字典树,又称单词查找树,Trie树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
字典树与字典很相似,当你要查一个单词是不是在字典树中,首先看单词的第一个字母是不是在字典的第一层,如果不在,说明字典树里没有该单词,如果在就在该字母的孩子节点里找是不是有单词的第二个字母,没有说明没有该单词,有的话用同样的方法继续查找.字典树不仅可以用来储存字母,也可以储存数字等其它数据。
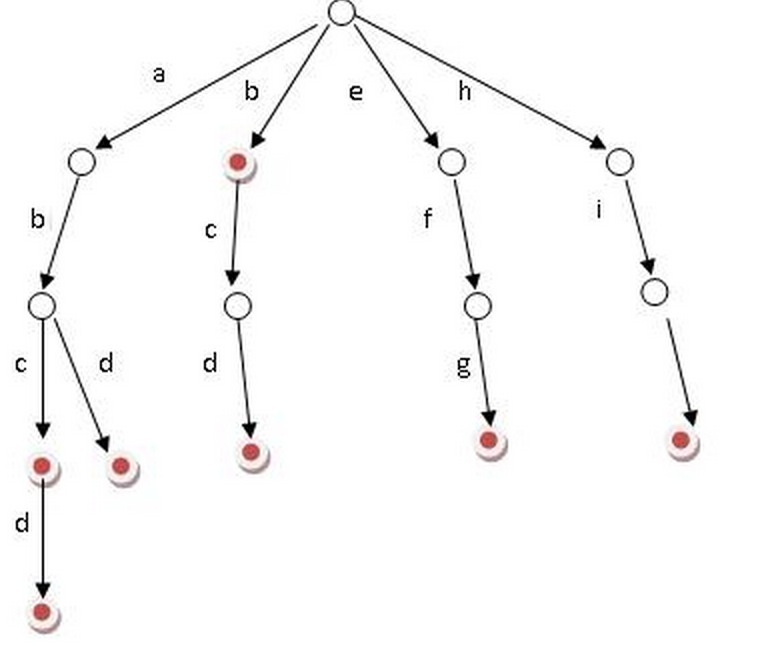
TrieNode结构定义:
const int MAX = 26;
typedef struct TrieNode
{
char *data; //储存结点数据,随需求变化
bool isWord; //判断此结点前的字符串是否是一个单词
TrieNode *branchs[MAX];
};
TireTree结构定义:
class TrieTree
{
public:
TrieNode *root;
void initTrieTree();
TrieNode *createNode();
int insert(const char* word);
int search(const char* word);
};
TireTree实现:
Trie的查找(最主要的操作):
(1) 每次从根结点开始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找关键词的第一个字母,并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索; (3) 在相应的子树上,取得要查找关键词的第二个字母,并进一步选择对应的子树进行检索。
(4) 迭代过程……
(5) 在某个结点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该结点上的信息,即完成查找。
void TrieTree::initTrieTree()
{
root = NULL;
}
TrieNode *TrieTree::createNode()
{
TrieNode *node = (TrieNode*)malloc(sizeof(TrieNode));
node->data = NULL;
node->isWord = false;
for(int i = 1; i < MAX; i++)
node->branchs[i] = NULL;
return node;
}
int TrieTree::insert(const char* word)
{
if (root == NULL)
root = createNode();
TrieNode *p = root;
int k = 0;
while(*word)
{
/*确定Branch ID*/
if (*word >= 'a' && *word <= 'z')
k = *word - 'a';
else if (*word >= 'A' && *word <= 'Z')
k = *word - 'A';
else
return 0;
if(p->branchs[k] == NULL)
{
p->branchs[k] = createNode();
p->branchs[k]->data = (char *)&word;
}
word++;
if(!*word)
p->branchs[k]->isWord = true;
p = p->branchs[k];
}
// delete p;
return 1;
}
int TrieTree::search(const char* word)
{
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
TrieNode *p = root;
int k = 0;
while(*word)
{
/*确定Branch ID*/
if (*word >= 'a' && *word <= 'z')
k = *word - 'a';
else if (*word >= 'A' && *word <= 'Z')
k = *word - 'A';
else
return 0;
if(p->branchs[k] == NULL)
return 0;
word++;
if(!*word && p->branchs[k]->isWord)
return 1;
p = p->branchs[k];
}
return 0;
}
测试代码:
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
TrieTree t;
t.insert("ac");
t.insert("abacus");
t.insert("abalone");
t.insert("abandon");
t.insert("abandoned");
t.insert("abashed");
t.insert("abate");
t.insert("this");
if (t.search("ac"))
cout<<"'ac' was found. pos: "<<endl;
if (t.search("this"))
cout<<"'this' was found. pos: "<<endl;
if (t.search("abat"))
cout<<"'abat' is found. pos: "<<endl;
if (t.search("baby"))
if (t.search("abacus"))
cout<<"'abacus' is found. pos: "<<endl;
if (t.search("baby"))
cout<<"'baby' is found. pos: "<<endl;
else
cout<<"'baby' does not exist at all!"<<endl;
if (t.search("ac1"))
cout<<"'ac1 was found. pos: "<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
'ac' was found. pos: 'this' was found. pos: 'baby' does not exist at all!