官网说明
1.1 创建自己的 FailureAnalyzer
FailureAnalyzer是一种在启动时拦截 exception 并将其转换为 human-readable 消息的好方法,包含在故障分析中。 Spring Boot 为 application context 相关的 exceptions,JSR-303 验证等提供了这样的分析器。实际上很容易创建自己的。
AbstractFailureAnalyzer是FailureAnalyzer的方便扩展,它检查 exception 中是否存在指定的 exception 类型来处理。你可以从中扩展,这样你的 implementation 只有在它实际存在时才有机会处理 exception。如果由于某种原因你无法处理 exception,return null给另一个 implementation 一个处理 exception 的机会。
FailureAnalyzer __mplement 将在META-INF/spring.factories中注册:以下寄存器ProjectConstraintViolationFailureAnalyzer:
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=
com.example.ProjectConstraintViolationFailureAnalyzer
1.2 排除故障 auto-configuration
Spring Boot auto-configuration 尽力'做正确的事',但有时事情会失败,而且很难说出原因。
在 Spring Boot ApplicationContext中有一个非常有用的ConditionEvaluationReport可用。如果启用DEBUG logging 输出,您将看到它。如果使用spring-boot-actuator,还有一个端点,用 JSON 呈现报表。使用它来调试 application 并查看 Spring Boot 在运行时添加了哪些 features(以及哪些没有)。
通过查看 source code 和 Javadoc 可以回答更多问题。一些经验法则:
-
查找名为
*AutoConfiguration的 classes 并读取它们的源,特别是@Conditional*注释,以找出它们启用的 features 和何时启用。将--debug添加到命令 line 或 System property-Ddebug以在 console 上添加 log 在您的应用程序中做出的所有 auto-configuration 决策。在 running Actuator 应用程序中,查看autoconfig端点('/autoconfig'或 JMX 等效项)以获取相同的信息。 -
查找
@ConfigurationProperties(e.g. ServerProperties)的 classes 并从那里读取可用的外部 configuration 选项。@ConfigurationProperties有一个name属性,作为外部 properties 的前缀,因此ServerProperties有prefix="server",其 configuration properties 是server.port,server.address等。在 running Actuator 应用程序中查看configprops端点。 -
寻找使用
RelaxedPropertyResolver从Environment中明确地提取 configuration 值。它通常与前缀一起使用。 -
查找直接绑定到
Environment的@Value注释。这不如RelaxedPropertyResolver方法灵活,但允许一些轻松的 binding,特别是 OS 环境变量(因此CAPITALS_AND_UNDERSCORES是period.separated的同义词)。 -
查找
@ConditionalOnExpression注释,以响应 SpEL 表达式打开和关闭 features,通常使用从Environment解析的占位符进行评估。
1.3 在启动之前自定义 Environment 或 ApplicationContext
SpringApplication具有ApplicationListeners和ApplicationContextInitializers,用于将自定义应用于 context 或环境。 Spring Boot 加载了许多此类自定义项,以便在META-INF/spring.factories内部使用。注册其他方法的方法不止一种:
-
通过在_运行之前调用
SpringApplication上的addListeners和addInitializers方法,以编程方式为每个 application。 -
通过设置
context.initializer.classes或context.listener.classes来声明每个 application。 -
通过添加
META-INF/spring.factories并打包_appar 全部用作 library 的 jar 文件来声明所有 applications。
SpringApplication向 listeners 发送一些特殊的ApplicationEvents(甚至在创建 context 之前的一些),然后为ApplicationContext发布的 events 注册 listeners
在使用EnvironmentPostProcessor刷新 application context 之前,还可以自定义Environment。每个 implementation 都应该在META-INF/spring.factories中注册:
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=com.example.YourEnvironmentPostProcessor
implementation 可以加载任意 files 并将它们添加到Environment。例如,此 example 从 classpath 加载 YAML configuration 文件:
public class EnvironmentPostProcessorExample implements EnvironmentPostProcessor { private final YamlPropertySourceLoader loader = new YamlPropertySourceLoader(); @Override public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) { Resource path = new ClassPathResource("com/example/myapp/config.yml"); PropertySource<?> propertySource = loadYaml(path); environment.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource); } private PropertySource<?> loadYaml(Resource path) { if (!path.exists()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Resource " + path + " does not exist"); } try { return this.loader.load("custom-resource", path, null); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Failed to load yaml configuration from " + path, ex); } } }
Environment已经准备好了 Spring Boot 默认加载的所有常用 property 源。因此,可以从环境中获取文件的位置。此 example 在列表末尾添加custom-resourceproperty 源,以便在任何其他常用位置中定义的 key 优先。自定义 implementation 显然可以定义另一个 order。
虽然在
@SpringBootApplication上使用@PropertySource似乎方便且容易在Environment中加载自定义资源,但我们不推荐它为 Spring Boot 在ApplicationContext刷新之前准备Environment。通过@PropertySource定义的任何 key 都将被加载太晚而不会对 auto-configuration 产生任何影响。
代码示例
2.1 指定异常分析
SpringBoot内部提供的启动异常分析都是指定具体的异常类型实现的,最常见的一个错误就是端口号被占用(PortInUseException),虽然SpringBoot内部提供一个这个异常的启动分析,我们也是可以进行替换这一异常分析的,我们只需要创建PortInUseException异常的AbstractFailureAnalyzer,并且实现类注册给SpringBoot即可,实现自定义如下所示
/** * @author WGR * @create 2019/11/24 -- 23:00 */ public class PortInUseFailureAnalyzer extends AbstractFailureAnalyzer<PortInUseException> { /** * logger instance */ static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PortInUseFailureAnalyzer.class); @Override protected FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable rootFailure, PortInUseException cause) { logger.error("端口被占用。", cause); return new FailureAnalysis("端口号:" + cause.getPort() + "被占用", "PortInUseException", rootFailure); } }
注册启动异常分析
在上面我们只是编写了指定异常启动分析,我们接下来需要让它生效,这个生效方式比较特殊,类似于自定义SpringBoot Starter AutoConfiguration的形式,我们需要在META-INF/spring.factories文件内进行定义,如下所示:
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=
com.topcheer.activiti.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer
那我们为什么需要使用这种方式定义呢?
