输入:
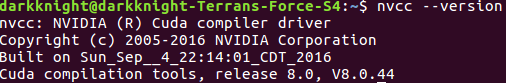
nvcc --version
2. 若下载run文件
终端中输入:
sudo sh cuda_8.0.61_375.26_linux.run
之后按照说明安装即可(没用过这种方式,因而不确定是否需要添加PATH变量。如果不能识别nvcc,添加PATH变量之后,source ~/.bashrc即可)。
170121更新结束
============================================================================================