Association Rule(关联规则)
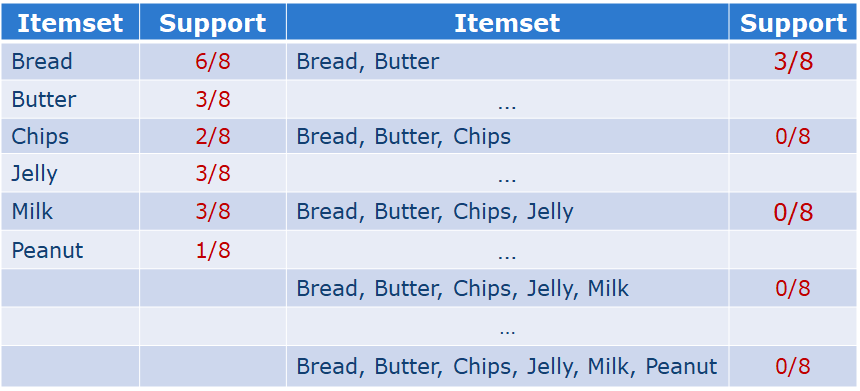
(1)Support of an Itemset(支持项集)
The support of an item (or itemset) X is the percentage of transactions in which that item (or itemset) occurs.项(或项集)X的支持是该项(或项集)发生的事务的百分比。
![]()
(2)Support & Confidence of Association Rule(关联规则的支持度与置信度)
The support of an association rule X->Y is the percentage of transactions that contain X and Y.
![]() (包含X和Y的事务百分比)
(包含X和Y的事务百分比)
The confidence of an association rule X->Y is the ratio of the number of transactions that contain {X, Y} to the number of transactions that contain X.
![]() ===>
===>![]() (包含x、y的事务数与包含x的事务数的比率)
(包含x、y的事务数与包含x的事务数的比率)
例: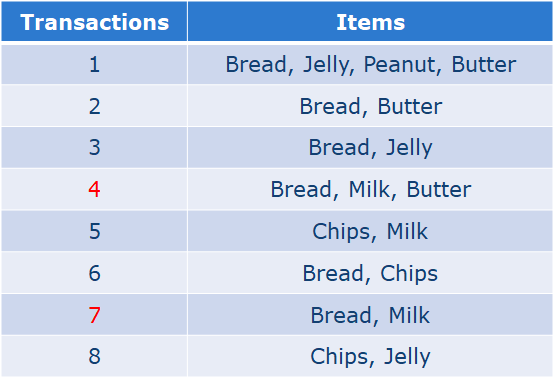
1、Bread ->Milk
Support: 2/8
Confidence: 1/3
2、Milk -> Bread
Support: 2/8
Confidence: 2/3
Support and Confidence are bounded by thresholds:Minimum support σ、Minimum confidence Φ;
A frequent (large) itemset is an itemset with support larger than σ.A strong rule is a rule that is frequent and its confidence is higher than Φ.
误区:(1)一个规则很强并不不代表有意义。例:

现在我们有了一个强有力的规则:磁带->DVD。似乎磁带有助于推销DVD,但是,P(DVD)=75%>P(DVD|Tape),磁带购买者不太可能购买DVD。
置信度很大,但是小于先验概率;
(2)当两个商品出现的概率相差很打时,产生的规则没有意义。
(3)两件事情相关不等于因果关系。Association ≠ Causality。
The Apriori Method:
Key ideas:(1)A subset of a frequent itemset must be frequent. eg:{Milk, Bread, Coke} is frequent -> {Milk, Coke} is frequent;
(2)The supersets of any infrequent itemset cannot be frequent. eg:{Battery} is infrequent -> {Milk, Battery} is infrequent.
一般程序:
![]()
(扫描数据库一次,看哪些是频繁的,再使用频繁项集来生成侯选项集,尽量避免去生成不频繁的候选项集,缺点:要多次扫描数据库)
Aprior 算法:
Ck: Candidate itemset of size k(长度为k的候选集)
Lk: Frequent itemset of size k(长度为k的频繁项集)
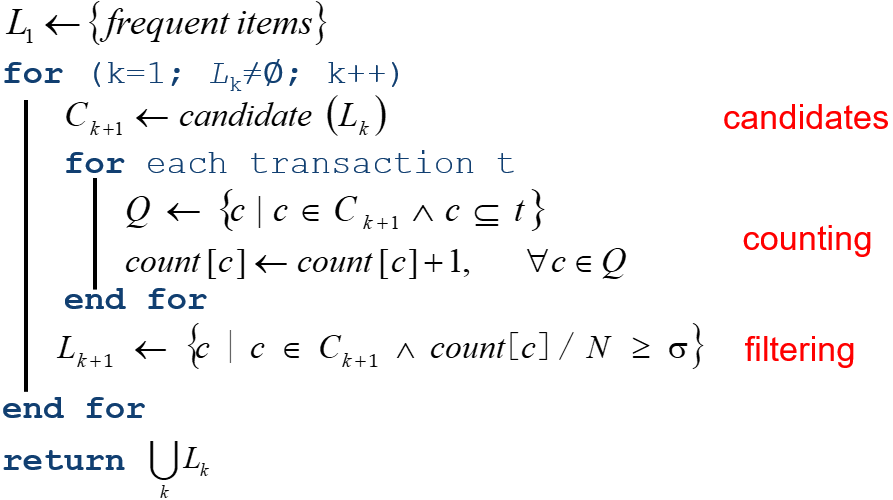
对数据集中的每条记录transaction
对每个候选项集candidate:
检查一下candidate是否是transaction的子集:
如果是,则增加candidate的计数值
对每个候选项集:
如果其支持度不低于最小值,则保留该项集
返回所有的频繁项集列表