项目启动遇到的异常顺序不能确定,很可能在Spring IOC并未执行初始化之前就出现了异常,我们不能通过@Component注解的形式使其生效,所以SpringBoot提供了通过spring.factories配置文件的方式定义。
测试:启动2个8080端口
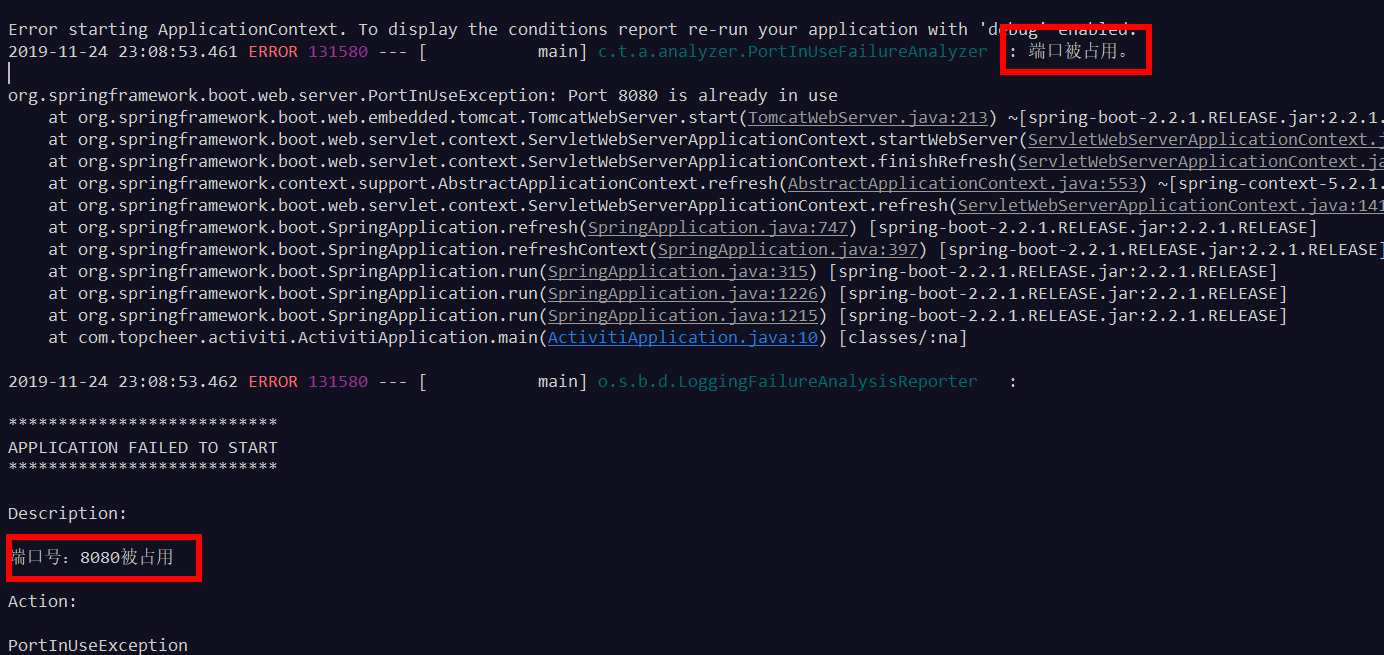
启动异常分析继承关系
自定义的运行异常一般都是继承自RuntimeException,如果我们定义一个RuntimeException的异常启动分析实例会是什么效果呢?
public class ProjectBootUnifiedFailureAnalyzer extends AbstractFailureAnalyzer<RuntimeException> { /** * logger instance */ static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProjectBootUnifiedFailureAnalyzer.class); @Override protected FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable rootFailure, RuntimeException cause) { logger.error("遇到运行时异常", cause); return new FailureAnalysis(cause.getMessage(), "error", rootFailure); } }
将该类也一并注册到spring.factories文件内,如下所示:
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=
com.topcheer.activiti.analyze.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,
com.topcheer.activiti.analyze.ProjectBootUnifiedFailureAnalyzer
运行项目并测试端口号被占用异常我们会发现,并没有执行ProjectBootUnifiedFailureAnalyzer内的analyze方法,而是继续执行了PortInUseFailureAnalyzer类内的方法。
那我们将PortInUseFailureAnalyzer这个启动分析从spring.factories文件内暂时删除掉,再来运行项目我们会发现这时却是会执行ProjectBootUnifiedFailureAnalyzer类内分析方法。
总结
根据本章我们了解了SpringBoot提供的启动异常分析接口以及基本抽象实现类的运作原理,而且启动异常分析存在分析泛型异常类的上下级继承关系,异常子类的启动分析会覆盖掉异常父类的启动分析,如果你想包含全部异常的启动分析可以尝试使用Exception作为AbstractFailureAnalyzer的泛型参数。